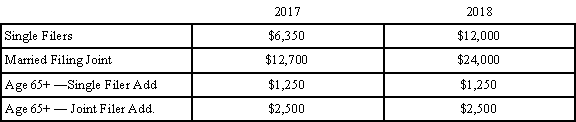Business Owners: Strategies To Reduce Your Taxable Income To Qualify For The New 20% Qualified Business Income Deduction
Now that small business owners have the 20% deduction available for their pass-through income in 2018, as a business owner, you will need to begin to position your business to take full advantage of the new tax deduction. However, the Qualified Business Income ("QBI") deduction has taxable income thresholds. Once the owner's personal taxable
Now that small business owners have the 20% deduction available for their pass-through income in 2018, as a business owner, you will need to begin to position your business to take full advantage of the new tax deduction. However, the Qualified Business Income ("QBI") deduction has taxable income thresholds. Once the owner's personal taxable income begins to exceed specific dollar amounts, the 20% deduction with either phase out or it will trigger an alternative calculation that could lower the deduction.
First: Understand The 20% Deduction
If you are not already familiar with how the new 20% deduction works, I encourage you to read our article:"How Pass-Through Income Will Be Taxes In 2018 For Small Business Owners"If you are already familiar with how the Qualified Business Income deduction works, please continue reading.
The Taxable Income Thresholds
Regardless of whether you are considered a “services business” or “non-services business” under the new tax law, you will need to be aware of the following income thresholds:
Individual: $157,500
Married: $315,000
These threshold amounts are based on the “total taxable income” listed on the tax return of the business owner. Not “AGI” and not just the pass-through income from the business. Total taxable income. For example, if I make $100,000 in net profit from my business and my wife makes $400,000 in W-2 income, our total taxable income on our married filing joint tax return is going to be way over the $315,000 threshold. So do we completely lose the 20% deduction on the $100,000 in pass-through income from the business? Maybe not!!
The Safe Zone
For many business owners, to maximize the new 20% deduction, they will do everything that they can to keep their total taxable income below the thresholds. This is what I call the “safe zone”. If you keep your total taxable income below these thresholds, you will be allowed to take your total qualified business income, multiply it by 20%, and you’re done. Once you get above these thresholds, the 20% deduction will either begin to phase out or it will trigger the alternative 50% of W-2 income calculation which may reduce the deduction. The phase out ranges are listed below:
Inidividuals: $157,500 to $207,500
Married: $315,000 to $415,000
As you get closer to the top of the range the deduction begins to completely phase out for “services businesses” and for “non-services business” the “lesser of 20% of QBI or 50% of wages paid to employees” is fully phased in.
What Reduces "Total Taxable Income"?
There are four main tools that business owners can use to reduce their total taxable income:
Standard Deduction or Itemized Deductions
Self-Employment Tax
Retirement Plan Contributions
Timing Expenses
Standard & Itemized Deductions
Since tax reform eliminated many of the popular tax deductions that business owners have traditionally used to reduce their taxable income, for the first time in 2018, a larger percentage of business owners will elect taking the standard deduction instead of itemizing. You do not need to itemize to capture the 20% deduction for your qualified business income. This will allow business owners to take the higher standard deduction and still capture the 20% deduction on their pass-through income. Whether you take the standard deduction or continue to itemize, those deductions will reduce your taxable income for purposes of the QBI income thresholds.
Example: You are a business owner, you are married, and your only source of income is $335,000 from your single member LLC. At first look, it would seem that your total income is above the $315,000 threshold and you are subject to the phase out calculation. However, if you elect the standard deduction for a married couple filing joint, that will reduce your $335,000 in gross income by the $24,000 standard deduction which brings your total taxable income down to $311,000. Landing you below the threshold and making you eligible for the full 20% deduction on your qualified business income.
The point of this exercise is for business owners to understand that if your gross income is close to the beginning of the phase out threshold, somewhere within the phase out range, or even above the phase out range, there may be some relief in the form of the standard deduction or your itemized deductions.
Self-Employment Tax
Depending on how your business is incorporated, you may be able to deduct half of the self-employment tax that you pay on your pass-through income. Sole proprietors, LLCs, and partnership would be eligible for this deduction. Owners of S-corps receive W2 wages to satisfy the reasonable compensation requirement and receive pass-through income that is not subject to self-employment tax. So this deduction is not available for S-corps.
The self-employment tax deduction is an “above the line” deduction which means that you do not need to itemize to capture the deduction. The deduction is listed on the first page of your 1040 and it reduces your AGI.
Example: You are a partner at a law firm, not married, the entity is taxed as a partnership, and your gross income is $200,000. Like the previous example, it looks like your income is way over the $157,500 threshold for a single tax filer. But you have yet to factor in your tax deductions. For simplicity, let’s assume you take the standard deduction:
Total Pass-Through Income: $200,000
Less Standard Deduction: ($12,000)
Less 50% Self-Employ Tax: ($15,000) $200,000 x 7.5% = $15,000
Total Taxable Income: $173,000
While you total taxable income did not get you below the $157,500 threshold, you are now only mid-way through the phase out range so you will capture a portion of the 20% deduction on your pass-through income.
Retirement Plans – "The Golden Goose"
Retirement plans will be the undisputed Golden Goose for purposes of reducing your taxable income for purposes of the qualified business income deduction. Take the example that we just went through with the attorney in the previous section. Now, let’s assume that same attorney maxes out their pre-tax employee deferrals in the company’s 401(k) plan. The limit in 2018 for employees under the age of 50 is $18,500.
Total Pass-Through Income: $200,000
Less Standard Deduction: ($12,000)
Less 50% Self-Employ Tax: ($15,000)
Pre-Tax 401(k) Contribution: ($18,500)
Total Taxable Income: $154,500
Jackpot!! That attorney has now reduced their taxable income below the $157,500 QBI threshold and they will be eligible to take the full 20% deduction against their pass-through income.
Retirement plan contributions are going to be looked at in a new light starting in 2018. Not only are you reducing your tax liability by shelter your income from taxation but now, under the new rules, you are simultaneously increasing your QBI deduction amount.
When tax reform was in the making there were rumors that Congress may drastically reduce the contribution limits to retirement plans. Thankfully this did not happen. Long live the goose!!
Start Planning Now
Knowing that this Golden Goose exists, business owners will need to ask themselves the following questions:
How much should I plan on contributing to my retirement accounts this year?
Is the company sponsoring the right type of retirement plan?
Should we be making changes to the plan design of our 401(k) plan?
How much will the employer contribution amount to the employees increase if we try to max out the pre-tax contributions for the owners?
Business owners are going to need to engage investment firms and TPA firms that specialize in employer sponsored retirement plan. Up until now, sponsoring a Simple IRA, SEP IRA, or 401(K), as a way to defer some income from taxation has worked but tax reform will require a deeper dive into your retirement plan. The golden question:
“Is the type of retirement plan that I’m currently sponsoring through my company the right plan that will allow me to maximize my tax deductions under the new tax laws taking into account contribution limits, admin fees, and employer contributions to the employees.”
If you are not familiar with all of the different retirement plans that are available for small businesses, please read our article “Comparing Different Types Of Employer Sponsored Plans”.
DB / DC Combo Plans Take Center Stage
While DB/DC Combo plans have been around for a number of years, you will start to hear more about them beginning in 2018. A DB/DC Combo plan is a combination of a Defined Benefit Plan (Pension Plan) and a Defined Contribution Plan (401k Plan). While pension plans are usually only associated with state and government employers or large companies, small companies are eligible to sponsor pension plans as well. Why is this important? These plans will allow small business owners that have total taxable income well over the QBI thresholds to still qualify for the 20% deduction.
While defined contribution plans limit an owner’s aggregate pre-tax contribution to $55,000 per year in 2018 ($61,000 for owners age 50+), DB/DC Combo plans allow business owners to make annual pre-tax contributions ranging from $60,000 – $300,000 per year. Yes, per year!!
Example: A married business owner makes $600,000 per year and has less than 5 full time employees. Depending on their age, that business owner may be able to implement a DB/DC Combo plan prior to December 31, 2018, make a pre-tax contribution to the plan of $300,000, and reduce their total taxable income below the $315,000 QBI threshold.
Key items to make these plans work:
You need to have the cash to make the larger contributions each year
These DB/DC plan needs to stay in existence for at least 3 years
This plan design usually works for smaller employers (less than 10 employees)
Shelter Your Spouse's W-2 Income
It's not uncommon for a business owner to have a spouse that earns W-2 wages from employment outside of the family business. Remember, the QBI thresholds are based on total taxable income on the joint tax return. If you think you are going to be close to the phase out threshold, you may want to encourage your spouse to start putting as much as they possibly can pre-tax into their employer's retirement plan. Unlike self-employment income, W-2 income is what it is. Whatever the number is on the W-2 form at the end of the year is what you have to report as income. By contrast, business owners can increase expenses in a given year, delay bonuses into the next tax year, and deploy other income/expense maneuvers to play with the amount of taxable income that they are showing for a given tax year.
Timing Expenses
One of the last tools that small business owners can use to reduce their taxable income is escalating expense. Now, it would be foolish for businesses to just start spending money for the sole purpose of reducing income. However, if you are a dental practice and you were planning on purchasing some new equipment in 2018 and purchasing a software system in 2019, depending on where your total taxable income falls, you may have a tax incentive to purchase both the equipment and the software system all in 2018. As you get toward the end of the tax year, it might be worth making that extra call to your accountant, before spending money on those big ticket items. The timing of those purchases could have big impact on your QBI deduction amount.
Disclosure: The information in this article is for educational purposes. For tax advice, please consult your tax advisor.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
How Much Will The Value Of Your House Drop Under The New Tax Law?
It's not a secret to anyone at this point that the new tax bill is going to inflict some pain on the U.S. housing market in 2018. The questions that most homeowners and real estate investors are asking is: "How much are home prices likely to decrease within the next year due to the tax changes?" The new $10,000 limitation on SALT deductions, the lower
It's not a secret to anyone at this point that the new tax bill is going to inflict some pain on the U.S. housing market in 2018. The questions that most homeowners and real estate investors are asking is: "How much are home prices likely to decrease within the next year due to the tax changes?" The new $10,000 limitation on SALT deductions, the lower deduction cap mortgages interest, and the higher standard deduction are all lining up to take a bite out of real estate prices. The size of the bite will largely depend on where you live and the value of your house.
3 Bites That Will Hurt
The Trump tax reform made three significant changes to the tax laws that will impact housing prices:
Capped state and local tax ("SALT") deductions at $10,000 (includes property taxes)
Lowered the deduction cap on the first $750,000 of a mortgage
Doubled the standard deduction
The New Standard Deduction
There is a reason why I'm starting this analysis with the doubling of the standard deduction in 2018. For many households in the U.S., the doubling of the standard deduction will make the cap on the SALT deductions irrelevant. Let me explain. Below is a comparison of the standard deduction limits in 2017 versus 2018:
In 2018, a married couple filing a joint tax return would need over $24,000 in itemized deductions to justify not taking the standard deduction and calling it a day. For a married couple, both W-2 employees, $7,000 in property taxes, $9,000 in state income taxes, if those are their only itemized deductions, then it will most likely makes sense for them to take the $24,000 standard deduction. So the $10,000 cap on property taxes and state income taxes becomes irrelevant because it’s an itemized deduction. This will be a big change for many U.S. households. In 2017, that same family may have itemized because their property and state taxes exceeded the $12,700 standard deduction threshold.
For taxpayers age 65 and older, the new tax law kept the additional standard deduction amounts: $1,250 for single filers and $2,500 for married filing joint which are over and above the normal limits.
$10,000 Cap On State & Local Taxes
Starting in 2018, taxpayers are limited to a $10,000 deduction for a combination of their property taxes, school taxes, and state & local income tax. For states that have both high property taxes and high income taxes like New York, New Jersey, and California, homeowners will most likely be looking at a larger decrease in the value of their homes versus states like Florida that have lower property taxes and no state income taxes. The houses with the higher dollar value may experience a larger drop in price.
If you live in a $200,000 house, the property / school taxes are $5,000, and you decided to sell your house, the family looking to buy your house may already be planning on taking the $24,000 standard deduction at that income level, so the new tax cap would not really decrease the “value” of the house to the potential buyer.
On the flip side, if you own a $600,000 house, your property/school taxes are $18,000, and you are looking to sell your house, the new $10,000 cap will most likely have a negative impact on the value of your house. As you might assume, the individuals and families with the higher incomes that could afford to purchase a $600,000 house will naturally be the homeowners that will continue to itemize their deduction in 2018. So owning that $600K house in 2018 comes at an additional annual cost to the buyer because they lose $8,000 in property tax deductions. For individuals and families in the top federal tax bracket (37%), the cost to live in that house just went up by $3,120 per year. I have personally already had two clients call me that just purchased a house in 2017 with property taxes above the $10,000 cap and they said “I might not have purchased this big of a house if I knew I was not going to be able to deduct all of the property taxes”.
$750,000 Deduction Cap On Mortgages
Prior to 2018, taxpayers could only deduct interest on the first $1,000,000 of a mortgage. For all new mortgages, beginning in 2018, the cap was reduced from $1,000,000 to $750,000. The new tax law grandfathered the $1M cap for mortgages that were already in existence prior to December 31, 2017. Obviously this change will only impact very high income earning individuals and families living in houses valued at $1M+ but it still may have a negative impact on the prices of those big houses. I say "may" because if you can afford a $3M condo in Manhattan, you may not care that you lost a $7,500 tax deduction.
It Depends Where You Live
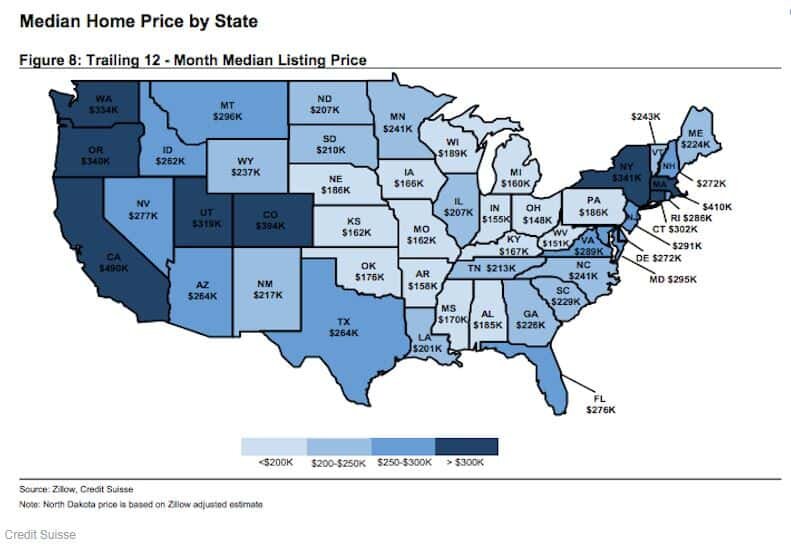
Given these changes to tax law, it seems likely that the states with higher property taxes and higher home values will be the most vulnerable to price adjustments. Below is a map, from Zillow and Credit Suisse, showing the median home price by state:
Let's also locate the states that have a high concentration of mortgages over $500,000. As mentioned above, this may put price pressure on homeowners trying to sell houses above the new $750,000 mortgage interest deduction threshold:
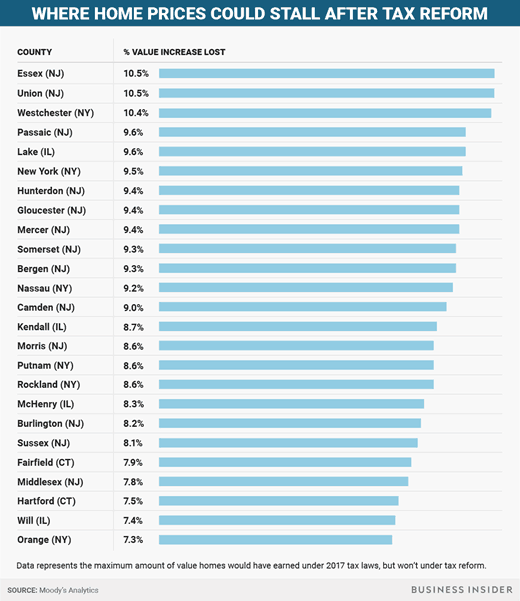
And the "Non-Winners" are New York, California, and New Jersey. Moody's published a list of the 25 counties that are expect to lose the largest percentage of value. Note, that only six of those counties are located outside of New York or New Jersey:
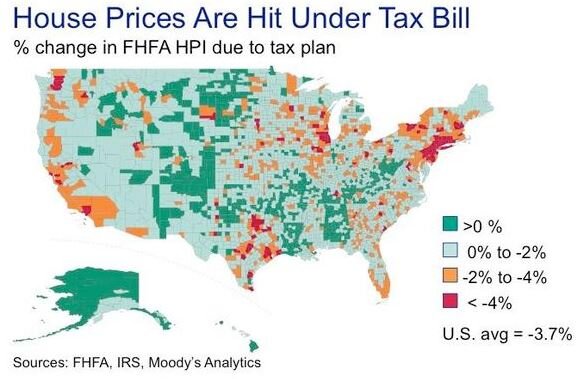
To bring it all together, Moody's and FHFA published the illustration below showing the percentage change in the Federal Housing Finance Agency – House Price Index as a result of the new tax bill:
It's safe to assume that geographically, the negative impact that the new tax rules will have on the U.S. house market will occur in concentrated pockets as opposed to a widespread reduction in housing prices across the country.
Do Not Move To Alaska Just Yet!!
Before you show the chart above to your family at dinner tonight with a “Go Alaska” hat on, I urge you to read on. (Disclosure, I have nothing against Alaska. I was born in Fairbanks, Alaska) If you live in one of the “red spots” on the heat map above or in one of the counties in the list of “where home prices could stall after tax reform”, the charts above do not necessarily mean that at the end of 2018 your house is going to be worth 5% less than it was at the beginning of 2018. Moody’s has done the comparison of the tax bill passing versus no tax bill. If prior to the tax bill being passed it was estimated in 2018 that homes in your area were going to increase in value by 5% and the heat map above shows a 4% drop as a result of tax reform, then that means instead the value of your home growing by 5% it may only grow by 1%.
As with any forecast, it’s anyone’s guess at this point how the math will actually work itself out but in general I think it will be more positive than the consensus expects.
House Values Under $250,000 – Status Quo
Given the changes to the tax law, if you live in a house that is valued under $250,000, regardless of where you live, the downward pressure on the price of your house as a result of tax reform should be minimal. Why? Most buyers in this range will most likely be electing the standard deduction anyways so the new $10,000 cap on SALT deductions should have little to no impact. This should even be true for states that have high property taxes because the homeowners would need over $24,000 in itemized deductions before the $10,000 cap would potentially hurt them tax wise.
The Sandwich: House Values $250,000 - $750,000
The homeowners at the highest risk of a reduction in the value of their house are located in what I call “The Sandwich”. They have a house that is valued somewhere between $250,000 – $750,000 and they live in a high property tax state. While Congress touts that the doubling of the standard deduction is a “fix all” for all of the tax deductions that have been taken away, it’s unfortunately not. There are a number of individuals and families that are in the income range customarily associated with buying a $250K – $750K house that may actually pay more in taxes under the new rules.
Taxpayers in this group are also moving from their “starter house” in their first “big house”. Unlike the super wealthy that may care less about paying an extra $5,000 in taxes per year, for an upper middle class family that has kids, that is saving for college, and contributing to 401(k) plans, the loss of that tax benefit may mean they can’t take a family vacation if they buy that bigger house. Less buyers in the market for houses in this “Sandwich” range translates to lower prices.
How much lower? Probably nothing dramatic in the short term because the U.S. economy is doing so well. When the economy is growing, people feel secure in their jobs, wages are going up, workers are getting bonuses, and that provides them with the additional income needed to make that larger mortgage payment and pay a little more in taxes.
My concern would be for someone that is planning to purchase a house and then sell within the next 5 years. If the economy goes into a recession, people start losing their jobs, and the U.S. consumer starts look for more ways to stretch their dollars, the homeowners that stretched themselves to buy the bigger house based on the big bonus that they received when the economy was humming are at a big risk of losing their house. In addition, there may be fewer buyers in the market because families may not want to waste money on property taxes that they can’t deduct.
The Millionaire Club: House Values $750,000+
It would seem that houses in the $750,000+ range have the most lose to for two reasons. First, homeowners in this category pay the highest property taxes and they are typically not electing the standard deduction at this income level. Second, home buyers at this price point would also be negatively impacted by the lower $750,000 cap on the mortgage interest deduction.
But I doubt this will be the case. Why? There is only so much lake front property. If you make over $5M per year and you fall in love with a lake house in upstate New York that has a $1.5M price tag, while you could try to find a similar lake house in a more tax friendly state, if you make $5M per year, what’s another $15,000 in expenses for buy your first choice.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
How Rental Income Will Be Taxed In Years 2019+
Tax reform will change the way rental income is taxed to landlords beginning in 2018. Under current law, rental income is classified as "passive income" and that income simply passes through to the owner's personal tax return and they pay ordinary income tax on it. Beginning in 2018, rental income will be eligible to receive the same preferential tax
Tax reform will change the way rental income is taxed to landlords beginning in 2018. Under current law, rental income is classified as "passive income" and that income simply passes through to the owner's personal tax return and they pay ordinary income tax on it. Beginning in 2018, rental income will be eligible to receive the same preferential tax treatment as the "qualified business income" (QBI) for small business owners.
20% Deduction
Starting in 2018, taxpayers with qualified business income (including rental income), may be eligible to take a tax deduction up to 20% of their QBI. Determining whether or not you will be eligible to capture the full 20% deduction on your rental income will be based on your total taxable income for year. The taxable income thresholds are as follows:Single filers: $157,500Married filing joint: $315,000"Total taxable income" is not your AGI (adjusted gross income) and it's not just income from your real estate business or self-employment activities. It's your total taxable income less some deductions. The IRS has yet to provide us with full guidance on the definition of "total taxable income". For example, let's assume you have three rental properties owned by an LLC and you net $50,000 in income from the LLC each year. But your wife is a lawyer that makes $350,000 per year. Your total taxable income for the year would be $400,000 landing you above the $315,000 threshold.
Below The Income Threshold
If your total taxable income is below the income thresholds listed above, the calculation is very easy. Take your total QBI and multiply it by 20% and that's your tax deduction.
Above The Income Threshold
If your total taxable income is above the thresholds, the calculation gets more complex. If you exceed the income thresholds, your deduction is the LESSER of:
20% of QBI
The GREATER OF:
50% of W-2 wages paid to employees
25% of W-2 wages paid to employees PLUS 2.5% of the unadjusted asset basis
The best way to explain the calculation is by using an example. Assume the following:
I bought a commercial building 3 years ago for $1,000,000
I have already captured $100,000 in depreciation on the building
After expenses, I net $150,000 in income each year
The LLC that owns the property has no employees
I'm married
I own a separate small business that makes $400,000 in income
Since I'm over the $315,000 total taxable income threshold for a married couple filing joint, I will calculate my deduction as follows:The LESSER of:
20% of QBI = $30,000 ($150,000 x 20%)
The GREATER of:
50% of W-2 wage paid to employees = $0 (no employees)
25% of W-2 wages page to employees plus 2.5% of unadjusted basis
(25% of wages = $0) + (2.5% of unadjusted basis = $25,000) = $25KIn this example, my deduction would be limited to $25,000. Here are a few special notes about the calculation listed above. In the 11th hour, Congress added the "2.5% of unadjusted basis" to the calculation. Without it, it would have left most landlords with a $0 deduction. Why? Real estate owners typically do not have W-2 employees, so 50% of W-2 wages would equal $0. Some larger real estate investors have "property management companies" but they are usually set up as a separate entity. In which case, the W-2 income of the property management company would not be included in the calculation for the QBI deduction. If you are someone who owns a property or properties and is need of a Property management company to help you with organizing and operating your property, then doing research in your general area to find a real estate company that can help you with that is important.Another special note, 2.5% is based on an unadjusted basis and it's not reduced by depreciation. However, the tangible property has to be subject to depreciation on the last day of the year to be eligible for the deduction. Meaning, even though the 2.5% is not reduced for the amount of depreciation already taken on the property, the property must still be in the "depreciation period" on the last day of the year to be eligible for the QBI deduction.Tony Nitti, a writer for Forbes, also makes the following key points:
The depreciable period starts on the date the property is placed in service and ends on the LATER of:
- 10 years, or- The last day of the last full year in the asset's "regular" (not ADS) depreciation periodMeaning, if you purchase a non-residential rental building that is depreciated over 39 years, the owner can continue to capture the depreciation on the building but that will not impact the 2.5% unadjusted basis number for the full 39 years of the depreciation period.
Any asset that was fully depreciated prior to 2018, unless it was placed in service after 2008, will not count toward the basis.
Shareholders or partners may only take into consideration for purposes of applying the limitation 2.5% his or her allocable share of the basis of the property. So if the total basis of commercial property is $1,000,000 and you are a 20% owner, you basis limitation is $1,000,000 x 20% x 2.5% = $5,000
Phase-In Of The Threshold
The questions I usually get next is: "If I'm married and our total taxable income is $320,000 which is only $5,000 over the threshold, do I automatically have to use the more complex calculation?" The special calculation "phases in" over the following total taxable income thresholds:Single filers: $157,500 - $207,500Married filing joint: $315,000 - $415,000I won't get into the special phase-in calculation because it's more complex than the special "above the income threshold" calculation that we already walked through but just know that it will be a blend of the straight 20% deduction and the W-2 & 2.5% adjusted basis calculation.
Qualified Trade or Business Requirement
In August 2018, the IRS came out with further clarification of how the QBI deduction would apply to real estate. In order to qualify for the QBI deduction for real estate income, your real estate holdings have to qualify as a "trade or business". The definition of a trade or business for QBI purposes deviates slightly from the traditional IRS definition. There is a safe harbor that states if you spend more than 250 hours a year working on that business it will qualify for the deduction.There are a few items to consider in the 250 hour calculation. So called "drive bys" where the owner is spending time driving by their properties to check on them does not count toward the 250 hours. If you have a property management company, the hours that they spend managing your propoerty can be credited toward your 250 hour requirement. However, the property management company has to provide you with proper documentation to qualify for those credited hours.
Consult Your Accountant
I'm a Certified Financial Planner®, not an accountant. I wrote this article to give real estate investors a broad view of what tax reform may have instore for them in 2018. If you own rental property, you should be actively consulting with our accountant through the year. As the IRS continues to release guidance regarding the QBI deduction throughout 2018, you will want to make sure that your real estate holdings are positioned properly to take full advantage of the new tax rules.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
What Does Tax Reform Mean For The Markets In 2018?
2017 ended up being a huge year for the U.S. stock market. The rally in the stock market was unmistakably driven by the anticipated passing of tax reform and Congress delivered. However, the sheer magnitude of the stock market rally has presented investors with a moment of pause and a lot of unanswered questions as we enter into the first quarter
2017 ended up being a huge year for the U.S. stock market. The rally in the stock market was unmistakably driven by the anticipated passing of tax reform and Congress delivered. However, the sheer magnitude of the stock market rally has presented investors with a moment of pause and a lot of unanswered questions as we enter into the first quarter of 2018. The two main questions being:
What does tax reform mean for the markets in 2018?
We are now in the second longest economic expansion of ALL TIME!!! I know what goes up, eventually comes down. Are we overdue for a major correction in the stock market?
Without a crystal ball, no one knows for sure. However, the purpose of this article is to identify indicators in the economy and the financial markets that may help us gauge the direction of the U.S. economy and equity markets as we progress through 2018.
Tax Reform: Uncharted Waters
While tax reform is a welcome friend for corporate America, we have to acknowledge that this also puts us in uncharted waters. Looking back, there has never been a time in history where the U.S. has injected fiscal stimulus (tax reform) into an economy that is already healthy. The last major tax reform was in the early 1980’s when the U.S. economy was trying to dig itself out of the long 1970’s recession.
When the economy is in a recession, the U.S. can either inject fiscal stimulus or monetary stimulus to get the economy growing again. The U.S. used monetary stimulus to dig us out of the Great Recession of 2008 – 2009. They lowered interest rates to basically 0%, pumped cash into the economy in the form of bond buying, and provided a financial back stop for the U.S. banking system.
These economic stimulus tools are similar to the concept of giving a patient in a hospital a shot of adrenaline. If a patient is flat lining, it provides that patient with a huge surge of energy. The patient’s body goes from 0% to 60%+ in under a minute. So what happens when you give someone who is completely healthy a shot of adrenaline? Do they go from 100% to 110%? My point is a healthy patient does not go from 100% to 160%. Both patients get a boost but the boost to the healthy patient is much lower as a percentage of where they started.
While we have never given the U.S. economy an adrenaline shot after a long economic expansion, I think it’s reasonable to apply the same general concept as our two hospital patients. Tax reform may very well lead to another year of positive returns for the stock market in 2018 but I think it’s very important for investors to set a reasonable expectation of return for the U.S. equity markets given the fact that we are injecting growth into an economy that is already at “full employment”.
Not Enough Workers
One of the greatest challenges that the U.S. economy may face in 2018 is a shortage of qualified workers. Prior to tax reform being passed, companies both large and small, have had plenty of job openings but have not been able to find the employees with the skills necessary to fill those positions.
For example, if Apple had 1000 job openings in November 2017 just to meet the current demand for their goods and services but in 2018, due to tax reform, consumers have more money to spend, and the demand for Apple products increases further, Apple may need to find another 2000 employee to meet the increase in demand. They are having trouble now finding the 1000 employees to meet their current demand, how are they going to find another 2000 quick enough in 2018 to meet the increase in demand? If they can’t make the phones, they can’t sell the phones. Fewer sales equals less revenue, which equals less net profit, which may lead to a lower appreciation rate of the stock price. For disclosure purposes, I’m not picking on Apple. I’m just highlighting an issue that may be common among the companies that make up the S&P 500 Index if tax reform leads to a spike in demand in 2018. If Wall Street is expecting accelerated earnings, how are the companies expected to deliver those enhanced earnings without the employees that they need to increase supply?
The unemployment rate in the U.S. is currently 4.1%. You have to go all the way back to the late 1960’s to find an employment rate below 4%. So we are essentially at “full employment”.
Rising Wages
The blue line in the chart above is also very important. The blue line represents wage growth. This answers the question: "Are people making more for doing the same amount of work?" If you look back historically on the chart, when the unemployment rate was falling, typically wage growth was increasing. It makes sense. When the economy is good and the job market is healthy, companies have to pay their employees more to keep them. Otherwise they will go work for a competitor, who has 10 job openings, and they get paid more. Wage growth is good for employees but it's bad for companies. For companies, employee wages are usually their largest expense. If you increase wages, you are increasing expenses, which decreases profits. Lower profits typically results in lower stock prices. Companies in 2017 had the luxury of strong demand but limited wage growth. My guess is you will begin to see meaningful wage growth in 2018 as companies see an increase in demand as a result of tax reform and end up having to raise wages to retain and attract employees. This is just another reason why 2018 may be a good year for the stock market but not a great one.
What Fuels GDP Growth?
Gross Domestic Product ("GDP") is the economic indicator that is used to measure how much the U.S. economy produces in a year. It's how we gauge whether our economy is growing or contracting. Since March 2009, the GDP growth rate has averaged about 2.2% per year. This is subpar by historic standards. In most economic expansions, GDP is growing at an annual rate of 4%+.
Before we get into what pieces of tax reform may help to increase the GDP growth rate, let us first look at what GDP is made of. Our GDP is comprised of 5 categories (for my fellow econ nerds that assign 4 categories to GDP, we split capital spending into two separate categories):
Consumption or "Consumer Spending" 69.1%
Government Spending (includes defense) 17.3%
Investment (ex-housing) – "Business Spending 12.7%
Housing 3.8%
Net Exports -2.9%
Consumer Spending (+)
Consumer spending which makes up 69.1% of our GDP should increase as a result of tax reform in 2018. In general, if people have more discretionary income, they will spend all or a portion of it. Tax reform will lower the tax bill, for not all, but many U.S. households, increasing their disposable income. Also, if we see an increase in wage growth in 2018, people will be taking home more in their paychecks, allowing them to spend more.
Dr James Kelly, the chief economist of JP Morgan, made a very interesting observation about the evolution of the tax bill. When the tax bills were in their proposed state, one for the Senate and a separate bill for the House, each bill to stay under the $1.5 Trillion 10 year debt cap reduced taxes by about $150 Billion dollars per year. 50% of the annual tax reduction was going to businesses with the other 50% going to individual tax payers.
In order to get the bill passed before the end of the year, Congress was forced to shift a larger proportion of the $150 billion in tax brakes per year to individual taxpayers. In the tax bill’s final form, Dr Kelly estimated that approximately 75% of the tax reductions were now being retained by individual taxpayers with only 25% going to businesses. With a larger proportion of the tax breaks going to individual taxpayers that could increase the amount of discretionary income available to the U.S. consumer.
Government Spending (Push)
The anticipated increase in government spending really stems from the Trump agenda that has been communicated. One of the items that he campaigned on was increasing government spending on infrastructure. At this point we do not have many details as to when the infrastructure spending will begin or how much will be spent. Whatever ends up happening, we are not forecasting a dramatic increase or decrease in government spending in 2018.
Investment - Business Spending (+)
Even though business spending only represents 12.7% of our GDP, we could see a sizable increase in spending by businesses in 2018 for the following reasons:
Corporate tax rate is reduced from 35% to 21%
The repatriation tax will allow companies to bring cash back from overseas at a low tax rate
Prior to tax reform, companies already had historically high levels of cash on their balance sheet. What are they going to do with more cash? (See the chart below)
If having more cash was not a large enough incentive by itself for companies to spend money, the new tax rules allowing immediate expensing of the full cost of most assets purchased for the next five years should be. Under the current tax rules, when a business purchases a new piece of equipment, a fleet of trucks, office furniture, whatever it is, the IRS does not allow them to deduct 100% of purchase price in the year that they buy it. They have to follow a "depreciation schedule" and they can only realize a piece of that expense each year. The current tax rules put companies at a tax disadvantage because companies are always trying to shelter as much income as possible from taxation. If Company XYZ buys a piece of equipment that cost $1,000,000, the IRS may require Company XYZ to depreciate that expense over a 10 year period. Meaning they can only realize $100,000 in expenses each year over that 10 year period, even though they already paid the full $1,000,000 for that new piece of equipment.Under the new tax reform, if Company XYZ buys that same new piece of equipment for $1,000,000, they can deduct the full $1,000,000 expense against their income in 2018. Whoa!!! That's huge!! Yes it is and it's a big incentive for companies to spend money over the next five years.
Housing & Net Exports (Push)
We do not expect any significant change from either of these two categories and they represent the smallest portion of our total GDP.
Watch GDP In 2018
The GDP growth rate in 2018 may give us the first indication as to how many "extra innings" we have left in this already long bull market rally. If we do not see a meaningful acceleration in the annual growth rate of GDP above its 2.2% average rate, the rally could be very short lived. On the flip side, if due to tax reform consumer spending and business spending leaps forward in 2018 and 2019, we may be witnessing the longest economic expansion of all time. Time will tell.
Share Buybacks
You will undoubtedly hear a lot about “Share Buybacks” in 2018. Remember, U.S. corporations will most likely have piles of cash on their balance sheets. Instead of spending that money on hiring new employees, buying new equipment, or building a new plant, what else might they do with the cash? The answer, share buybacks.
If a public company like Nike has extra cash, they can go into the market, purchase their own stock, and then get rid of those outstanding shares. Basically it increases the earnings per share for the remaining shareholders.
Example: Let’s assume there are only 4 shares of Nike owned by 4 different people and Nike is worth $100,000. That means that each shareholder is entitled to 25% of that $100,000 or $25,000 each. Now because of tax reform, Nike has $50,000 of extra cash just sitting in its coffers that it otherwise would have paid to the government in taxes. Nike can go into the market with $50,000, purchase 2 shares back from 2 of the shareholders (assuming they would be willing to sell), and then “retire” those two outstanding shares. After that is done, there are 2 outstanding shares remaining but the value of Nike did not change. So the two remaining shareholders, without paying anything extra, now own 50% of Nike, and their shares are worth $50,000 each.
Share buyback may push stock prices higher from a simple math standpoint. If the formula is the value of the company divided by the number of shares outstanding, the fewer shares there are, assuming the value of the company stays the same, the price per share will go up. The incentive for these share buybacks will most likely be there in 2018. Not only will companies have the cash but share buybacks are a way that public companies can reward their current shareholders..
Is The Stock Market Too Expensive?
The P/E ratio of the S&P 500 Index is another barometer that investors will need to keep a close eye on in 2018. P/E ratios help us to answer the questions: “Is the stock market cheap, fairly valued, or expensive at this point?” The “Forward P/E Ratio” divides the price of a stock by the estimated future 12 months of earnings. The average Forward P/E ratio for the S&P 500 Index between December 1989 – September 30, 2017 was 16.0. As of December 22, 2017, the Forward P/E ratio of the S&P 500 Index is 19.99. In other words, it’s running at 25% above its 25 year historic average. See the chart below:
Conclusion, the U.S. stock market is not “cheap” and it’s a stretch to even classify it as “fairly valued”. I think we are well into what I would consider “expensive territory”. What does that mean for investors? You have to stay on your toes!!
Now, we have an anomaly in the mix with tax reform and history does not speak to how this could play out. If tax reform leads to an acceleration in corporate earnings, that in turn could slow the steady climb in the P/E ratio of the S&P 500 because earnings are the denominator in the formula. If stock prices and earnings are accelerating at the same pace, the stock market can go up without a further acceleration of the P/E ratio. Thus, keeping the stock market from becoming more overpriced and further increasing the risk of owning stocks in the S&P 500.
Summary
In 2018, investors should keep a close eye on the U.S. GDP growth rate, the level of spending by corporations and consumers, the volume of share buybacks by U.S. companies, and the P/E ratio of the S&P 500 Index.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Tax Reform: Changes To 529 Accounts & Coverdell IRA's
Included in the new tab bill were some changes to the tax treatment of 529 accounts and Coverdell IRA's. Traditionally, if you used the balance in the 529 account to pay for a "qualified expense", the earnings portion of the account was tax and penalty free which is the largest benefit to using a 529 account as a savings vehicle for college.So what's the
Included in the new tab bill were some changes to the tax treatment of 529 accounts and Coverdell IRA's. Traditionally, if you used the balance in the 529 account to pay for a "qualified expense", the earnings portion of the account was tax and penalty free which is the largest benefit to using a 529 account as a savings vehicle for college.So what's the change? Prior to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (tax reform), qualified distributions were only allowed for certain expenses associated with the account beneficiary's college education. Starting in 2018, 529 plans can also be used to pay for qualified expenses for elementary, middle school, and high school.
Kindergarten – 12th Grade Expenses
Tax reform included a provision that will allow owners of 529 account to take tax-free distributions from 529 accounts for K – 12 expenses for the beneficiary named on the account. This is new for 529 accounts. Prior to this provision, 529 accounts could only be used for college expenses. Now 529 account holders can distribute up to $10,000 per student per year for K – 12 qualified expenses. Another important note, this is not limited to expenses associated with private schools. K – 12 qualified expense will be allowed for:
Private School
Public School
Religious Schools
Homeschooling
529 Accounts Will Largely Replace Coverdell IRA's
Prior to this rule change, the only option that parents had to save and accumulate money tax-free to K – 12 expenses for their children were Coverdell IRA's. But Coverdell IRA's had a lot of hang ups
Contributions were limited to $2,000 per year
You could only contribute to a Coverdell IRA if your income was below certain limits
You could not contribution to the Coverdell IRA after your child turned 18
Account balance had to be spend by the time the student was age 30
By contrast, 529 accounts offer a lot more flexibility and higher contributions limits. For example, 529 accounts have no contribution limits. The only limits that account owners need to be aware of are the "gifting limits" since contributions to 529 accounts are considered a "gift" to the beneficiary listed on the account. In 2018, the annual gift exclusion will be $15,000. However, 529 accounts have a provision that allow account owners to make a "5 year election". This election allows account owners to make an upfront contribution of up to 5 times the annual gift exclusion for each beneficiary without trigger the need to file a gift tax return. In 2018, a married couple could contribution up to $150,000 for each child to a 529 account without trigger a gift tax return.If I have a child in private school, they are in 6th grade, and I'm paying $20,000 in tuition each year, that means I have $140,000 that I'm going to spend in tuition between 6th grade – 12th grade and then I have college tuition to pile on top of that amount. Instead of saving that money in an after-tax investment account which is not tax sheltered and I pay capital gains tax when I liquidate the account to pay those expenses, why not setup a 529 account and shelter that huge dollar amount from income tax? It will probably saves me thousands, if not tens of thousands of dollars in taxes, in taxes over the long run. Plus, if I live in a state that allows tax deductions for 529 contributions, I get that benefit as well.
Income Limits and Tax Deductions
Unlike Coverdell IRA's, 529 accounts do not have income restrictions for making contributions. Plus, some states have a state tax deduction for contributions to 529 account. In New York, a married couple filing joint, receive a state tax deduction for up to $10,000 for contribution to 529 account. A quick note, that is $10,000 in aggregate, not $10,000 per child or per account.
Rollovers Count Toward State Tax Deductions
Here is a fun fact. If you live in New York and you have a 529 account established in another state for your child, if you rollover the balance into a NYS 529 account, the rollover balance counts toward your $10,000 annual NYS state tax deduction. Also, you can rollover balances in Coverdell IRA's into 529 accounts and my guess is many people will elect to do so now that 529 account can be used for K – 12 expenses.
Contributions Beyond Age 18
Unlike Coverdell IRA's which restrict contributions once the child reaches age 18, 529 accounts have no age restriction for contributions. We will often encourage clients to continue to contribute their child's 529 account while they are attending college for the sole purpose of continuing to capture the state tax deduction. If you receive the tuition bill in the mail today for $10,000, you can send in a $10,000 check to your 529 account provider as a current year contribution, as soon as the check clears the account you can turn around and request a qualified withdrawal from the account for the tuition bill, and pay the bill with the cash that was distributed from the 529 account. A little extra work but if you live in NYS and you are in a high tax bracket that $10,000 deduction could save you $600 - $700 in state taxes.
What Happens If There Is Money Left In The 529 Account?
If there is money left over in a 529 account after the child has graduated from college, there are a number of options available. For more on this, see our article "5 Options For Money Left Over In College 529 Plans"
Qualified Expenses
The most frequent question that I get is "what is considered a qualified expense for purposes of tax-free withdrawals from a 529 account?" Here is a list of the most common:
Tuition
Room & Board
Technology Items: Computers, Printers, Required Software
Supplies: Books, Notebooks, Pens, Etc.
Just as important, here are a list of expense that are NOT considered a "qualified expense" for purposes of tax free withdrawals from a 529 account:
Transportation & Travel: Expense of going back and forth from school / college
Student Loan Repayment
General Electronics and Cell Phone Plans
Sports and Fitness Club Memberships
Insurance
If there is ever a question as to where or not an expense is a qualified expense or not, I would recommend that you contact the provider of your 529 account before making the withdrawal form your 529 account. If you take a withdrawal for an expense that is not a "qualified expenses" you will pay income taxes and a 10% penalty on the earnings portion of the withdrawal.
Do I Have To Close My Coverdell IRA?
While 529 accounts have a number of advantages compared to Coverdell IRA's, current owners of Coverdell IRAs will not be required to close their accounts. They will continue to operate as they were intended. Like 529 accounts, Coverdell IRA withdrawals will also qualify for the tax-free distributions for K – 12 expenses including the provision for expenses associated with homeschooling.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
How Pass-Through Income Will Be Taxed For Small Business Owners
While one of the most significant changes incorporated in the new legislation was reducing the corporate tax rate from the current 35% rate to a 21% rate in 2018, the tax bill also contains a big tax break for small business owners. Unlike large corporations that are taxed at a flat rate, most small businesses, are "pass-through" entities, meaning that the
While one of the most significant changes incorporated in the new legislation was reducing the corporate tax rate from the current 35% rate to a 21% rate in 2018, the tax bill also contains a big tax break for small business owners. Unlike large corporations that are taxed at a flat rate, most small businesses, are "pass-through" entities, meaning that the profits from the business flow through to the business owner's personal tax return and then are taxed at ordinary income tax rates.While pass-through income will continue to be taxed at ordinary income tax rates, many small business owners will be eligible to deduct 20% of their "qualified business income" (QBI) starting in 2018. In other words, some pass-through entities will only be taxes on 80% of their pass-through income.
Pass-through entities include
Sole proprietorships
Partnerships
LLCs
S-Corps
Unanswered Questions
I wanted to write this article to give our readers the framework of what we know at this point about the treatment of the pass-through income in 2018. However, as many accountants will acknowledge, there seems to be more questions at this point then there are answers. The IRS will need to begin issuing guidance at the beginning of 2018 to clear up many of the unanswered questions as to who will be eligible and not eligible for the new 20% deduction.
Above or Below "The Line"
This 20% deduction will be a below-the-line deduction which is an important piece to understand. Tax lingo makes my head spin as well, so let's pause for a second to understand the difference between an "above-the-line deduction" and a "below-the-line deduction".The "line" refers to the AGI line on your tax return which is the bottom line on the first page of your Form 1040. While both above-the-line and below-the-line deductions reduce your taxable income, it's important to understand the difference between the two.
Above-The-Line Deductions
Above-the-line deductions happen on the first page of your tax return. These deductions reduce your gross income to eventually reach your AGI (adjusted gross income) for the year. Above-the-line deductions include:
Contributions to health savings accounts
Contributions to retirement plans
Deduction for one-half of the self-employment taxes
Health insurance premiums paid
Alimony paid, student loan interest, and a few others
The AGI is important because the AGI is used to determine your eligibility for certain tax credits and it will also have an impact on which below-the-line deductions you are eligible for. In general, the lower your AGI is, the more deductions and credits you are eligible to receive.
Below-The-Line Deductions
Below-the-line deductions are reported on lines that come after the AGI calculation. They are comprised mainly of your “standard deduction” or “itemized deductions” and “personal exemptions” (most of which will be gone starting in 2018). The 20% deduction for qualified business income will fall into this below-the-line category. It will lower the income of small business owners but it will not lower their AGI.
However, it was stated in the tax legislation that even though the 20% qualified business deduction will be a below –the-line deduction it will not be considered an “itemized deduction”. This is a huge win!!! Why? If it’s not an itemized deduction, then small business owners can claim the 20% qualified business income deduction and still claim the standard deduction. This is an important note because many small business owners may end up taking the standard deduction for the first time in 2018 due to all of the deductions and tax exemptions that were eliminated in the new tax bill. The tax bill took away a lot of big deductions:
Capped state and local taxes at $10,000 (this includes state income taxes and property taxes)
Eliminated personal exemptions ($4,050 for each individual) (Eliminated in 2018)
Family of 4 = $4,050 x 4 = $16,200 (Eliminated in 2018)
Miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to 2% of AGI floor (Eliminated in 2018)
Restrictions On The 20% Deduction
If life were easy, you could just assume that I'm a sole proprietor, I make $100,000 all in pass-through income, so I will get a $20,000 deduction and only have to pay tax on $80,000 of my income. For many small business owners it may be that easy but what's a tax law without a list of restrictions.The restriction were put in place to prevent business owners from reclassifying their W2 wages into 100% pass-through income to take advantage of the 20% deduction . They also wanted to restrict employees from leaving their company as a W2 employee, starting a sole proprietorship, and entering into a sub-contractor relationship with their old employer just to reclassify their W2 wages into 100% pass-through income.
S-Corps
Qualified business income will specifically exclude "reasonable compensation" paid to the owner-employee of an S-corp. While it would seem like an obvious reaction by S-corp owners to reduce their W2 wages in 2018 to create more pass through income, they will still have to adhere to the "reasonable compensation" restriction that exists today.
Partnerships & LLCs
Qualified business income will specifically exclude guaranteed payments associated with partnerships and LLCs. This creates a grey area for these entities. Partnerships do not have a “reasonable compensation” requirement like S-corps since companies taxed as partnerships are not allowed to pay W2 wages to the owners. Also the owners of partnerships are not required to take guaranteed payments. My guess is, and this is only a guess, that as we get further into 2018, the IRS may require partnerships to classify a percentage of a owners total compensation as a “guaranteed payment” similar to the “reasonable compensation” restriction that S-corps currently adhere too. Otherwise, partnerships can voluntarily eliminate guaranteed payments and take the 20% deduction on 100% of the pass-through income.
This may also prompt some S-corps to look at changing their structure to a partnership or LLC. For high income earners, S-corps have an advantage over the partnership structure in that the owners do not pay self-employment tax on the pass-through income that is distribution to the owner over and above their W2 wages. However, S-corp owners will have to weigh the self-employment tax benefit against the option of changing their corporate structure to a partnership and potentially receiving a 20% deduction on 100% of their income.
Sole Proprietors
Sole proprietors do not have "reasonable compensation" requirement or "guaranteed payments" so it would seem that 100% of the income generated by sole proprietors will count as qualified business income. Unless the IRS decides to enact a "reasonable compensation" requirement for sole proprietors in 2018, similar to S-corps. Before everyone runs from a single member LLC to a sole proprietorship, remember, a sole proprietorship offers no liability barrier between the owner and liabilities that could arise from the business.
Income Restrictions
There are limits that are imposed on the 20% deduction based on how much the owner makes in “taxable income”. The thresholds are set at the following amounts:
Individual: $157,500
Married: $315,000
The thresholds are based on each business owner’s income level, not on the total taxable income of the business. We need help from the IRS to better define what is considered “taxable income” for purposes of this phase out threshold. As of right now, it seems that “taxable income” will be defined as the taxpayer’s own taxable income (not AGI) less deductions.
If the owner’s taxable income is below this threshold, then the calculation is a simple 20% deduction of the pass-through income. If the owner’s taxable income exceeds the threshold, the qualified business deduction is calculated as follows:
The LESSER of:
20% of its business income OR 50% of the total wages paid by the business to its employees
Let’s look at this in a real life situation. A manufacturing company has a net profit of $2M in 2018 and pays $500,000 in wages to its employees during the year. That company would only be able to take the qualified business income deduction for $250,000 since 50% of the total employee wages ($500,000 x 50% = $250,000) are less than 20% of the net income of the business ($2M x 20% = $400,000).
This creates another grey area because it seems that the additional calculation is triggered by the taxable income of each individual owner but the calculation is based on the total profitability and wages paid by the company. For the owners that required this special calculation for exceeding the threshold, how is their portion of the lower deduction amount allocated? Multiplying the lower total deduction amount by the percent of their ownership? Just more unanswered questions.:
Restrictions For "Service Business"
There will be restrictions on the 20% deduction for pass-through entities that are considered a "service business" under IRC Section 1202(e)(3)(A). The businesses specifically included in this definition as a services business are:
Health
Law
Accounting
Actuarial Sciences
Performing Arts
Consulting
Athletics
Financial Services
Any other trade or business where the principal asset of the business is the reputation or skill of 1 or more of its employees
In a last minute change to the regulations, to their favor, engineers and architects were excluded from the definition of “service businesses”.
This is another grey area. Many small businesses that fall outside of the categories listed above will undoubtedly be asking the question: “Am I considered a service business or not?” Outside of the industries specifically listed in the tax bill, we really need more guidance from the IRS.
If you are a “services business”, when the tax reform was being negotiated it looked like service businesses were going to be completely excluded from the 20% deduction. However, the final regulations were more kind and instead implemented a phase out of the 20% deduction for owners of service businesses over a specified income threshold. The restriction will only apply to those whose “taxable income” exceeds the following thresholds:
Individual: $157,500
Married: $315,000
If you are a consultant or owner of a services business and your taxable income is below these thresholds, it would seem at this point that you will be able to capture the 20% deduction for your pass-through income. As mentioned above, we need help from the IRS to clarify the definition of “taxable income”.
Phase Out For Service Businesses
The amounts listed above: $157,500 for individual and $315,000 for a married couple filing joint, are where the thresholds for the phase out begins. The service business owners whose income rises above those thresholds will phase out of the 20% deduction over the next $50,000 of taxable income for individual filers and $100,000 of taxable income for married filing joint. This means that the 20% pass-through deduction is completely gone by the following income levels:
Individual: $207,500
Married: $415,000
Any taxpayer’s falling in between the threshold and the phase out limit will receive a portion of the 20% deduction.
Since the thresholds are assessed based on the taxpayer’s own taxable income and not the total income of the business, a service business could be in a situation, like in an accounting firm, where the partners with the largest ownership percentage may not qualify for 20% deduction but the younger partners may qualify for the deduction because their income is lower.
Tax Planning For 2018
It's an understatement to say that most small business owners will need to spend a lot of time with their accountant in the first quarter of 2018 to determine the best of course of action for their company and their personal tax situation.While we are still waiting for clarification on a number of very important items associated with the 20% deduction for qualified business income, hopefully this article has provided our small business owners with a preview of things to come in 2018.
Disclosure: I'm a Certified Financial Planner® but not an accountant. The information contained in this article was generated from hours and hours of personal research on the topic. I advise each of our readers to consult with your personal tax advisor for tax advice.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Tax Reform: Summary Of The Changes
The conference version of the tax bill was released on Friday. The House and the Senate will be voting to approve the updated tax bill this week with what seems to be wide spread support from the Republican party which is all they need to sign the bill into law before Christmas. Most of the changes will not take effect until 2018 with new tax rates for
The conference version of the tax bill was released on Friday. The House and the Senate will be voting to approve the updated tax bill this week with what seems to be wide spread support from the Republican party which is all they need to sign the bill into law before Christmas. Most of the changes will not take effect until 2018 with new tax rates for individuals set to expire in 2025. At which time the tax rates and brackets will return to their current state. Here is a run down of some of the main changes baked into the updated tax bill:
Individual Tax Rates
They are keeping 7 tax brackets with only minor changes to percentages in each bracket. The top tax bracket was reduced from 39.6% to 37%.
Capital Gains Rates
There were no changes to the capital gains rates and they threw out the controversial mandatory FIFO rule for calculating capital gains tax when selling securities.
Standard Deduction and Personal Exemptions
They did double the standard deduction limits. Single tax payers will receive a $12,000 standard deduction and married couples filing joint will receive a $24,000 standard deduction.The personal exemptions are eliminated.
Mortgage Interest Deduction
New mortgages would be capped at $750,000 for purposes of the home mortgage interest deduction.
State and Local Tax Deductions
State and local tax deduction will remain but will be capped at $10,000. An ouch for New York State. That $10,000 can be a combination of your property tax and either sales or income tax (whichever is larger or will get you to the cap of $10,000).Oh and you cannot prepay your 2018 state income taxes in 2017 to avoid the cap. They made it clear that if you prepay your 2018 state income taxes in 2017, you will not be able to deduct them in 2017.
Medical Expense Deductions
Medical expense deductions will remain for 2017 and 2018 and they lowered the AGI threshold to 7.5%. Beginning in 2019, the threshold will change back to the 10% threshold.
Miscellaneous Expense Deductions
Under the current rules, you are able to deduct miscellaneous expenses that exceed 2% of your AGI. That was eliminated. This includes unreimbursed business expenses and home office expenses.
A Few Quick Ones
Student Loan Interest: Still deductible
Teacher Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Still deductible
Tuition Waivers: Still not taxable
Fringe Benefits (including moving expenses): Will be taxable starting in 2018 (except for military)
Child Tax Credit: Doubled to $2,000 per child
Gain Exclusion On Sale Of Primary Residence: No Change
Obamacare Individual Mandate: Eliminated
Corporate AMT: Eliminated
Individual AMT: Remains but exemption is increased: Individuals: $70,300 Married: $109,400
Corporate Tax Rate: Drops to 21% in 2018
Federal Estate Tax: Remains but exemption limit doubles
Alimony
For divorce agreements signed after December 31, 2018, alimony will no longer be deducible. This only applies to divorce agreements executed or modified after December 31, 2018.
529 Plans
Under current tax law, you do not pay taxes on the earnings for distributions from 529 accounts for qualified college expenses. The new tax reform allows 529 account owners to distribute up to $10,000 per student for public, private and religious elementary and secondary schools, as well as home school students.
Pass-Through Income For Business
This is still a little cloudy but in general under the conference bill, owners of pass-through companies and sole proprietors will be taxed at their individual tax rates less a 20% deduction for business-related income, subject to certain wage limits and exceptions. The deduction would be disallowed for businesses offering "professional services" above a threshold amount; phase-ins begin at $157,500 for individual taxpayers and $315,000 for married taxpayers filing jointly.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The House Passed The Tax Bill. What's The Next Step?
Last night the house passed the Tax Cut & Jobs Act Bill with ease. Next up is the Senate vote. It’s important to understand the House and the Senate are voting on two different tax reform bills. Below is a chart illustrating the main differences between the House version and the Senate version of the tax reform bill.
Last night the house passed the Tax Cut & Jobs Act Bill with ease. Next up is the Senate vote. It’s important to understand the House and the Senate are voting on two different tax reform bills. Below is a chart illustrating the main differences between the House version and the Senate version of the tax reform bill.
As you can see, there are a number of dramatic differences between the two bills. The easy part was getting the House to approve their version because the Republican Party own 239 of the 435 seats. In other words, they own 55% of the votes.
The Senate Vote
Next, the Senate will put their tax reform bill to a vote. The vote is expected to take place during the week of Thanksgiving. However, in the Senate , which the Republican have the majority, they only have 52 of the 100 seats. In this case, they would need at least 50 “Yes” votes to get the bill approved in the senate. It’s 50, not 51 votes, because in the event of a “tie”, the Vice President gets a vote to break the tie and he is likely to vote “Yes” to keep tax reform moving along.
Reconciliation Process
Once the House and Senate have approved their own separate tax bills, they will then have to begin the reconciliation process of blending the two bills together. This will be the difficult part. The two tax bills are dramatically different so there will be a fair amount of grappling between the House and the Senate committees as to which features stay and which features get tossed out or adjusted as part of the final tax bill. In the end, the final tax reform bill cannot add more than $1.5 Trillion to the national debt over the next 10 years. Otherwise, the bill would need to return to the Senate and would require “60” votes to approve the bill. There is a slim too no chance of that happening.
Tax Reform by Christmas
President Trump wants the bill on his desk to sign into law before Christmas. While it seems likely that the Senate will pass their tax bill next week, the battle will take place in the reconciliation process that will begin immediately after that vote. It’s a tall order to fill given that there are only six weeks left in the year and how different the two bills are in their current form. However, don’t underestimate how badly the Republican party wants to put a run on the scoreboard before the end of the year. If they get tax reform through in the last week of the year, it’s an understatement to say that it will be an intense final week of December for year-end tax planning. Stay tuned for more………
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Tax Reform: Your Company May Voluntarily Terminate Your Retirement Plan
Make no mistake, your company retirement plan is at risk if the proposed tax reform is passed. But wait…..didn’t Trump tweet on October 23, 2017 that “there will be NO change to your 401(k)”? He did tweet that, however, while the tax reform might not directly alter the contribution limits to employer sponsored retirement plans, the new tax rates
Make no mistake, your company retirement plan is at risk if the proposed tax reform is passed. But wait…..didn’t Trump tweet on October 23, 2017 that “there will be NO change to your 401(k)”? He did tweet that, however, while the tax reform might not directly alter the contribution limits to employer sponsored retirement plans, the new tax rates will produce a “disincentive” for companies to sponsor and make employer contributions to their plans.
What Are Pre-Tax Contributions Worth?
Remember, the main incentive of making contributions to employer sponsored retirement plans is moving income that would have been taxed now at a higher tax rate into the retirement years, when for most individuals, their income will be lower and that income will be taxed at a lower rate. If you have a business owner or executive that is paying 45% in taxes on the upper end of the income, there is a large incentive for that business owner to sponsor a retirement plan. They can take that income off of the table now and then realize that income in retirement at a lower rate.
This situation also benefits the employees of these companies. Due to non-discrimination rules, if the owner or executives are receiving contributions from the company to their retirement accounts, the company is required to make employer contributions to the rest of the employees to pass testing. This is why safe harbor plans have become so popular in the 401(k) market.
But what happens if the tax reform is passed and the business owners tax rate drops from 45% to 25%? You would have to make the case that when the business owner retires 5+ years from now that their tax rate will be below 25%. That is a very difficult case to make.
An Incentive NOT To Contribute To Retirement Plans
This creates an incentive for business owners NOT to contribution to employer sponsored retirement plans. Just doing the simple math, it would make sense for the business owner to stop contributing to their company sponsored retirement plan, pay tax on the income at a lower rate, and then accumulate those assets in a taxable account. When they withdraw the money from that taxable account in retirement, they will realize most of that income as long term capital gains which are more favorable than ordinary income tax rates.
If the owner is not contributing to the plan, here are the questions they are going to ask themselves:
Why am I paying to sponsor this plan for the company if I’m not using it?
Why make an employer contribution to the plan if I don’t have to?
This does not just impact 401(k) plans. This impacts all employer sponsored retirement plans: Simple IRA’s, SEP IRA’s, Solo(k) Plans, Pension Plans, 457 Plans, etc.
Where Does That Leave Employees?
For these reasons, as soon as tax reform is passed, in a very short time period, you will most likely see companies terminate their retirement plans or at a minimum, lower or stop the employer contributions to the plan. That leaves the employees in a boat, in the middle of the ocean, without a paddle. Without a 401(k) plan, how are employees expected to save enough to retire? They would be forced to use IRA’s which have much lower contribution limits and IRA’s don’t have employer contributions.
Employees all over the United States will become the unintended victim of tax reform. While the tax reform may not specifically place limitations on 401(k) plans, I’m sure they are aware that just by lowering the corporate tax rate from 35% to 20% and allowing all pass through business income to be taxes at a flat 25% tax rate, the pre-tax contributions to retirement plans will automatically go down dramatically by creating an environment that deters high income earners from deferring income into retirement plans. This is a complete bomb in the making for the middle class.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Lower Your Tax Bill By Directing Your Mandatory IRA Distributions To Charity
When you turn 70 1/2, you will have the option to process Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCD) which are distirbution from your pre-tax IRA directly to a chiartable organizaiton. Even though the SECURE Act in 2019 changed the RMD start age from 70 1/2 to age 72, your are still eligible to make these QCDs beginning the calendar year that you
When you turn 70 1/2, you will have the option to process Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCD) which are distribution from your pre-tax IRA directly to a chartable organization. Even though the SECURE Act in 2019 changed the RMD start age from 70 1/2 to age 72, your are still eligible to make these QCDs beginning the calendar year that you turn age 70 1/2. At age 72, you must begin taking required minimum distributions (RMD) from your pre-tax IRA’s and unless you are still working, your employer sponsored retirement plans as well. The IRS forces you to take these distributions whether you need them or not. Why is that? They want to begin collecting income taxes on your tax deferred retirement assets.
Some retirees find themselves in the fortunate situation of not needing this additional income so the RMD’s just create additional tax liability. If you are charitably inclined and would prefer to avoid the additional tax liability, you can make a charitable contribution directly from your IRA and avoid all or a portion of the tax liability generated by the required minimum distribution requirement.
It Does Not Work For 401(k)’s
You can only make “qualified charitable contributions” from an IRA. This option is not available for 401(k), 403(b), and other qualified retirement plans. If you wish to execute this strategy, you would have to process a direct rollover of your FULL 401(k) balance to a rollover IRA and then process the distribution from your IRA to charity.
The reason why I emphases the word “full” for your 401(k) rollover is due to the IRS “aggregation rule”. Assuming that you no longer work for the company that sponsors your 401(k) account, you are age 72 or older, and you have both a 401(k) account and a separate IRA account, you will need to take an RMD from both the 401(k) account and the IRA separately. The IRS allows you to aggregate your IRA’s together for purposes of taking RMD’s. If you have 10 separate IRA’s, you can total up the required distribution amounts for each IRA, and then take that amount from a single IRA account. The IRS does not allow you to aggregate 401(k) accounts for purposes of satisfying your RMD requirement. Thus, if it’s your intention to completely avoid taxes on your RMD requirement, you will have to make sure all of your retirement accounts have been moved into an IRA.
Contributions Must Be Made Directly To Charity
Another important rule. At no point can the IRA distribution ever hit your checking account. To complete the qualified charitable contribution, the money must go directly from your IRA to the charity or not-for-profit organization. Typically this is completed by issuing a “third party check” from your IRA. You provide your IRA provider with payment instructions for the check and the mailing address of the charitable organization. If at any point during this process you take receipt of the distribution from your IRA, the full amount will be taxable to you and the qualified charitable contribution will be void.
Tax Lesson
For many retirees, their income is lower in the retirement years and they have less itemized deductions since the kids are out of the house and the mortgage is paid off. Given this set of circumstances, it may make sense to change from itemizing to taking the standard deduction when preparing your taxes. Charitable contributions are an itemized deduction. Thus, if you take the standard deduction for your taxes, you no longer receive the tax benefit of your contributions to charity. By making IRA distributions directly to a charity, you are able to take the standard deduction but still capture the tax benefit of making a charitable contribution because you avoid tax on an IRA distribution that otherwise would have been taxable income to you.
Example: Church Offering
Instead of putting cash or personal checks in the offering each Sunday, you may consider directing all or a portion of your required minimum distribution from your IRA directly to the church or religious organization. Usually having a conversation with your church or religious organization about your new “offering structure” helps to ease the awkward feeling of passing the offering basket without making a contribution each week.
Example: Annual Contributions To Charity
In this example, let’s assume that each year I typically issue a personal check of $2,000 to my favorite charity, Big Brother Big Sisters, a not-for-profit organization. I’m turning 70½ this year and my accountant tells me that it would be more beneficial to take the standard deduction instead of itemizing. My RMD for the year is $5,000. I can contact my IRA provider, have them issuing a check directly to the charity for $2,000 and issue me a check for the remaining $3,000. I will only have to pay taxes on the $3,000 that I received as opposed to the full $5,000. I win, the charity wins, and the IRS kind of loses. I’m ok with that situation.
Don’t Accept Anything From The Charity In Return
This is a very important rule. Sometimes when you make a charitable contribution, as a sign of gratitude, the charity will send you a coffee mug, gift basket, etc. When this happens, you will typically get a letter from the charity confirming your contribution but the amount listed in the letter will be slightly lower than the actual dollar amount contributed. The charity will often reduce the contribution by the amount of the gift that was given. If this happens, the total amount of the charitable contribution fails the “qualified charitable contribution” requirement and you will be taxed on the full amount. Plus, you already gave the money to charity so you have spend the funds that you could use to pay the taxes. Not good
Limits
While this will not be an issue for many of us, there is a $100,000 per person limit for these qualified charitable contributions from IRA’s.
Summary
While there are a number of rules to follow when making these qualified charitable contributions from IRA’s, it can be a great strategy that allows retirees to continue contributing to their favorite charities, religious organizations, and/or not-for-profit organizations, while reducing their overall tax liability.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.