Potential Consequences of Taking IRA Distributions to Pay Off Debt
Once there is no longer a paycheck, retirees will typically meet expenses with a combination of social security, withdrawals from retirement accounts, annuities, and pensions. Social security, pensions, and annuities are usually fixed amounts, while withdrawals from retirement accounts could fluctuate based on need. This flexibility presents
Potential Consequences of Taking IRA Distributions to Pay Off Debt
Once there is no longer a paycheck, retirees will typically meet expenses with a combination of social security, withdrawals from retirement accounts, annuities, and pensions. Social security, pensions, and annuities are usually fixed amounts, while withdrawals from retirement accounts could fluctuate based on need. This flexibility presents opportunities to use retirement savings to pay off debt; but before doing so, it is important to consider the possible consequences.
Clients often come to us saying they have some amount left on a mortgage and they would feel great if they could just pay it off. Lower monthly bills and less debt when living on a fixed income is certainly good, both from a financial and psychological point of view, but taking large distributions from retirement accounts just to pay off debt may lead to tax consequences that can make you worse off financially.
Below are three items I typically consider before making a recommendation for clients. Every retiree is different so consulting with a professional such as a financial planner or accountant is recommended if you’d like further guidance.
Impact on State Income and Property Taxes
Depending on what state you are in, withdrawals from IRA’s could be taxed very differently. It is important to know how they are taxed in your state before making any big decision like this. For example, New York State allows for tax free withdrawals of IRA accounts up to a maximum of $20,000 per recipient receiving the funds. Once the $20,000 limit is met in a certain year, any distribution you take above that will be taxed.
If someone normally pulls $15,000 a year from a retirement account to meet expenses and then wanted to pull another $50,000 to pay off a mortgage, they have created $45,000 of additional taxable income to New York State. This is typically not a good thing, especially if in the future you never have to pull more than $20,000 in a year, as you would have never paid New York State taxes on the distributions.
Note: Another item to consider regarding states is the impact on property taxes. For example, New York State offers an “Enhanced STAR” credit if you are over the age of 65, but it is dependent on income. Here is an article that discusses this in more detail STAR Property Tax Credit: Make Sure You Know The New Income Limits.
What Tax Bracket Are You in at the Federal Level?
Federal income taxes are determined using a “Progressive Tax” calculation. For example, if you are filing single, the first $9,700 of taxable income you have is taxed at a lower rate than any income you earn above that. Below are charts of the 2019 tax tables so you can review the different tax rates at certain income levels for single and married filing joint ( Source: Nerd Wallet ).
There isn’t much of a difference between the first two brackets of 10% and 12%, but the next jump is to 22%. This means that, if you are filing single, you are paying the government 10% more on any additional taxable income from $39,475 – $84,200. Below is a basic example of how taking a large distribution from the IRA could impact your federal tax liability.
How Will it Impact the Amount of Social Security You Pay Tax on?
This is usually the most complicated to calculate. Here is a link to the 2018 instructions and worksheets for calculating how much of your Social Security benefit will be taxed ( IRS Publication 915 ). Basically, by showing more income, you may have to pay tax on more of your Social Security benefit. Below is a chart put together with information from the IRS to show how much of your benefit may be taxed.
To calculate “Combined Income”, you take your Adjusted Gross Income + Nontaxable Interest + Half of your Social Security benefit. For the purpose of this discussion, remember that any amount you withdraw from your IRA is counted in your Combined Income and therefore could make more of your social security benefit subject to tax.
Peace of mind is key and usually having less bills or debt can provide that, but it is important to look at the cost you are paying for it. There are times that this strategy could make sense, but if you have questions about a personal situation please consult with a professional to put together the correct strategy.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
The Accountant Put The Owner’s Kids On Payroll And Bomb Shelled The 401(k) Plan
The higher $12,000 standard deduction for single filers has produced an incentive in some cases for business owners to put their kids on the payroll in an effort to shift income out of the owner’s high tax bracket into the children’s lower tax bracket. However, there was a non-Wojeski accountant that advised his clients not only to put his kids on the
Big Issue
The higher $12,000 standard deduction for single filers has produced an incentive in some cases for business owners to put their kids on the payroll in an effort to shift income out of the owner’s high tax bracket into the children’s lower tax bracket. However, there was a non-Wojeski accountant that advised his clients not only to put his kids on the payroll but also to have their children put all of that W2 compensation in the company’s 401(k) plan as a Roth deferral.
At first look it would seem to be a dynamite tax strategy but this strategy blew up when the company got their year end discrimination testing back for the 401(k) plan and all of the executives, including the owner, were forced to distribute their pre-tax deferrals from the plan due to failed discrimination testing. It created a huge unexpected tax liability for the owners and all of the executives completely defeating the tax benefit of putting the kids on payroll. Not good!!
Why This Happened
If your client sponsors a 401(k) plan and they are not a “safe harbor plan”, then each year the plan is subject to “discrimination testing”. This discrimination testing is to ensure that the owners and “highly compensated employees” are not getting an unfair level of benefits in the 401(k) plan compared to the rest of the employees. They look at what each employee contributes to the plan as a percent of their total compensation for the year. For example, if you make $3,000 in employee deferrals and your W2 comp for the year is $60,000, your deferral percentage is 5%.
They run this calculation for each employee and then they separate the employees into two groups: “Highly Compensated Employees” (HCE) and “Non-Highly Compensation Employees” (NHCE). A highly compensated employee is any employee that in 2019:
is a 5% or more owner, or
Makes $125,000 or more in compensation
They put the employees in their two groups and take an average of each group. In most cases, the HCE’s average cannot be more than 2% higher than the NHCE average. If it is, then the HCE’s get pre-tax money kicked back to them out of the 401(k) plan that they have to pay tax on. It really ticks off the HCE’s when this happens because it’s an unexpected tax bill.
Little Known Attribution Rule
ATTRIBUTION RULE: Event though a child of an owner may not be a 5%+ owner or make more than $125,000 in compensation, they are automatically considered an HCE because they are related to the owner of the business. So in the case that I referred above, the accountant had the client pay the child $12,000 and defer $12,000 into the 401(k) plan as a Roth deferral making their deferral percentage 100% of compensation. That brought the average for the HCE way way up and caused the plan fail testing.
To make matters worse, when 401(k) refunds happen to the HCE’s they do not go back to the person that deferred the highest PERCENTAGE of pay, they go to the person that deferred the largest DOLLAR AMOUNT which was the owner and the other HCE’s that deferred over $18,000 in the plan each.
How To Avoid This Mistake
Before advising a client to put their children on payroll and having them defer that money into the 401(k) plan, ask them these questions:
Does your company sponsor a 401(k) plan?
If yes, is your plan a “safe harbor 401(k) plan?
If the company sponsors a 401(k) plan AND it’s a safe harbor plan, you are in the clear with using this strategy because there is no discrimination testing for the employee deferrals.
If the company sponsors a 401(k) plan AND it’s NOT a safe harbor plan, STOP!! The client should either consult with the TPA (third party administrator) of their 401(k) plan to determine how their kids deferring into the plan will impact testing or put the kids on payroll but make sure they don’t contribute to the plan.
Side note, if the company sponsors a Simple IRA, you don’t have to worry about this issue because Simple IRA’s do not have discrimination testing. The children can defer into the retirement plan without causing any issues for the rest of the HCE’s.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Percentage of Pay vs Flat Dollar Amount
Enrolling in a company retirement plan is usually the first step employees take to join the plan and it is important that the enrollment process be straight forward. There should also be a contact, i.e. an advisor (wink wink), who can guide the employees through the process if needed. Even with the most efficient enrollment process, there is a lot of
Retirement Contributions - Percentage of Pay vs Flat Dollar Amount
Enrolling in a company retirement plan is usually the first step employees take to join the plan and it is important that the enrollment process be straight forward. There should also be a contact, i.e. an advisor (wink wink), who can guide the employees through the process if needed. Even with the most efficient enrollment process, there is a lot of information employees must provide. Along with basic personal information, employees will typically select investments, determine how much they’d like to contribute, and document who their beneficiaries will be. This post will focus on one part of the contribution decision and hopefully make it easier when you are determining the appropriate way for you to save.
A common question you see on the investment commercials is “What’s Your Number”? Essentially asking how much do you need to save to meet your retirement goals. This post isn’t going to try and answer that. The purpose of this post is to help you decide whether contributing a flat dollar amount or a percentage of your compensation is the better way for you to save.
As we look at each method, it may seem like I favor the percentage of compensation because that is what I use for my personal retirement account but that doesn’t mean it is the answer for everyone. Using either method can get you to “Your Number” but there are some important considerations when making the choice for yourself.
Will You Increase Your Contribution As Your Salary Increases?
For most employees, as you start to earn more throughout your working career, you should probably save more as well. Not only will you have more money coming in to save but people typically start spending more as their income rises. It is difficult to change spending habits during retirement even if you do not have a paycheck anymore. Therefore, to have a similar quality of life during retirement as when you were working, the amount you are saving should increase.
By contributing a flat dollar, the only way to increase the amount you are saving is if you make the effort to change your deferral amount. If you do a percentage of compensation, the amount you save should automatically go up as you start to earn more without you having to do anything.
Below is an example of two people earning the same amount of money throughout their working career but one person keeps the same percentage of pay contribution and the other keeps the same flat dollar contribution. The percentage of pay person contributes 5% per year and starts at $1,500 at 25. The flat dollar person saves $2,000 per year starting at 25.
The percentage of pay person has almost $50,000 more in their account which may result in them being able to retire a full year or two earlier.
A lot of participants, especially those new to retirement plans, will choose the flat dollar amount because they know how much they are going to be contributing each pay period and how that will impact them financially. That may be useful in the beginning but may harm someone over the long term if changes aren’t made to the amount they are contributing. If you take the gross amount of your paycheck and multiply that amount by the percent you are thinking about contributing, that will give you close to, if not the exact, amount you will be contributing to the plan. You may also be able to request your payroll department to run a quick projection to show the net impact on your paycheck.
There are a lot of factors to take into consideration to determine how much you need to be saving to meet your retirement goals. Simply setting a percentage of pay and keeping it the same your entire working career may not get you all the way to your goal but it can at least help you save more.
Are You Maxing Out?
The IRS sets limits on how much you can contribute to retirement accounts each year and for most people who max out it is based on a dollar limit. For 2024, the most a person under the age of 50 can defer into a 401(k) plan is $23,000. If you plan to max out, the fixed dollar contribution may be easier to determine what you should contribute. If you are paid weekly, you would contribute approximately $442.31 per pay period throughout the year. If the IRS increases the limit in future years, you would increase the dollar amount each pay period accordingly.
Company Match
A company match as it relates to retirement plans is when the company will contribute an amount to your retirement account as long as you are eligible and are contributing. The formula on how the match is calculated can be very different from plan to plan but it is typically calculated based on a dollar amount or a percentage of pay. The first “hurdle” to get over with a company match involved is to put in at least enough money out of your paycheck to receive the full match from the company. Below is an example of a dollar match and a percent of pay match to show how it relates to calculating how much you should contribute.
Dollar for Dollar Match Example
The company will match 100% of the first $1,000 you contribute to your plan. This means you will want to contribute at least $1,000 in the year to receive the full match from the company. Whether you prefer contributing a flat dollar amount or percentage of compensation, below is how you calculate what you should contribute per pay period.
Flat Dollar – if you are paid weekly, you will want to contribute at least $19.23 ($1,000 / 52 weeks = $19.23). Double that amount to $38.46 if you are paid bi-weekly.
Percentage of Pay – if you make $30,000 a year, you will want to contribute at least 3.33% ($1,000 / $30,000).
Percentage of Compensation Match Example
The company will match 100% of every dollar up to 3% of your compensation.
Flat Dollar – if you make $30,000 a year and are paid weekly, you will want to contribute at least $17.31 ($30,000 x 3% = $900 / 52 weeks = $17.31). Double that amount to $34.62 if you are paid bi-weekly.
Percentage of Pay – no matter how much you make, you will want to contribute at least 3%.
If the match is based on a percentage of pay, not only is it easier to determine what you should contribute by doing a percent of pay yourself, you also do not have to make changes to your contribution amount if your salary increases. If the match is up to 3% and you are contributing at least 3% as a percentage of pay, you know you should receive the full match no matter what your salary is.
If you do a flat dollar amount to get the 3% the first year, when your salary increases you will no longer be contributing 3%. For example, if I set up my contributions to contribute $900 a year, at a salary of $30,000 I am contributing 3% of my compensation (900 / 30,000) but at a salary of $35,000 I am only contributing 2.6% (900 / 35,000) and therefore not receiving the full match.
Note: Even though in these examples you are receiving the full match, it doesn’t mean it is always enough to meet your retirement goals, it is just a start.
In summary, either the flat dollar or percentage of pay can be effective in getting you to your retirement goal but knowing what that goal is and what you should be saving to get there is key.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
After A Divorce, Who Gets To File As Head of Household For Their Taxes?
There are often issues with money and taxes when a couple separates, or even when an ex-divorcee gets married again but this is one of most common tax questions that we receive when a married couple with children are in the process of getting divorced.
There are often issues with money and taxes when a couple separates, or even when an ex-divorcee gets married again but this is one of most common tax questions that we receive when a married couple with children are in the process of getting divorced.
With regards to divorces and taxes though, there are five different tax filing types:
Single
Married Filing Joint
Married Filing Separately
Head of Household
Qualifying widow(er) with dependent child
There are a number of advantages for the spouse that is able to use the Head of Household (“HOH”) filing status after the divorce is finalized. They include:
Lower tax brackets
A higher standard deduction
The possibility of qualifying for more tax credits and deductions
Joint Custody
When parents are awarded joint custody, you would think that there is some flexibility as to who is allowed to file as HOH or at a minimum that the spouses can alternate who files as HOH each year. In a divorce, even with a joint custody arrangement, there is typically one custodial parent. The custodial parent is the parent that the children spend the greatest number of days during the year.In simple terms, it literally comes down to counting the number of days during the calendar year that the children spends with each parent. The parent that spends the most days with the children during the year is the custodial parent and has the right to file as Head of Household, to claim the children as a dependent, claim the child tax credits, and the dependent child care credit.
Form 8332
At any time after the divorce, the custodial parent has the ability to file Form 8332 with their tax return which allows the noncustodial parent to claim one or any number of the children as a dependent on their own tax return. However, even if the custodial party files Form 8332 with their return allowing their ex-spouse to claim one or more of the children as dependents for that tax year, they still retain the right to file under the Head of Household filing status. The Head of Household filing status cannot be transferred to the noncustodial parent via Form 8332.
Both Parents Claim HOH
There are a few rare cases where it could be possible for both parents to file as Head of Household in the same tax year. For example, if there are two children, one child spends 51% of the year with one parent, and the second child spends 51% of the year with the other parent, both parents may be able to file as Head of Household in the same tax year. If you feel like you and your ex-spouse qualify for this exception, you will need to keep very careful records of where the children spend their days and nights throughout the year.
You should keep a “child custody log” because there is a good chance that both parents filing as HOH post-divorce will trigger an audit by the IRS. But there is nothing guaranteeing that a child custody log by itself will satisfy the IRS in the event of an audit. The IRS could request additional information to determine that the 51% time requirement was met by each parent.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Beware of the 5 Year Rule for Your Roth Assets
Being able to save money in a Roth account, whether in a company retirement plan or an IRA, has great benefits. You invest money and when you use it during retirement you don't pay taxes on your distributions. But is that always the case? The answer is no. There is an IRS rule that you must take note of known as the "5 Year Rule". There are a number
Beware of the 5 Year Rule for Your Roth Assets
Being able to save money in a Roth account, whether in a company retirement plan or an IRA, has great benefits. You invest money and when you use it during retirement you don't pay taxes on your distributions. But is that always the case? The answer is no. There is an IRS rule that you must take note of known as the "5 Year Rule". There are a number of scenarios where this rule could impact you and rather than getting too much into the weeds, this post is meant to serve as a public service announcement so you are aware it exists.
Advantages of a Roth
As previously mentioned, the benefit of Roth assets is that the account grows tax deferred and if the distributions are "qualified" you don't have to pay taxes. This is compared to a Traditional IRA/401(k) where the full distribution is taxed at ordinary income tax rates and regular investment accounts where you pay taxes on dividends/interest each year and capital gains taxes when you sell holdings. A quick example of Roth vs. Traditional below:
Roth Traditional
Original Investment $ 10,000.00 $ 10,000.00
Earnings $ 10,000.00 $ 10,000.00
Total Account Balance $ 20,000.00 $ 20,000.00
Taxes (Assume 25%) $ - $ 5,000.00
Account Value at Distribution $ 20,000.00 $ 15,000.00
This all seems great, and it is, but there are benefits of both Roth and Traditional (Pre-Tax) accounts so don’t think you have to start moving everything to Roth now. This article gives more detail on the two different types of accounts and may help you decide which is best for you Traditional vs. Roth IRA’s: Differences, Pros, and Cons.
Qualified Disbursements
Note the “occurs at least five years after the year of the employee’s first designated Roth contribution”. This is the “5 Year Rule”. The other qualifications are the same for Traditional IRA’s, but the “5 Year Rule” is special for Roth money. Not always good to be special.
It seems pretty straight forward and in most cases it is. Open a Roth IRA, let it grow at least 5 years, and as long as I’m 59.5 my distributions are qualified. Someone who has Roth money in a 401(k) or other employer sponsored plan may think it is just as easy. That isn’t always the case. Typically, an employee retires, and they roll their retirement savings into a Traditional or a Roth IRA. Say I worked at the company for 10 years, and I now retire and want to use all the savings I’ve created for myself throughout the years. I can start taking qualified distributions from my Roth IRA because I started contributing 10 years ago, correct? Wrong! The time you we’re contributing to the Roth 401(k) is not transferred to the new Roth IRA. If you took distributions directly from the 401(k) and we’re at least 59.5 they would be qualified. In most cases however, people don’t start using their 401(k) money until retirement and most plans only allow for lump sum distributions once you are no longer with the company.
So what do you do?
Open a Roth IRA outside of the plan with a small balance well before you plan to use the money. If I fund a Roth IRA with $100, 10 years from now I retire and roll my Roth 401(k) into that Roth IRA, I have satisfied the 5 year rule because I opened that Roth IRA account 10 years ago. The clock starts on the date the Roth IRA was opened, not the date the assets are transferred in.
About Rob.........
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Moving Expenses Are No Longer Deductible
If you were planning on moving this year to take a new position with a new company or even a new position within your current employer, the moving process just got a little more expensive. Not only is it expensive, but it can put you under an intense amount of stress as there will be lots of things that you need to have in place before packing up and
If you were planning on moving this year to take a new position with a new company or even a new position within your current employer, the moving process just got a little more expensive. Not only is it expensive, but it can put you under an intense amount of stress as there will be lots of things that you need to have in place before packing up and moving. Even things like how you are going to transport your car over to your new home, can take up a lot of your time, and on top of that, you have to think about how much it's going to cost. Prior to the tax law changes that took effect January 1, 2018, companies would often offer new employees a "relocation package" or "moving expense reimbursements" to help subsidize the cost of making the move. From a tax standpoint, it was great benefit because those reimbursements were not taxable to the employee. Unfortunately that tax benefit has disappeared in 2018 as a result of tax reform.
Taxable To The Employee
Starting in 2018, moving expense reimbursements paid to employee will now represent taxable income. Due to the change in the tax treatment, employees may need to negotiate a higher expense reimbursement rate knowing that any amount paid to them from the company will represent taxable income.
For example, let’s say you plan to move from New York to California and you estimate that your moving expense will be around $5,000. In 2017, your new employer would have had to pay you $5,000 to fully reimburse you for the moving expense. In 2018, assuming you are in the 35% tax bracket, that same employer would need to provide you with $6,750 to fully reimburse you for your moving expenses because you are going to have to pay income tax on the reimbursement amount.
Increased Expense To The Employer
For companies that attract new talent from all over the United States, this will be an added expense for them in 2018. Many companies limit full moving expense reimbursement to executives. Coincidentally, employees at the executive level are usually that highest paid. Higher pay equals higher tax brackets. If you total up the company's moving expense reimbursements paid to key employees in 2017 and then add another 40% to that number to compensate your employees for the tax hit, it could be a good size number.
Eliminated From Miscellaneous Deductions
As an employee, if your employer did not reimburse you for your moving expenses and you had to move at least 50 miles to obtain that position, prior to 2018, you were allowed to deduct those expenses when you filed your taxes and you were not required to itemize to capture the deduction. However, this expense will no longer be deductible even for employees that are not reimbursed by their employer for the move starting in 2018.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Warning To All Employees: Review The Tax Withholding In Your Paycheck Otherwise A Big Tax Bill May Be Waiting For You
As a result of tax reform, the IRS released the new income tax withholding tables in January and your employer probably entered those new withholding amounts into the payroll system in February. It was estimated that about 90% of taxpayers would see an increase in their take home pay once the new withholding tables were implemented.
As a result of tax reform, the IRS released the new income tax withholding tables in January and your employer probably entered those new withholding amounts into the payroll system in February. It was estimated that about 90% of taxpayers would see an increase in their take home pay once the new withholding tables were implemented. While lower tax rates and more money in your paycheck sounds like a good thing, it may come back to bite you when you file your taxes.
The Tax Withholding Guessing Game
Knowing the correct amount to withhold for federal and state income taxes from your paycheck is a bit of a guessing game. Withhold too little throughout the year and when you file your taxes you have a tax bill waiting for you equal to the amount of the shortfall. Withhold too much and you will receive a big tax refund but that also means you gave the government an interest free loan for the year.
There are two items that tell your employer how much to withhold for federal income tax from your paycheck:
Income Tax Withholding Tables
Form W-4
The IRS provides your employer with the Income Tax Withholding Tables. On the other hand, you as the employee, complete the Form W-4 which tells your employer how much to withhold for taxes based on the “number of allowances” that you claim on the form.
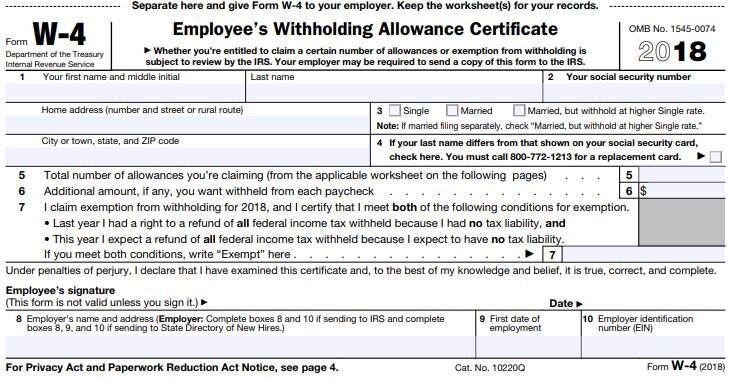
What Is A W-4 Form?
The W-4 form is one of the many forms that HR had you complete when you were first hired by the company. Here is what it looks like:
Section 3 of this form tells your employer which withholding table to use:
Single
Married
Married, but withhold at higher Single Rate
Section 5 tells your employer how many "allowances" you are claiming. Allowance is just another word for "dependents". The more allowances your claim, the lower the tax withholding in your paycheck because it assumes that you will have less "taxable income" because in the past you received a deduction for each dependent. This is where the main problem lies. Due to the changes in the tax laws, the tax deduction for personal exemptions was eliminated. This may adversely affect some taxpayers the were claiming a high number of allowances on their W-4 form because even though the number of their dependents did not change, their taxable income may be higher in 2018 because the deduction for personal exemptions no longer exists.
Even though everyone should review their Form W-4 form this year, employees that claimed allowances on their W-4 form are at the highest risk of either under withholding or over withholding taxes from their paychecks in 2018 due to the changes in the tax laws.
How Much Should I Withhold From My Paycheck For Taxes?
So how do you go about calculating that right amount to withhold from your paycheck for taxes to avoid an unfortunate tax surprise when you file your taxes for 2018? There are two methods:
Ask your accountant
Use the online IRS Withholding Calculator
The easiest and most accurate method is to ask your personal accountant when you meet with them to complete your 2017 tax return. Bring them your most recent pay stub and a blank Form W-4. Based on the changes in the tax laws, they can assist you in the proper completion of your W-4 Form based on your estimated tax liability for the year.If you complete your own taxes, I would highly recommend visiting the updated IRS Withholding Calculator. The IRS calculator will ask you a series of questions, such as:
How many dependents you plan to claim in 2018
Are you over the age of 65
The number of children that qualify for the dependent care credit
The number of children that will qualify for the new child tax credit
Estimated gross wages
How much fed income tax has already been withheld year to date
Payroll frequency
At the end of the process it will provide you with your personal results based on the data that you entered. It will provide you with guidance as to how to complete your Form W-4 including the number of allowances to claim and if applicable, the additional amount that you should instruct your employer to withhold from your paycheck for federal income taxes. Additional withholding requests are listed in Section 6 of the Form W-4.
Avoid Disaster
Having this conversation with your accountant and/or using the new IRS Withholding Calculator will help you to avoid a big tax disaster in 2018. Unfortunately, many employees may not learn about this until it's too late. Employees that are used to getting a tax refund may find out in the spring of next year that they owe thousands of dollars to the IRS because the combination of the new tax tables and the changes in the tax law that caused them to inadvertently under withhold federal income taxes throughout the year.
Action Item!!
Take action now. The longer you wait to run this calculation or to have this conversation with your accountant, the larger the adjustment may be to your paycheck. It's easier to make these adjustments now when you have nine months left in the year as opposed to waiting until November.I would strongly recommend that you share this article with your spouse, children in the work force, and co-workers to help them avoid this little known problem. The media will probably not catch wind of this issue until employees start filing their tax returns for 2018 and they find out that there is a tax bill waiting for them.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
No Deduction For Entertainment Expenses In 2019. Ouch!!
There is a little known change that was included in tax reform that will potentially have a big impact on business owners. The new tax laws that went into effect on January 1, 2018 placed stricter limits on the ability to deduct expenses associated with entertainment and business meals. Many of the entertainment expenses that businesses
There is a little known change that was included in tax reform that will potentially have a big impact on business owners. The new tax laws that went into effect on January 1, 2018 placed stricter limits on the ability to deduct expenses associated with entertainment and business meals. Many of the entertainment expenses that businesses were able to deduct in 2017 will no longer we allowed in 2018 and beyond. A big ouch for business owners that spend a lot of money entertaining clients and prospects.
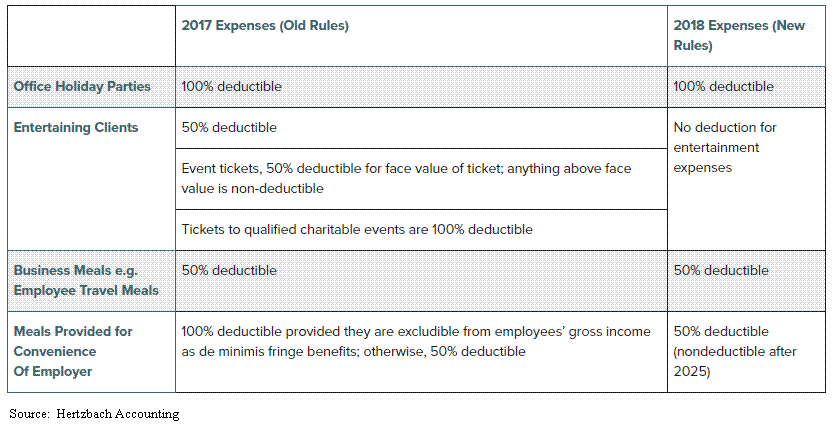
A Quick Breakdown Of The Changes
No Deduction in 2019
Prior to 2018, if the business spent money to take a client out to a baseball game, meet a client for 18 holes of golf, or to host a client event, the business would be able to take a deduction equal to 50% of the total cost associated with the entertainment expense. Starting in 2018, you get ZERO. There is no deduction for those expenses.
The new law specifically states that there is no deduction for:
Any activity generally considered to be entertainment, amusement, or recreation
Membership dues to any club organization for recreation or social purpose
A facility, or portion thereof, used in connection with the above items
This will inevitably cause business owners to ask their accountant: “If I spend the same amount on entertainment expenses in 2018 as I did in 2017, how much are the new tax rules going to cost me tax wise?”
Impact On Sales Professionals
If you are in sales and big part of your job is entertaining prospects in hopes of winning their business, if your company can no longer deduct those expenses, are you going to find out at some point this year that the company is going to dramatic limit the resources available to entertain clients? If they end up limiting these resources, how are you supposed to hit your sales numbers and how does that change the landscape of how you solicit clients?
Impact On The Entertainment Industry
This has to be bad news for golf courses, casinos, theaters, and sports arena. As the business owner, if you were paying $15,000 per year for your membership to the local country club and you justified spending that amount because you knew that you could take a tax deduction for $7,500, now what? Now that you can’t deduct any of it, you may decide to cancel your membership or seek out a cheaper alternative.
Impact On Charitable Organizations
How do most charities raise money? Events. As you may have noticed in the chart, in 2017 tickets to a qualified charitable event were 100% deductible. In 2018, it goes from 100% deductible to Zero!! It’s bad enough that the regular entertainment expenses went from 50% to zero but going from 100% to zero hurts so much more. Also charitable events usually have high price tags because they have to cover the cost of event and raise money for the charity. In 2018, it will be interesting to see how charitable organizations get over this hurdle. It may have to disclose right on the registration form for the event that the ticket cost is $500 but $200 of that amount is the cost of the event (non-deductible) and $300 is the charitable contribution.
Exceptions To The New Rules
There are some unique exceptions to the new rules. Many business owners will not find any help within these exceptions but here they are:
Entertainment, amusement, and recreation expenses you treat as compensation to your employees in their wages (In other words, the cost ends up in your employee’s W2)
Expenses for recreation, social, or similar activities, including facilities, primarily for employees, and it can’t be highly compensation employees (“HCE”). In 2018 an HCE employee is an employee that makes more than $120,000 or is a 5%+ owners of the company.
Expenses for entertainment goods, services, and facilities that you sell to customers
What’s The Deal With Meals?
Prior to 2018, employers could deduct 50% of expenses for business-related meals while traveling. Also meals provided to an employee for the convenience of the employer on the employer’s business premises were 100% deductible by the employer and tax-free to the recipient employee.
Starting in 2018, meal expenses incurred while traveling on business remain 50% deductible to the business. However, meals provided via an on-premises cafeteria or otherwise on the employers premise for the convenience of the employer will now be limited to a 50% deduction.
There is also a large debate going on between tax professional as to which meals or drinks may fall into the “entertainment” category and will lose their deduction entirely.
Impact On Business
This is just one of the many “small changes” that was made to the new tax laws that will have a big impact on many businesses. It may very well change the way that businesses spend money to attract new clients. This in turn will most likely lead to unintended negative consequences for organizations that operate in the entertainment, catering, and charitable sectors of the U.S. economy.
Disclosure: For education purposes only. Please seek tax advice from your tax professional
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Past (kind of)
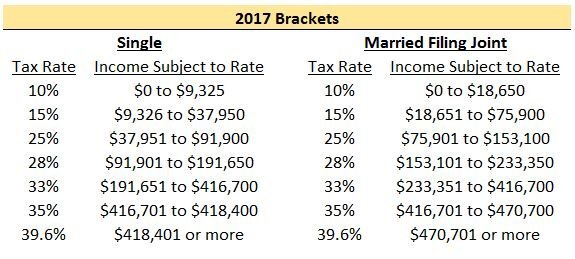
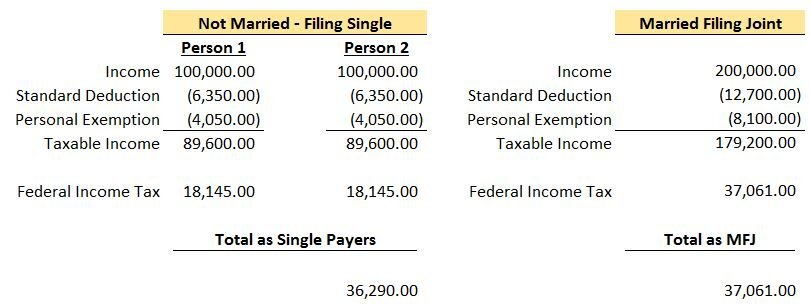
I say "kind of" because most people still have to file their 2017 tax return. Here is the 2017 tax table for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
A reasonable person would think that the income subject to tax would simply double if you went from filing Single to Married Filing Joint. As you can see, this isn't the case once you are in the 25%+ tax bracket and it can mean big dollars! Let's take a look at a simple example where each person makes the same amount of money. We will also assume they will be taking the standard deduction in 2017.
Note: To calculate the “Federal Income Tax” amount above, you can use the IRS tables here 2017 1040 Tax Table Instructions. All of your income is not taxed at your top rate. For example, if your top income falls in the 25% tax bracket, as a single payer you will only pay 25% on income from $37,951 to $91,900. Everything below that range will be taxed at either 10% or 15%.
As you can see, because of the change in filing status, this couple owed a total of $771 more to the federal government. This is the “Marriage Penalty”. Typically as incomes rise, the dollar amount of the penalty becomes larger. For this couple, their top tax bracket went from 25% each when filing single to 28% filing joint.
The Present
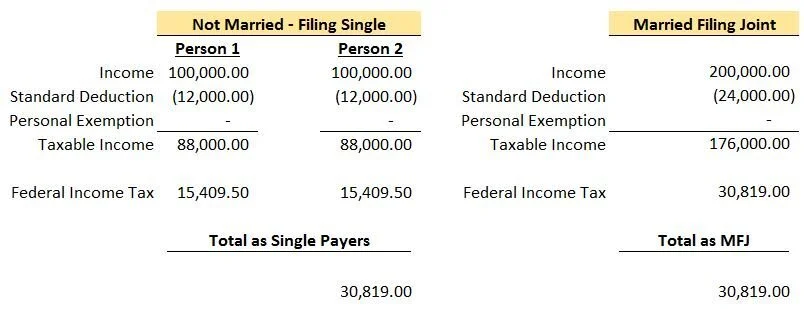
Here is the 2018 tax table in the new tax legislation for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
Upon review, you can see that the top income brackets are not doubled for Married Filing Joint. At 37%, a single person filing would reach the top rate at $500,001 while married filing joint would reach at $600,001. That being said, the “Marriage Penalty” appears to kick in at higher income levels compared to the past and therefore should impact less people. The income bracket for Married Filing Joint is doubled up until $400,000 of combined income compared to just $75,901 under the 2017 brackets.
Let’s take a look at the same couple in the example above.
Due to the income brackets doubling from single to married filing joint for this couple, the “Marriage Penalty” they would have incurred in 2017 appears to go away. In this example, they would also pay less in federal taxes in both situations. This article is more focused on the impact on the “Marriage Penalty” but having a lower tax bill is always a plus.
Standard vs. Itemized Deductions
The tax brackets aren’t the only penalty. Another common tax increase people see when going from single to married filing joint are the deductions they lose. If I’m single and own a home, it is likely I will itemized because the sum of my property taxes, mortgage interest, and state income taxes exceed the standard deduction amount. Assume the couple in the example above is still not married but Person 1 owns a home and rather than taking the standard deduction, Person 1 itemizes for an amount of $15,000. For 2017, their total deductions will be $21,350 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $6,350 Person 2) and for 2018, their total deductions will be $27,000 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $12,000 Person 2).
Now they get married and have to choose whether to itemize or take the standard deduction.
2017: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2017 they would still itemize because they have deductions of $15,000 for Person 1 and some additional items that Person 2 would bring to the table (i.e. their state income taxes). Say their total itemized deductions are $18,000 when married filing joint. They would still itemize because $18,000 is more than the Married Filing Joint standard deduction of $12,700. But now compare the $18,000 to the $21,350 they got filing single. They lose out on $3,350 of deductions. Usually, less deductions equals more taxes.
2018: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2018 they would no longer itemize. Assuming their total itemized deductions are still $18,000, that is less than the $24,000 standard deduction they can take when married filing joint. $24,000 standard deduction in 2018 is still less than the $27,000 they got filing separately by $3,000. Again, less deductions usually means more taxes. The “Marriage Penalty” lives on!
A lot of people will still lose out on deductions in 2018 but the “Marriage Penalty” will hit less people because of the increase in the standard deduction. If Person 1 has itemized deductions of $10,000 in 2017, they would itemize if they filed single and possibly take the standard deduction of $12,700 filing joint. In 2018 however, Person 1 would take the standard deduction both as a single tax payer ($12,000) and married filing joint ($24,000) which takes away the “Marriage Penalty” related to the deduction.
The Why?
Why do tax brackets work this way? Like most taxes, I assume the idea was to generate more income for the government. Some may also argue that typical couples don't make the same salaries which seems like an archaic point of view.Was it all fixed with the new tax legislation? It doesn't appear so but it does look like less people will be struck by Cupid's Marriage Penalty.
About Rob.........
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
More Taxpayers Will Qualify For The Child Tax Credit
There is great news for parents in the middle to upper income tax brackets in 2018. The new tax law dramatically increased the income phaseout threshold for claiming the child tax credit. In 2017, parents were eligible for a $1,000 tax credit for each child under the age of 17 as long as their adjusted gross income (“AGI”) was below $75,000 for single
There is great news for parents in the middle to upper income tax brackets in 2018. The new tax law dramatically increased the income phaseout threshold for claiming the child tax credit. In 2017, parents were eligible for a $1,000 tax credit for each child under the age of 17 as long as their adjusted gross income (“AGI”) was below $75,000 for single filers and $110,000 for married couples filing a joint return. If your AGI was above those amounts, the $1,000 credit was reduced by $50 for every $1,000 of income above those thresholds. In other words, the child tax credit completely phased out for a single filer with an AGI greater than $95,000 and for a married couple with an AGI greater than $130,000.
Note: If you are not sure what the amount of your AGI is, it’s the bottom line on the first page of your tax return (Form 1040).
New Phaseout Thresholds In 2018+
Starting in 2018, the new phaseout thresholds for the Child Tax Credit begin at the following AGI levels:
Single Filer: $200,000
Married Filing Joint: $400,000
If your AGI falls below these thresholds, you are eligible for the full Child Tax Credit. For taxpayers with an AGI amount that exceeds these thresholds, the phaseout calculation is the same as 2017. The credit is reduced by $50 for every $1,000 in income over the AGI threshold.
Wait......It Gets Better
Not only will more families qualify for the child tax credit in 2018 but the amount of the credit was doubled. The new tax law increased the credit from $1,000 to $2,000 for each child under the age of 17.
In 2017, a married couple, with three children, with an AGI of $200,000, would have received nothing for the child tax credit. In 2018, that same family will receive a $6,000 tax credit. That’s huge!! Remember, “tax credits” are more valuable than “tax deductions”. Tax credits reduce your tax liability dollar for dollar whereas tax deductions just reduce the amount of your income subject to taxation.
Tax Reform Giveth & Taketh Away
While the change to the tax credit is good news for most families with children, the elimination of personal exemptions starting in 2018 is not.
In 2017, taxpayers were able to take a tax deduction equal to $4,050 for each dependent (including themselves) in addition to the standard deduction. For example, a married couple with 3 children and $200,000 in income, would have been eligible received the following tax deductions:
Standard Deduction: $12,700
Husband: $4,050
Wife: $4,050
Child 1: $4,050
Child 2: $4,050
Child 3: $4,050
Total Deductions $32,950
Child Tax Credit: $0
This may lead you to the following question: “Does the $6,000 child tax credit that this family is now eligible to receive in 2018 make up for the loss of $20,250 ($4,050 x 5) in personal exemptions?”
By itself? No. But you have to also take into consideration that the standard deduction is doubling in 2018. For that same family, in 2018, they will have the following deductions and tax credits:
Standard Deduction: $24,000
Personal Exemptions: $0
Total Deductions: $24,000
Child Tax Credit: $6,000
Even though $24,000 plus $6,000 is not greater than $32,950, remember that credits are worth more than tax deductions. In 2017, a married couple, with $200,000 in income, put the top portion of their income subject to the 28% tax bracket. Thus, $32,950 in tax deductions equaled a $9,226 reduction in their tax bill ($32,950 x 28%).
In 2018, due to the changes in the tax brackets, instead of their top tax bracket being 28%, it’s now 24%. The $24,000 standard deduction reduces their tax bill by $5,760 ($24,000 x 24%) but now they also have a $6,000 tax credit with reduces their remaining tax bill dollar for dollar, resulting in a total tax savings of $11,760. Taxes saved over last year: $2,534. Not a bad deal.
For many families, the new tax brackets combined with the doubling of the standard deduction and the doubling of the child tax credit with higher phaseout thresholds, should offset the loss of the personal exemptions in 2018.
This information is for educational purposes only. Please consult your accountant for personal tax advice.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.