How Pass-Through Income Will Be Taxed For Small Business Owners
While one of the most significant changes incorporated in the new legislation was reducing the corporate tax rate from the current 35% rate to a 21% rate in 2018, the tax bill also contains a big tax break for small business owners. Unlike large corporations that are taxed at a flat rate, most small businesses, are "pass-through" entities, meaning that the
While one of the most significant changes incorporated in the new legislation was reducing the corporate tax rate from the current 35% rate to a 21% rate in 2018, the tax bill also contains a big tax break for small business owners. Unlike large corporations that are taxed at a flat rate, most small businesses, are "pass-through" entities, meaning that the profits from the business flow through to the business owner's personal tax return and then are taxed at ordinary income tax rates.While pass-through income will continue to be taxed at ordinary income tax rates, many small business owners will be eligible to deduct 20% of their "qualified business income" (QBI) starting in 2018. In other words, some pass-through entities will only be taxes on 80% of their pass-through income.
Pass-through entities include
Sole proprietorships
Partnerships
LLCs
S-Corps
Unanswered Questions
I wanted to write this article to give our readers the framework of what we know at this point about the treatment of the pass-through income in 2018. However, as many accountants will acknowledge, there seems to be more questions at this point then there are answers. The IRS will need to begin issuing guidance at the beginning of 2018 to clear up many of the unanswered questions as to who will be eligible and not eligible for the new 20% deduction.
Above or Below "The Line"
This 20% deduction will be a below-the-line deduction which is an important piece to understand. Tax lingo makes my head spin as well, so let's pause for a second to understand the difference between an "above-the-line deduction" and a "below-the-line deduction".The "line" refers to the AGI line on your tax return which is the bottom line on the first page of your Form 1040. While both above-the-line and below-the-line deductions reduce your taxable income, it's important to understand the difference between the two.
Above-The-Line Deductions
Above-the-line deductions happen on the first page of your tax return. These deductions reduce your gross income to eventually reach your AGI (adjusted gross income) for the year. Above-the-line deductions include:
Contributions to health savings accounts
Contributions to retirement plans
Deduction for one-half of the self-employment taxes
Health insurance premiums paid
Alimony paid, student loan interest, and a few others
The AGI is important because the AGI is used to determine your eligibility for certain tax credits and it will also have an impact on which below-the-line deductions you are eligible for. In general, the lower your AGI is, the more deductions and credits you are eligible to receive.
Below-The-Line Deductions
Below-the-line deductions are reported on lines that come after the AGI calculation. They are comprised mainly of your “standard deduction” or “itemized deductions” and “personal exemptions” (most of which will be gone starting in 2018). The 20% deduction for qualified business income will fall into this below-the-line category. It will lower the income of small business owners but it will not lower their AGI.
However, it was stated in the tax legislation that even though the 20% qualified business deduction will be a below –the-line deduction it will not be considered an “itemized deduction”. This is a huge win!!! Why? If it’s not an itemized deduction, then small business owners can claim the 20% qualified business income deduction and still claim the standard deduction. This is an important note because many small business owners may end up taking the standard deduction for the first time in 2018 due to all of the deductions and tax exemptions that were eliminated in the new tax bill. The tax bill took away a lot of big deductions:
Capped state and local taxes at $10,000 (this includes state income taxes and property taxes)
Eliminated personal exemptions ($4,050 for each individual) (Eliminated in 2018)
Family of 4 = $4,050 x 4 = $16,200 (Eliminated in 2018)
Miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to 2% of AGI floor (Eliminated in 2018)
Restrictions On The 20% Deduction
If life were easy, you could just assume that I'm a sole proprietor, I make $100,000 all in pass-through income, so I will get a $20,000 deduction and only have to pay tax on $80,000 of my income. For many small business owners it may be that easy but what's a tax law without a list of restrictions.The restriction were put in place to prevent business owners from reclassifying their W2 wages into 100% pass-through income to take advantage of the 20% deduction . They also wanted to restrict employees from leaving their company as a W2 employee, starting a sole proprietorship, and entering into a sub-contractor relationship with their old employer just to reclassify their W2 wages into 100% pass-through income.
S-Corps
Qualified business income will specifically exclude "reasonable compensation" paid to the owner-employee of an S-corp. While it would seem like an obvious reaction by S-corp owners to reduce their W2 wages in 2018 to create more pass through income, they will still have to adhere to the "reasonable compensation" restriction that exists today.
Partnerships & LLCs
Qualified business income will specifically exclude guaranteed payments associated with partnerships and LLCs. This creates a grey area for these entities. Partnerships do not have a “reasonable compensation” requirement like S-corps since companies taxed as partnerships are not allowed to pay W2 wages to the owners. Also the owners of partnerships are not required to take guaranteed payments. My guess is, and this is only a guess, that as we get further into 2018, the IRS may require partnerships to classify a percentage of a owners total compensation as a “guaranteed payment” similar to the “reasonable compensation” restriction that S-corps currently adhere too. Otherwise, partnerships can voluntarily eliminate guaranteed payments and take the 20% deduction on 100% of the pass-through income.
This may also prompt some S-corps to look at changing their structure to a partnership or LLC. For high income earners, S-corps have an advantage over the partnership structure in that the owners do not pay self-employment tax on the pass-through income that is distribution to the owner over and above their W2 wages. However, S-corp owners will have to weigh the self-employment tax benefit against the option of changing their corporate structure to a partnership and potentially receiving a 20% deduction on 100% of their income.
Sole Proprietors
Sole proprietors do not have "reasonable compensation" requirement or "guaranteed payments" so it would seem that 100% of the income generated by sole proprietors will count as qualified business income. Unless the IRS decides to enact a "reasonable compensation" requirement for sole proprietors in 2018, similar to S-corps. Before everyone runs from a single member LLC to a sole proprietorship, remember, a sole proprietorship offers no liability barrier between the owner and liabilities that could arise from the business.
Income Restrictions
There are limits that are imposed on the 20% deduction based on how much the owner makes in “taxable income”. The thresholds are set at the following amounts:
Individual: $157,500
Married: $315,000
The thresholds are based on each business owner’s income level, not on the total taxable income of the business. We need help from the IRS to better define what is considered “taxable income” for purposes of this phase out threshold. As of right now, it seems that “taxable income” will be defined as the taxpayer’s own taxable income (not AGI) less deductions.
If the owner’s taxable income is below this threshold, then the calculation is a simple 20% deduction of the pass-through income. If the owner’s taxable income exceeds the threshold, the qualified business deduction is calculated as follows:
The LESSER of:
20% of its business income OR 50% of the total wages paid by the business to its employees
Let’s look at this in a real life situation. A manufacturing company has a net profit of $2M in 2018 and pays $500,000 in wages to its employees during the year. That company would only be able to take the qualified business income deduction for $250,000 since 50% of the total employee wages ($500,000 x 50% = $250,000) are less than 20% of the net income of the business ($2M x 20% = $400,000).
This creates another grey area because it seems that the additional calculation is triggered by the taxable income of each individual owner but the calculation is based on the total profitability and wages paid by the company. For the owners that required this special calculation for exceeding the threshold, how is their portion of the lower deduction amount allocated? Multiplying the lower total deduction amount by the percent of their ownership? Just more unanswered questions.:
Restrictions For "Service Business"
There will be restrictions on the 20% deduction for pass-through entities that are considered a "service business" under IRC Section 1202(e)(3)(A). The businesses specifically included in this definition as a services business are:
Health
Law
Accounting
Actuarial Sciences
Performing Arts
Consulting
Athletics
Financial Services
Any other trade or business where the principal asset of the business is the reputation or skill of 1 or more of its employees
In a last minute change to the regulations, to their favor, engineers and architects were excluded from the definition of “service businesses”.
This is another grey area. Many small businesses that fall outside of the categories listed above will undoubtedly be asking the question: “Am I considered a service business or not?” Outside of the industries specifically listed in the tax bill, we really need more guidance from the IRS.
If you are a “services business”, when the tax reform was being negotiated it looked like service businesses were going to be completely excluded from the 20% deduction. However, the final regulations were more kind and instead implemented a phase out of the 20% deduction for owners of service businesses over a specified income threshold. The restriction will only apply to those whose “taxable income” exceeds the following thresholds:
Individual: $157,500
Married: $315,000
If you are a consultant or owner of a services business and your taxable income is below these thresholds, it would seem at this point that you will be able to capture the 20% deduction for your pass-through income. As mentioned above, we need help from the IRS to clarify the definition of “taxable income”.
Phase Out For Service Businesses
The amounts listed above: $157,500 for individual and $315,000 for a married couple filing joint, are where the thresholds for the phase out begins. The service business owners whose income rises above those thresholds will phase out of the 20% deduction over the next $50,000 of taxable income for individual filers and $100,000 of taxable income for married filing joint. This means that the 20% pass-through deduction is completely gone by the following income levels:
Individual: $207,500
Married: $415,000
Any taxpayer’s falling in between the threshold and the phase out limit will receive a portion of the 20% deduction.
Since the thresholds are assessed based on the taxpayer’s own taxable income and not the total income of the business, a service business could be in a situation, like in an accounting firm, where the partners with the largest ownership percentage may not qualify for 20% deduction but the younger partners may qualify for the deduction because their income is lower.
Tax Planning For 2018
It's an understatement to say that most small business owners will need to spend a lot of time with their accountant in the first quarter of 2018 to determine the best of course of action for their company and their personal tax situation.While we are still waiting for clarification on a number of very important items associated with the 20% deduction for qualified business income, hopefully this article has provided our small business owners with a preview of things to come in 2018.
Disclosure: I'm a Certified Financial Planner® but not an accountant. The information contained in this article was generated from hours and hours of personal research on the topic. I advise each of our readers to consult with your personal tax advisor for tax advice.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Should You Prepay Your Property Taxes?
If you live in New York or any other state with "higher" property taxes you should determine whether or not it makes sense to pay your 2018 property taxes prior to December 31, 2017. Why? Tax reform will be capping your state and local tax deductions at $10,000 beginning in 2018. Don't forget though, that it's important to make sure you keep on
If you live in New York or any other state with "higher" property taxes you should determine whether or not it makes sense to pay your 2018 property taxes prior to December 31, 2017. Why? Tax reform will be capping your state and local tax deductions at $10,000 beginning in 2018. Don't forget though, that it's important to make sure you keep on top of your taxes, as you don't want to cause an issue further down the line.
To prevent taxpayers from navigating around the $10,000 deduction cap that will take effect in 2018, Congress wrote right into the tax bill that taxpayers will not be able to prepay their 2018 state income taxes and take the tax deduction in 2017. However, they left the door open for prepaying your 2018 property taxes in 2017 and taking the deduction in 2017 before the cap goes into effect.
Should you do this? The answer depends on your expected income for the 2017 tax year.
Alternative Minimum Tax
Before you rush down to your town office in the last week of December to prepay your 2018 taxes, if you think your income level in 2017 is going to make you subject to AMT, I will save you the trip. Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) is a special tax calculation that was implemented back in 1969 to make sure the "wealthy" pay their fair share of taxes. The AMT calculation allows fewer deductions and exemptions than the standard tax system. Taxpayers have to calculate their taxes the "normal way" and then calculate their taxes under the AMT method. Whichever method generates the higher tax liability is the one that you pay.
The problem with AMT is over time they did not index the exemption level adequately for wage inflation since its inception in 1969. Again it was supposed to stop the wealthy from taking advantage of tax deductions. In 2017, the exemptions amounts for AMT are as follows:
Single Filer: $54,300
Married Filing Joint: $84,500
Not exactly what many of us would considered wealthy. It gets better, that exemption begins to phase out at the following levels in 2017 making more of your income subject to the special AMT calculation.
Single Filers: $120,700
Married Filing Joint: $160,900
Why am I going into so much detail amount AMT? Remember, AMT adds back deductions that were previously allowed under the standard calculation. One of those add backs is property taxes. So if your AMT tax liability exceeds your tax liability calculated with the standard formula, there is no point in prepaying your 2018 property taxes because you won't be able to deduct them anyways. Those deductions get added back in as part of the AMT calculation.
Contact Your Accountant
The AMT calculation is complex. If you are not able to accurately estimate whether or not your AMT tax liability will be greater than the standard calculation, you should contact your accountant for guidance.
Those Not Subject To AMT
If you are not subject to AMT and you plan to itemize in 2017, it probably does makes sense to prepay your property taxes for 2018 by December 29, 2017. Otherwise you are just going to lose the deduction in 2018 because it will most likely be more advantageous at that income level to just take the larger standard deduction that will be available in 2018. You end up with the best of both worlds. You get to deduct your 2018 property taxes in 2017 which reduces your income and then capture the large standard deduction in 2018,
How Do You Prepay Your Property Taxes?
So how do you pay your property taxes early? It's most likely going to require your checkbook and a trip to your town office, First, call your town office to make sure the 2018 property tax invoices are available. Once you know that they are available, you should drive down to your town office prior to December 29, 2017 and pay the tax bill.
If you escrow taxes, which many homeowners do, there is a good chance that your mortgage company will not receive your property tax bill in time to issue a check from your escrow account prior to December 29th. For this reason, you should call your mortgage services company and determine what they need to prove that you paid your 2018 property taxes with a personal check. This will hopefully prevent them from issuing a check out of your escrow account for the property taxes that you already paid with your personal check for 2018.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Tax Reform: Summary Of The Changes
The conference version of the tax bill was released on Friday. The House and the Senate will be voting to approve the updated tax bill this week with what seems to be wide spread support from the Republican party which is all they need to sign the bill into law before Christmas. Most of the changes will not take effect until 2018 with new tax rates for
The conference version of the tax bill was released on Friday. The House and the Senate will be voting to approve the updated tax bill this week with what seems to be wide spread support from the Republican party which is all they need to sign the bill into law before Christmas. Most of the changes will not take effect until 2018 with new tax rates for individuals set to expire in 2025. At which time the tax rates and brackets will return to their current state. Here is a run down of some of the main changes baked into the updated tax bill:
Individual Tax Rates
They are keeping 7 tax brackets with only minor changes to percentages in each bracket. The top tax bracket was reduced from 39.6% to 37%.
Capital Gains Rates
There were no changes to the capital gains rates and they threw out the controversial mandatory FIFO rule for calculating capital gains tax when selling securities.
Standard Deduction and Personal Exemptions
They did double the standard deduction limits. Single tax payers will receive a $12,000 standard deduction and married couples filing joint will receive a $24,000 standard deduction.The personal exemptions are eliminated.
Mortgage Interest Deduction
New mortgages would be capped at $750,000 for purposes of the home mortgage interest deduction.
State and Local Tax Deductions
State and local tax deduction will remain but will be capped at $10,000. An ouch for New York State. That $10,000 can be a combination of your property tax and either sales or income tax (whichever is larger or will get you to the cap of $10,000).Oh and you cannot prepay your 2018 state income taxes in 2017 to avoid the cap. They made it clear that if you prepay your 2018 state income taxes in 2017, you will not be able to deduct them in 2017.
Medical Expense Deductions
Medical expense deductions will remain for 2017 and 2018 and they lowered the AGI threshold to 7.5%. Beginning in 2019, the threshold will change back to the 10% threshold.
Miscellaneous Expense Deductions
Under the current rules, you are able to deduct miscellaneous expenses that exceed 2% of your AGI. That was eliminated. This includes unreimbursed business expenses and home office expenses.
A Few Quick Ones
Student Loan Interest: Still deductible
Teacher Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Still deductible
Tuition Waivers: Still not taxable
Fringe Benefits (including moving expenses): Will be taxable starting in 2018 (except for military)
Child Tax Credit: Doubled to $2,000 per child
Gain Exclusion On Sale Of Primary Residence: No Change
Obamacare Individual Mandate: Eliminated
Corporate AMT: Eliminated
Individual AMT: Remains but exemption is increased: Individuals: $70,300 Married: $109,400
Corporate Tax Rate: Drops to 21% in 2018
Federal Estate Tax: Remains but exemption limit doubles
Alimony
For divorce agreements signed after December 31, 2018, alimony will no longer be deducible. This only applies to divorce agreements executed or modified after December 31, 2018.
529 Plans
Under current tax law, you do not pay taxes on the earnings for distributions from 529 accounts for qualified college expenses. The new tax reform allows 529 account owners to distribute up to $10,000 per student for public, private and religious elementary and secondary schools, as well as home school students.
Pass-Through Income For Business
This is still a little cloudy but in general under the conference bill, owners of pass-through companies and sole proprietors will be taxed at their individual tax rates less a 20% deduction for business-related income, subject to certain wage limits and exceptions. The deduction would be disallowed for businesses offering "professional services" above a threshold amount; phase-ins begin at $157,500 for individual taxpayers and $315,000 for married taxpayers filing jointly.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Attention Middle Class: The End Is Near
I'm not a fan of conspiracy theories and I'm not a fan of "doom and gloom" articles. However, I feel compelled to write this article because I want people to be aware of a trend that is unfolding right now in our economy. This trend will strengthen over time, we will cheer for it as it's happening, but like many great things in history, it may have an
I'm not a fan of conspiracy theories and I'm not a fan of "doom and gloom" articles. However, I feel compelled to write this article because I want people to be aware of a trend that is unfolding right now in our economy. This trend will strengthen over time, we will cheer for it as it's happening, but like many great things in history, it may have an unintended consequence. I fear that the unintended consequence of this new trend will be the elimination of the U.S. middle class.
More Profits
I’m an investment advisor so I naturally love a strong bull market that results in large investment gains for our clients. The stock market generally goes up when companies are more profitable than the consensus expects. Higher profits equal higher stock prices which equal more wealth for investors. Corporations have become laser-focused on findings new ways to increase profits. This is important because businesses that struggle to make profits and have constant losses are not so successful and will probably end up shutting down in the near future, according to websites like https://www.laraedo.com/signs-that-my-business-is-ripe-for-a-shutdown/. The equation for net profit is easy:
Revenue – Expenses = Net Profit
Let me ask you this question: What is typically a company’s largest expense?
Answer: Payroll. Said another way, the employees. Salaries, benefits, the building to house the employees, training, workers comp, payroll taxes, and the list goes on and on. If you are the owner of a company that makes cell phones and I told you that I have a way that you can make TWICE as many cell phones with HALF the number of employees, what do you think is going to happen to profits? Up!!! In a big way.
The scenario that I just described is not something that might happen in the future, it’s something that is happening right now. Here is the data to support it.
The chart below compares the 10 largest companies in the S&P 500 Index in 1990 to the 10 largest companies in the S&P 500 in 2016. First, you may notice that none of the companies that were the largest in 1990 remained on the list in 2016. But here is the trend that I want to point out. When you look at the 10 largest companies in 1990, they produced $368 Billion dollars of revenue and employed 1.4 Million workers. Fast forward to 2016, the top 10 largest companies produced $1.2 Trillion dollars in revenue and employed about 1.6 Million workers. Now let’s do some quick math, between 1990 and 2016 the gross revenue of the largest 10 companies in the S&P 500 increased by 239% but the number of workers employed by those companies only increased by 14%. Companies are already doing more with less people.
Just when you thought things were going good for the company, I now come to you, the owner of the company, and tell you I have a way to make profits double within the next 3 years. Are you interested? Of course you are. All we have to do is buy these three machines that will replace another 50% of the employees. These machines work 24 hours a day, don’t need health insurance, don’t get sick, and we can move to a smaller building which will reduce rent by 60%. How is that possible? Welcome to the party…..artificial intelligence.
Not A Terminator Movie
What do we think of when we hear the words “artificial intelligence”? Terminators!! Fortunately for us that’s not the artificial intelligence that I’m referring too. But a machine that thinks and learns from its mistakes? The human mind is not as unique as we would like to think it is. Just take a Myers Briggs personality test. You answer 100 questions and then it tells you how you react to things, what annoys you, what your strengths are, how you communicate, and what you have difficulties with. It’s kind of scary as you read the results and realize “Yup. That’s me”
Think about it. Google may know more about you than your spouse. What do you want for Christmas? Your spouse may not know but Google knows all of the items that you looked at over the past 3 months, what items you spent the most time looking at, did you click on the description to read more, and what other items did you look at after you click on the initial item. It tells Google how you search for information. Also Google acknowledges that we all search for things differently and what we are searching for tells Google more about us. Essentially Google learns at little bit more about you every time you search for something via their website.
What about a machine that can respond to questions and it sounds just like a person when it speaks? Oh and it speaks perfect English. No more overseas call centers with people you can’t understand. With most call centers, there are probably 20 questions that represent 80% of all the questions asked. If the machine is unable to answer the question, it automatically routes that call to a living, breathing person. The programmers of the machines are notified when a question triggers a transfer to a live person, they listen to the call, and then update the software to be able to answer the question the next time it is asked. The easy math, this could reduce the number of customer service representatives that the company needs to employ by 80%. Oh and the number of employees will continue to decrease as the machines learn to answer more questions and the software gets more sophisticated.
While a company may go this direction to reduce expenses, we as the consumer will also champion this change. Think about how painful it is to call the cable company. What if I told you that when you call you won’t have to wait on hold, the “person” that you are speaking to will know how to resolve your problem, and you will be off the phone in less than 2 minutes. Time is a valuable commodity to us. Fix my problem and fix it quickly. If a machine can do that better than a real person, be my guest. If companies want it and we as the consumer want it, how fast do you think it’s going to happen?
I Can't Be Replaced By A Machine.....Wrong
While we will cheer how the new A.I. technology saves us time and makes life easier, many of us will have the hubris that “a machine can’t do what I do?”. While a machine may not be able to replace 100% of what you do, could it replace 50%? It’s going to be presented like this, “you know all of those daily tasks that you don’t like to do: paperwork, scanning forms, payroll, and preparing financial reports for the weekly managers meeting. Well you don’t have to do those anymore.” Yes!!!! Oh and more good news you don’t have to train a new employee to complete those tasks and wonder if they are going to leave a year from now and have to train someone else.
Programming a machine to complete a task is not too different from training a new employee. When you hire a new employee many of them may know very little about your industry, they have no idea how your company operates, how to answer tough questions from prospects, etc. You have to train them or “program” them. Then they learn on the job from there. The value of having 20 years of experience is you have seen many difficult situations throughout your career and you learned from your past experiences. The next time the same or similar problem surfaces you know how to react. Normally what you do is you teach those lessons to each new manager and employee over and over again. That takes time. What if you only had to teach that lesson one more time and every new employee already knew how to react in the same tough situation? That’s artificial intelligence.
My point, this trend will not be limited to just manufacturing or customer services. This new technology will eventually impact each of our careers in some way, shape, or form.
3 Stages
I expect this to happen in three stages.
Stage 1: Companies do MORE with only a FEW MORE employees
Stage 2: Companies do MORE with the SAME number of employees
Stage 3: Companies do MORE with LESS employees
We are already through Stage 1 and we are entering Stage 2. How long will it be before we reach stage 3? That’s anyone’s guess. But with most evolution, Stage 1 takes the longest and the following stages evolve more rapidly. If Stage 1 took 16 years, my guess would be that stage 3 will be here a lot sooner than we think.
So What Happens To All Of The Employees?
The million dollar question and I don't know the answer. If I had to guess, the current middle class is going to be divided into two. Half of the middle class is going move up into the "upper class" and the other half will be "unemployed". The level of education will be the dividing line. Companies will continue to do more with less people. The only way to stop it is to tell companies that need to stop trying to be more profitable. Good luck. Our entire economy is built on the premise that you should accumulate as much as you can as fast as you can.
War and Conflict
When I look back in history, major conflicts arise when there is a large deviation between the “Have’s” and the “Have Not’s”. The fancy name that is used today is “income inequality”. When you have a robust middle class, everyone has something to lose if a conflict arises because that conflict generally disrupts the current system, uncertainty prevails, the economy goes into a recession, people lose their job, and they in turn cannot make their mortgage payment.
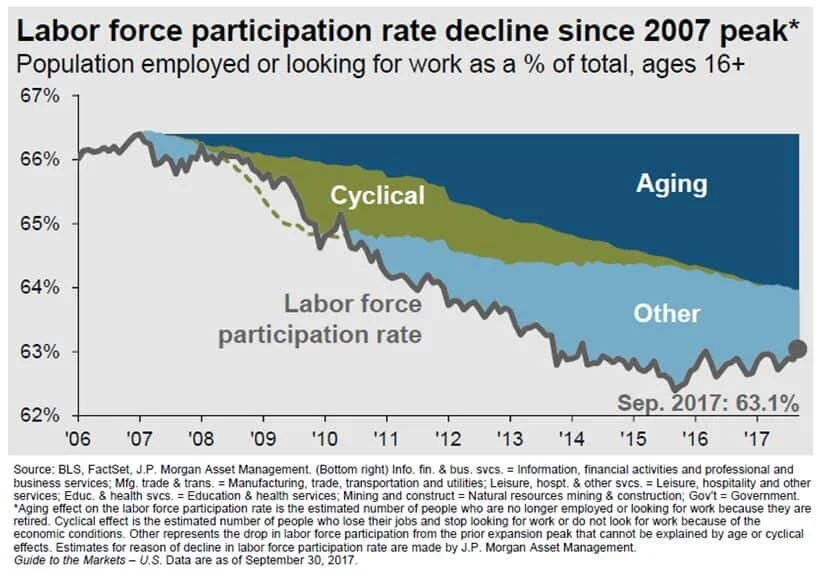
If instead, a majority of the population is unemployed and they can’t find a job because the jobs don’t exist anymore, that group of individuals has nothing to lose by burning the current system to the ground and rebuilding a new one from the ashes. I know that sounds dark but there is no arguing the gap between the Have’s and the Have Not’s is getting larger. Just look at the labor participation rate:
The Labor Participation Rate answers the question, how many people in the U.S. that could be working either are working or are looking for work? If there are individuals who could work, don’t have a job, and stop looking for work, they drop out of the labor force which decrease the labor participation rate because there are less citizens participating on the work force. As you can see in the chart above, in 2006 the labor participation rate was around 66%, and while we continue to experience one of the longest economic expansions of all time, the labor participation rate is still lower now than it was prior to the beginning of the economic recovery. Remember we are in an expansion and it has dropped by about 3%. What do you think will happen when we hit the next recession? While the baby boomer generation has had an impact on these numbers as you can see based on the large percentage of that decrease attributed to an “aging population”. Traditionally when someone retires, the company will promote the person below them and then hire another person to fill there spot. As many of us know, that’s not how it works anymore. Now that key employee retires, the company promotes one person into their role, but instead of hiring a new employee they just redistribute the work to the current staff. If anything, the baby boomer generation moving into retirement has made this transition to “do more with less people” easier on companies because they don’t have to fire anyone.
Tax Reform Will Accelerate The Trend
If you combine tax reform with the current 4.1% employment rate, I would expect this to accelerate the development of artificial intelligence. Companies are going to have cash from the tax savings to reinvest into new technologies which includes artificial intelligence. If the economy continues to grow at its current 2% pace or accelerates, one would expect consumption to increase which increases the demand for products and services. With the unemployment rate at 4.1%, we are already at "full employment". There are not enough qualified workers for companies to hire to meet the increase in demand for their product or service. The answer, let's accelerate the development of artificial intelligence that will allow the company to enter Phase 2 which is "Do MORE with the SAME number of workers".
People Will Cheer
These advances in technology are potentially setting the stage for levels of profitability that companies have only dreamed of. Higher profits traditionally equal higher stock prices. Investors will cheer this!! It may even lead us to the longest economic expansion of all time. In the short term, investors may have a lot to be excited about but we may look back years from now and realize that we were unintentionally cheering for the end of the middle class as we know it.
Again, this article is not meant to be a “dark cloud” or a new conspiracy theory but rather to keep our readers aware of the world that is changing rapidly around us. Like many of the economic challenges that the U.S. economy has experienced in the past, the hazard was in plain view, but investors failed to see it because they got caught up in the moment. When investing, it’s ok to take advantage of short term gains but never lose sight of the big picture.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
A Lesson From Bitcoin
I'm not writing this article to predict whether Bitcoin is going to $0 or $50,000. I have no idea whether it's going to go up or down from here. But I have had countless conversations with clients and friends over the past few weeks which starts like this "What do you think about Bitcoin?"My response is, before you make any type of investment, you should
I'm not writing this article to predict whether Bitcoin is going to $0 or $50,000. I have no idea whether it's going to go up or down from here. But I have had countless conversations with clients and friends over the past few weeks which starts like this "What do you think about Bitcoin?"
My response is, before you make any type of investment, you should be able to answer the following questions. If you can't answer these questions with confidence, you probably should not be investing in it.
"Explain It To Me In 30 Seconds"
Investing is as much of an art as it is a science which is why you can ask three different investment advisors about the same investment and get three different answers. While the full analysis of an investment can be complex and require a thorough understanding of markets, equity analysis, and financial reports, seasoned veterans have mastered their craft and have a way of simplifying the process. One of the lessons that I learned from my mentor and that I continue to apply to selecting investments today is "If you can't explain it to me in less than 30 seconds, I don't want to have anything to do with it."Before investing in anything, you should:
Develop an investment thesis
Identify the risks
Identify competitors
Know at what price to sell at
Let's look at each of these items and how they apply to the Bitcoin situation.
Develop an investment thesis
An investment thesis answers the question, why are you committing money to that particular investment? When buying a stock, you try to identify companies that have strong management, good cash flow, a promising new product or service, expanding market share, and a competitive advantage with the expectation that the company will outperform a given benchmark.
“Because I think it will go up” is not an investment thesis. You have to include in your investment thesis items that can be measured. If for example, I decide to invest in a cell phone company because they are expected to expand into China, India, and increase their market share over the next 3 years by 50%. I have identified a clear and measurable reason why I have chosen to invest in that company.
Bitcoin poses a challenge in this sense. When you invest in a company, you are essentially investing in the future cash flow that is expected to be produced by that company. Which is why the price to earnings ratio is often used to determine if a company is “reasonably priced”. Bitcoin is a currency that does not produce future cash flow so what metrics can you build into an investment thesis that will allow you to measure your expected outcome? I have yet to hear a good answer to that question. An “expert” making a prediction that Bitcoin is going to $30,000 is not a great metric to use. Remember, price appreciation is a by product of the improvement of the underlying financial drivers of an investment. If you can’t identify what those financial drivers are, price is irrelevant.
Identify the risks
Before making any investment, you should be able to take out a sheet of paper and list of the risks to your investment thesis. If you don’t know the risks, how do you know when to get out of that investment? In my cell phone company example, I bought that stock because I expected that company to gain 50% of the cell phone market share in China & India over the next 3 years. What are the risks to that investment thesis?
Currency risk: The value of the U.S. dollar increases versus the local currency decreasing profits
Execution risk: They do not successfully execute their strategy. It takes 5 years instead of 3.
Political risk: The Chinese government assumes ownership of the company
Market risk: The global economy goes into a recession
Competitor risk: Another reputable cell phone company enters that market
Management risk: The current CEO leaves the company and the new CEO takes the company in a different direction
Cash flow risk: The company takes on too much debt trying to expand and has to scale back
While everyone goes into a new investment with the hopes and dreams that it is the next Apple, you have to be able to identify what could send your great investment tumbling to the ground.
Can you list all of the risks associated with Bitcoin? It could go to zero but that’s true of any investment. With many new technologies, services, currencies, and medical devices, you have too unfortunately accept the fact that all of the risks associated with that investment are probably not known. It does not necessarily mean it’s a bad investment since most breakthrough technology and products are met with resistance and then uniformly accepted by the masses down the road. But it does imply that the investment comes with a much higher level of risk because a greater number of unknowns exists and you have to be able to live with the fact that it has just as much of a chance of going up by 100% as it does going to zero. While this line of thinking may not completely deter you from making a particular investment, it will hopefully influence the amount that you decide to commit to riskier investments.
Identify Competitors
When identifying competitors, my first question is usually "how large are the barriers to entry into are particular product or market?" The larger the barriers to entry, the longer it takes competitors to catch up to the market leaders. It would seem in the case of Bitcoin, that the barriers to entry for cryptocurrencies are fairly low. I'm already starting to hear the buzz at holiday parties about "ICO's" which stands for Initial Coin Offering. If I were looking to invest in Bitcoin, I would be asking the questions:
Who are the other main stream cryptocurrencies?
Do they have a competitive advantage over Bitcoin?
What would entice someone to switch from Bitcoin to another cryptocurrency?
How large is the cyptocurrency market?
Will regulations eventually come into play and create barriers to entry?
How many people that invested in Bitcoin do you think can answer these questions? My guess is not many. That in itself is risky.
Knowing At What Price To Sell
Of all the investment criteria that I have listed so far, I think this one is the most problematic when it comes to Bitcoin. When making any investment, you have to be able to answer the question: “Based on all of the information that I have today, at what price should I sell it at?” If I own a rental property and it’s fair market value is $250,000 and I collect $15,000 per year in rent, if someone offered me $300,000 to buy my rental property should I sell it? To answer that question, I would map out all of the income that I expect to receive from that property over my lifetime and apply a reasonable appreciation rate of the property value itself. It’s a similar process in evaluating a stock. You are looking at the annual earnings of the company and what you expect those earnings to be in the future. Both of these examples, like most investments, generate future cash flow and have reasonable appreciation rates that can be applied. With Bitcoin, as I mentioned earlier, there is no future cash flow. It’s value right now is being set based on what the next person is willing to buy it for. If one day people wake up and decide I don’t want to buy your Bitcoin or provide you with any good or services in exchange for your Bitcoin, there is nothing there. There are no earnings, there are no products, there are no services, there are no brick and mortar buildings, it’s vapor. With traditional currency, like the U.S. dollar, you have the taxing power and the assets of the United States government confirming that the dollar bill in your hand is worth something
So if I decide to buy Bitcoin today at $14,000 per coin, at what dollar amount should I sell it because it has become overvalued? I have no idea how anyone answers that question at this point. That’s problematic because if I start to make money, the difficult decision is “when do I get out?” When investing, it’s very easy to sell investments that have lost money. It’s emotionally much more difficult to sell your winners. So again, if I buy Bitcoin today and it goes to $30,000, do I sell it? Does it keep going to $50,000? I have absolutely nothing to based that on and that’s a problem.
Remember The Tulips
The single most important take away from this articles is "make sure you understand what you are investing in". If you can't explain it in less than 30 seconds, you probably should not be investing in it. Specific to Bitcoin, I use the saying, history does not repeat itself but it does rhyme. Some of the rhyming took place in the 1600's in the form of the Tulip bubble. In the Netherlands, during the Tulip mania, the cost of a tulip equaled to the cost of a house. Don't believe it? Just take a stroll down history lane. Here's the article: Tulip Mania
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Do I Make Too Much To Qualify For Financial Aid?
If you have children that are college-bound at some point you will begin the painful process of calculating how much college will cost for both you and them. However, you might be less worried about the financial aspects of your child going to college after viewing some of the Bloomsburg student apartments for rent on the market at the moment.
If you have children that are college-bound at some point you will begin the painful process of calculating how much college will cost for both you and them. However, you might be less worried about the financial aspects of your child going to college after viewing some of the Bloomsburg student apartments for rent on the market at the moment. Anyway, I have heard the statement, "well they will just have to take loans" but what parents don't realize is loans are a form of financial aid. Loans are not a given. Whether your children plan to attend a public college or private college, both have formulas to determine how much a family is expected to pay out of pocket before you even reach any "financial aid" which includes loans.
College Costs Are Increasing By 6.5% Per Year
The rise in the cost of college has outpaced the inflation rate of most other household costs over the past three decades.
To put this in perspective, if you have a 3 year old child and the cost of tuition / room & board for a state school is currently $25,000 by the time that child turns 17, the cost for one year of tuition / room & board will be $60,372. Multiply that by 4 years for a bachelor's degree: $241,488. Ouch!!! Which leads you to the next question, how much of that $60,372 per year will I have to pay out of pocket?
FAFSA vs CSS Profile Form
Public schools and private school have a different calculation for how much “aid” you qualify for. Public or state schools go by the FAFSA standards. Private schools use the “CSS Profile” form. The FAFSA form is fairly straight forward and is applied universally for state colleges. However, private schools are not required to follow the FAFSA financial aid guidelines which is why they have the separate CSS Profile form. By comparison the CSS profile form requests more financial information.
For example, for couples that are divorced, the FAFSA form only takes into consideration the income and assets of the parent that the child lives with for more than six months out of the year. This excludes the income and assets of the parent that the child does not live with for the majority of the year which could have a positive impact on the financial aid calculation. However, the CSS profile form, for children with divorced parents, requests and takes into consideration the income and assets of both parents regardless of their marital status.
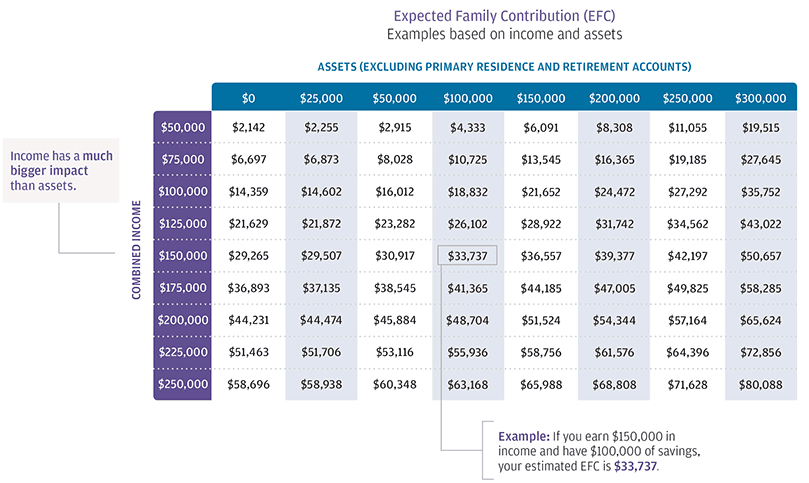
Expected Family Contribution
Both the FAFSA and CSS Profile form result in an "Expected Family Contribution" (EFC). That is the amount the family is expected to pay out of pocket for their child's college expense before the financial aid package begins. Below is a EFC award chart based on the following criteria:
FAFSA Criteria
2 Parent Household
1 Child Attending College
1 Child At Home
State of Residence: NY
Oldest Parent: 49 year old
As you can see in the chart, income has the largest impact on the amount of financial aid. If a married couple has $150,000 in AGI but has no assets, their EFC is already $29,265. For example, if tuition / room and board is $25,000 for SUNY Albany that means they would receive no financial aid.
Student Loans Are A Form Of Financial Aid
Most parents don't realize the federal student loans are considered "financial aid". While "grant" money is truly "free money" from the government to pay for college, federal loans make up about 32% of the financial aid packages for the 2016 – 2017 school year. See the chart below:
Start Planning Now
The cost of college is increasing and the amount of financial aid is declining. According to The College Board, between 2010 – 2016, federal financial aid declined by 25% while tuition and fees increased by 13% at four-year public colleges and 12% at private colleges. This unfortunate trend now requires parents to start running estimated EFC calculation when their children are still in elementary school so there is a plan for paying for the college costs not covered by financial aid.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Procedures For Splitting Retirement Accounts In A Divorce
If you are going through a divorce and you or your spouse have retirement accounts, the processes for splitting the retirement accounts will vary depending on what type of retirement accounts are involved.
If you are going through a divorce and you or your spouse have retirement accounts, the processes for splitting the retirement accounts will vary depending on what type of retirement accounts are involved.
401(k) & 403(b) Plan
The first category of retirement plans are called ?employer sponsored qualified plans?. This category includes 401(k) plans, 403(b) plans, 457 plans, and profit sharing plans. Once you and your spouse have agreed upon the split amount of the retirement plans, one of the attorneys will draft Domestic Relations Order, otherwise known as a QDRO. This document provides instruction to the plans TPA (third party administrator) as to how and when to split the retirement assets between the ex-spouses. Here is the procedures from start to finish:
One attorney drafts the Domestic Relations Order (?DRO?)
The attorney for the other spouse reviews and approved the DRO
The spouse covered by the retirement plan submits it to the TPA for review
The TPA will review the document and respond with changes that need to be made (if any)
Attorneys submit the DRO to the judge for signing
Once the judge has signed the DRO, its now considered a Qualified Domestic Relations Order (QDRO)
The spouse covered by the retirement plan submits the QDRO to the plans TPA for processing
The TPA splits the retirement account and will often issues distribution forms to the ex-spouse not covered by the plan detailing the distribution options
Step number four is very important. Before the DRO is submitting to the judge for signing, make sure that the TPA, that oversees the plan being split, has had a chance to review the document. Each plan is different and some plans require unique language to be included in the DRO before the retirement account can be split. If the attorneys skip this step, we have seen cases where they go through the entire process, pay the court fees to have the judge sign the QDRO, they submit the QDRO for processing with the TPA, and then the TPA firm rejects the QDRO because it is missing information. The process has to start all over again, wasting time and money.
Pension Plans
Like employer sponsored retirement plans, pension plans are split through the drafting of a Qualified Domestic Relations Order (QDRO). However, unlike 401(k) and 403(b) plans that usually provide the ex-spouse with distribution options as soon as the QDRO is processed, with pension plans the benefit is typically delayed until the spouse covered by the plan is eligible to begin receiving pension payments. A word of caution, pension plans are tricky. There are a lot more issues to address in a QDRO document compared to a 401(k) plan. 401(k) plans are easy. With a 401(k) plan you have a current balance that can be split immediately. Pension plan are a promise to pay a future benefit and a lot can happen between now and the age that the covered spouse begins to collect pension payments. Pension plans can terminate, be frozen, employers can go bankrupt, or the spouse covered by the retirement plan can continue to work past the retirement date.
I would like to specifically address the final option in the paragraph above. In pension plans, typically the ex-spouse is not entitled to a benefit until the spouse covered by the pension plan is eligible to receive benefits. While the pension plan may state that the employee can retire at 65 and start collecting their pension, that does not mean that they will with 100% certainty. We have seen cases where the ex-husband could have retired at age 65 and started collecting his pension benefit but just to prevent his ex-wife from collecting on his benefit decided to delay retirement which in turn delayed the pension payments to his ex-wife. The ex-wife had included those pension payments in her retirement planning but had to keep working because the ex-husband delayed the benefit. Attorneys will often put language in a QDRO that state that whether the employee retires or not, at a given age, the ex-spouse is entitled to turn on her portion of the pension benefit. The attorneys have to work closely with the TPA of the pension plan to make sure the language in the QDRO is exactly what it need to be to reserve that benefit for the ex-spouse.
IRA (Individual Retirement Accounts)
IRA? are usually the easiest of the three categories to split because they do not require a Qualified Domestic Relations Order to separate the accounts. However, each IRA provider may have different documentation requirements to split the IRA accounts. The account owner should reach out to their investment advisor or the custodian of their IRA accounts to determine what documents are needed to split the account. Sometimes it is as easy as a letter of instruction signed by the owner of the IRA detailing the amount of the split and a copy of the signed divorce agreement. While these accounts are easier to split, make sure the procedures set forth by the IRA custodians are followed otherwise it could result in adverse tax consequences and/or early withdrawal penalties.
About Michael??...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The House Passed The Tax Bill. What's The Next Step?
Last night the house passed the Tax Cut & Jobs Act Bill with ease. Next up is the Senate vote. It’s important to understand the House and the Senate are voting on two different tax reform bills. Below is a chart illustrating the main differences between the House version and the Senate version of the tax reform bill.
Last night the house passed the Tax Cut & Jobs Act Bill with ease. Next up is the Senate vote. It’s important to understand the House and the Senate are voting on two different tax reform bills. Below is a chart illustrating the main differences between the House version and the Senate version of the tax reform bill.
As you can see, there are a number of dramatic differences between the two bills. The easy part was getting the House to approve their version because the Republican Party own 239 of the 435 seats. In other words, they own 55% of the votes.
The Senate Vote
Next, the Senate will put their tax reform bill to a vote. The vote is expected to take place during the week of Thanksgiving. However, in the Senate , which the Republican have the majority, they only have 52 of the 100 seats. In this case, they would need at least 50 “Yes” votes to get the bill approved in the senate. It’s 50, not 51 votes, because in the event of a “tie”, the Vice President gets a vote to break the tie and he is likely to vote “Yes” to keep tax reform moving along.
Reconciliation Process
Once the House and Senate have approved their own separate tax bills, they will then have to begin the reconciliation process of blending the two bills together. This will be the difficult part. The two tax bills are dramatically different so there will be a fair amount of grappling between the House and the Senate committees as to which features stay and which features get tossed out or adjusted as part of the final tax bill. In the end, the final tax reform bill cannot add more than $1.5 Trillion to the national debt over the next 10 years. Otherwise, the bill would need to return to the Senate and would require “60” votes to approve the bill. There is a slim too no chance of that happening.
Tax Reform by Christmas
President Trump wants the bill on his desk to sign into law before Christmas. While it seems likely that the Senate will pass their tax bill next week, the battle will take place in the reconciliation process that will begin immediately after that vote. It’s a tall order to fill given that there are only six weeks left in the year and how different the two bills are in their current form. However, don’t underestimate how badly the Republican party wants to put a run on the scoreboard before the end of the year. If they get tax reform through in the last week of the year, it’s an understatement to say that it will be an intense final week of December for year-end tax planning. Stay tuned for more………
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Do Trusts Expire?
Do trusts have an expiration date after the death of the grantor? For most states, the answer is “Yes”. New York is one of those states that have adopted “The Rule Against Perpetuities” which requires all of the assets to be distributed from the trust by a specified date.
Do trusts have an expiration date after the death of the grantor? For most states, the answer is “Yes”. New York is one of those states that have adopted “The Rule Against Perpetuities” which requires all of the assets to be distributed from the trust by a specified date.
The Rule Against Perpetuities
For most states, the trust assets have to be distributed no later than the “lifetime of those then living plus 21 years.” In other words, the trust asset must be distributed 21 years after the death of the youngest beneficiary listed in the trust document. For example, if I setup a trust with my children listed as beneficiaries, after my passing the trust assets would have to be distributed no later than 21 years following the death of my youngest child.
Per Stirpes Beneficiaries
Some trust documents have the children listed as beneficiaries “per stirpes”. This mean that if a child is no longer alive their share of the trust passes to their heirs. In many cases their children. If the beneficiaries are listed in the trust document as per stirpes beneficiaries then you may be able to make the argument that the “youngest beneficiary” is really the grandchildren not the children which will allow the trust to retain the assets for a longer period of time. Typically trusts do not allow the perpetuity rule to extend beyond their grandchildren.
Consult An Estate Attorney
Trust can be tricky and the language in a trust document is not always black and white, so it’s highly recommended that you consult with an estate attorney that is familiar with the estate laws for you state of residence and can review the terms of the trust document.DISCLOSURE: The information listed above is not legal advice. For legal advice, please consult your attorney.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Divorce: Make Sure You Address The College Savings Accounts
The most common types of college savings accounts are 529 accounts, UGMA, and UTMA accounts. When getting divorce it’s very important to understand who the actual owner is of these accounts and who has legal rights to access the money in those accounts. Not addressing these accounts in the divorce agreement can lead to dire consequences
The most common types of college savings accounts are 529 accounts, UGMA, and UTMA accounts. When getting divorce it’s very important to understand who the actual owner is of these accounts and who has legal rights to access the money in those accounts. Not addressing these accounts in the divorce agreement can lead to dire consequences for your children if your ex-spouse drains the college savings accounts for their own personal expenses.
UGMA or UTMA Accounts
The owner of these types of accounts is the child. However, since a child is a minor there is a custodian assigned to the account, typically a parent, that oversees the assets until the child reaches age 21. The custodian has control over when withdraws are made as long as it could be proven that the withdrawals being made a directly benefiting the child. This can include school clothes, buying them a car at age 16, or buying them a computer. It’s important to understand that withdraws can be made for purposes other than paying for college which might be what the account was intended for. You typically want to have your attorney include language in the divorce agreement that addresses what these account can and can not be used for. Once the child reaches the age of majority, age 21, the custodian is removed, and the child has full control over the account.
529 accounts
When it comes to divorce, pay close attention to 529 accounts. Unlike a UGMA or UTMA accounts that are required to be used for the benefit of the child, a 529 account does not have this requirement. The owner of the account has complete control over the 529 account even though the child is listed as the beneficiary. We have seen instances where a couple gets divorced and they wrongly assume that the 529 account owned by one of the spouses has to be used for college. As soon as the divorce is finalized, the ex-spouse that owns the account then drains the 529 account and uses the cash in the account to pay legal fees or other personal expenses. If the divorce agreement did not speak to the use of the 529 account, there’s very little you can do since it’s technically considered an asset of the parent.
Divorce agreements can address these college saving accounts in a number of way. For example, it could state that the full balance has to be used for college before out-of-pocket expenses are incurred by either parent. It could state a fixed dollar amount that has to be withdrawn out of the 529 account each year with any additional expenses being split between the parents. There is no single correct way to address the withdraw strategies for these college savings accounts. It is really dependent on the financial circumstances of you and your ex spouse and the plan for paying for college for your children.
With 529 accounts there is also the additional issue of “what if the child decides not to go to college?” The divorce agreement should address what happens to that 529 account. Is the account balance move to a younger sibling? Is the balance distributed to the child at a certain age? Or will the assets be distributed 50-50 between the two parents?
Is for these reason that you should make sure that your divorce agreement includes specific language that applies to the use of the college savings account for your children
For more information on college savings account, click on the hyperlink below:
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.