Big Changes For 401(k) Hardship Distributions
While it probably seems odd that there is a connection between the government passing a budget and your 401(k) plan, this year there was. On February 9, 2018, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 was passed into law which ended the government shutdown by raising the debt ceiling for the next two years. However, also buried in the new law were
While it probably seems odd that there is a connection between the government passing a budget and your 401(k) plan, this year there was. On February 9, 2018, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 was passed into law which ended the government shutdown by raising the debt ceiling for the next two years. However, also buried in the new law were changes to rules that govern hardship distributions in 401(k) plans.
What Is A Hardship Distribution?
A hardship distribution is an optional distribution feature within a 401(k) plan. In other words, your 401(k) plan may or may not allow them. To answer that question, you will have to reference the plan’s Summary Plan Description (SPD) which should be readily available to plan participants.
If your plan allows hardship distributions, they are one of the few in-service distribution options available to employees that are still working for the company. There are traditional in-service distributions which allow employees to take all or a portion of their account balance after reaching the age 59½. By contrast, hardship distributions are for employees that have experienced a “financial hardship”, are still employed by the company, and they are typically under the age of 59½.
Meeting The "Hardship" Requirement
First, you have to determine if your financial need qualifies as a "hardship". They typically include:
Unreimbursed medical expenses for you, your spouse, or dependents
Purchase of an employee's principal residence
Payment of college tuition and relative education costs such as room and board for the next 12 months for you, your spouse, dependents, or children who are no longer dependents.
Payment necessary to prevent eviction of you from your home, or foreclosure on the mortgage of your primary residence
For funeral expenses
Certain expenses for the repair of damage to the employee's principal residence
Second, there are rules that govern how much you can take out of the plan in the form of a hardship distribution and restrictions that are put in place after the hardship distribution is taken. Below is a list of the rules under the current law:
The withdrawal must not exceed the amount needed by you
You must first obtain all other distribution and loan options available in the plan
You cannot contribute to the 401(k) plan for six months following the withdrawal
Growth and investment gains are not eligible for distribution from specific sources
Changes To The Rules Starting In 2019
Plan sponsors need to be aware that starting in 2019 some of the rules surrounding hardship distributions are going to change in conjunction with the passing of the Budget Act of 2018. The reasons for taking a hardship distribution did not change. However, there were changes made to the rules associated with taking a hardship distribution starting in 2019. More specifically, of the four rules listed above, only one will remain.
No More "6 Month Rule"
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 eliminated the rule that prevents employees from making 401(k) contributions until 6 months after the date the hardship distribution was issued. The purpose of the 6 month wait was to deter employees from taking a hardship distribution. In addition, for employees that had to take a hardship it was a silent way of implying that “if things are bad enough financially that you have to take a distribution from your retirement account, you probably should not be making contributions to your 401(k) plan for the next few months.”
However, for employees that are covered by a 401(k) plan that offers an employer matching contribution, not being able to defer in the plan for 6 months also meant no employer matching contribution during that 6 month probationary period. Starting in 2019, employees will no longer have to worry about that limitation.
Loan First Rule Eliminated
Under the current 401(k) rules, if loans are available in the 401(k) plan, the plan participant was required to take the maximum loan amount before qualifying for a hardship distribution. That is no longer a requirement under the new law.
We are actually happy to see this requirement go away. It never really made sense to us. If you have an employee, who’s primary residence is going into foreclosure, why would you make them take a loan which then requires loan payments to be made via deductions from their paycheck? Doesn’t that put them in a worse financial position? Most of the time when a plan participant qualifies for a hardship, they need the money as soon as possible and having to go through the loan process first can delay the receipt of the money needed to remedy their financial hardship.
Earnings Are Now On The Table
Under the current 401(k) rules, if an employee requests a hardship distribution, the portion of their elective deferral source attributed to investment earnings was not eligible for withdrawal. Effective 2019, that rule has also changed. Both contributions and earnings will be eligible for a hardship withdrawal.
Still A Last Resort
We often refer to hardship distributions as the “option of last resort”. This is due to the taxes and penalties that are incurred in conjunction with hardship distributions. Unlike a 401(k) loan which does not trigger immediate taxation, hardship distributions are a taxable event. To make matters worse, if you are under the age of 59½, you are also subject to the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
For example, if you are under the age of 59½ and you take a $20,000 hardship distribution to make the down payment on a house, you will incur taxes and the 10% penalty on the $20,000 withdrawal. Let’s assume you are in the 24% federal tax bracket and 7% state tax bracket. That $20,000 distribution just cost you $8,200 in taxes.
Gross Distribution: $20,000
Fed Tax (24%): ($4,800)
State Tax (7%): ($1,400)
10% Penalty: ($2,000)
Net Amount: $11,800
There is also an opportunity cost for taking that money out of your retirement account. For example, let’s assume you are 30 years old and plan to retire at age 65. If you assume an 8% annual rate of return on your 401(K) investment that $20,000 really cost you $295,707. That’s what the $20,000 would have been worth, 35 years from now, compounded at 8% per year.
Plan Amendment Required
These changes to the hardship distribution rule will not be automatic. The plan sponsor of the 401(k) will need to amend the plan document to adopt these new rules otherwise the old hardship distribution rules will still apply. We recommend that companies reach out to their 401(k) providers to determine whether or not amending the plan to adopt the new hardship distribution rules makes sense for the company and your employees.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
403(b) Lawsuits Continue To Spread To More Colleges
In the last 3 years, the number of lawsuits filed against colleges for excessive fees and compliance issues related to their 403(b) plans has increased exponentially. Here is a list of just some of the colleges that have had lawsuit brought against them by their 403(b) plan participants:
In the last 3 years, the number of lawsuits filed against colleges for excessive fees and compliance issues related to their 403(b) plans has increased exponentially. Here is a list of just some of the colleges that have had lawsuit brought against them by their 403(b) plan participants:
Yale
NYU
Duke
John Hopkins
MIT
Columbia
Emory
Cornell
Vanderbilt
Northeastern
USC
The fiduciary landscape has completely changed for organizations, like colleges, that sponsor ERISA 403(b) plans. In 2009, new regulations were passed that brought 403(b) plans up to the compliance standards historically found in the 401(k) market. Instead of slowly phasing in the new regulations, the 403(b) market basically went from zero to 60 mph in a blink of an eye. While some of the basic elements of the new rules were taken care of by the current service providers such as the required written plan documents, contract exchange provisions, and new participant disclosures, we have found that colleges, due to a lack of understanding of what is required to fulfill their fiduciary role to the plan, have fallen very short of putting the policies and procedures in place to protect the college from liabilities that can arise from the 403(b) plan.
Top Violations
Based on the lawsuits that have been filled against the various colleges, here is a list of the most common claims that have been included in these lawsuits:
Excessive fees
Fees associated with multiple recordkeepers
Too many investment options
Improper mutual fund share class
Variable annuity products
Excessive Fees
This is by far number one on the list. As you look at these lawsuits, most of them include a claim that the university breached their fiduciary duty under ERISA by allowing excessive fees to be charged to plan participants.
Here is the most common situation that we see when consulting with colleges that leads to this issue. A college had been with the same 403(b) provider for 60 years. Without naming names, they assume that their 403(b) plan has reasonable fees because all of the other colleges that they know of also use this same provider. So their fees must be reasonable right? Wrong!!
If you are member of the committee that oversees that 403(b) plan at your college, how do you answer this question? How do you know that the fees for your plan are reasonable? Can you show documented proof that you made a reasonable effort to determine whether or not the plan fees are reasonable versus other 403(b) providers?
The only way to answer this question is by going through an RFP process. For colleges that we consult with we typically recommend that they put an RFP out every 3 to 5 years. That is really the only way to be able to adequately answer the question: “Are the plan fees reasonable?” Now if you go through the RFP process and you find that another reputable provider is less expensive than your current provider, you are not required to change to that less expensive provider. However, from a fiduciary standpoint, you should acknowledge at the end of the RFP process that there were lower fee alternatives but the current provider was selected because of reasons X, Y, and Z. Document, document, document!!
Investment Fees / Underperformance / Investment Options
Liability is arising in these 403(b) plans due to
Revenue sharing fees buried in the mutual fund expense rations
Underperformance of the plan investments versus the benchmark / peer group
Too many investment options
Investment options concentrated all in one fund family
Restrictions associate with the plan investment
Investment Policy Statement violations or No IPS
Failure to document quarterly and annual investment reviews
Here is the issue. Typically members of these committees that oversee the 403(b) plan are not investment experts and you need to basically be an investment expert to understand mutual fund share classes, investment revenue sharing, peer group comparisons, asset classes represented within the fund menu, etc. To fill the void, colleges are beginning to hire investment firms to serve as third party consultants to the 403(b) committee. In most cases these firms charge a flat dollar fee to:
Prepare quarterly investment reports
Investment benchmarking
Draft a custom Investment Policy Statement
Coordinate the RFP process
Negotiation plan fees with the current provider
Conduct quarterly and annual reviews with the 403(b) committee
Compliance guidance
Multiple Recordkeepers
While multiple recordkeepers is becoming more common for college 403(b) plans, it requires additional due diligence on the part of the college to verify that it’s in the best interest of the plan participants. Multiple recordkeepers means that your 403(b) plan assets are split between two or more custodians. For example, a college may use both TIAA CREF and Principal for their 403(b) platform. Why two recordkeepers? Most of the older 403(b) accounts are setup as individual annuity contracts. As such, if the college decides to charge their 403(b) provider, unlike the 401(k) industry where all of the plan assets automatically move over to the new platform, each plan participant is required to voluntarily sign forms to move their account balance from the old 403(b) provider to the new 403(b) provider. It’s almost impossible to get all of the employee to make the switch so you end up with two separate recordkeepers.
Why does this create additional liability for the college? Even through the limitation set forth by these individual annuity contracts is out of the control of the college, by splitting the plan assets into two pieces you may be limiting the economies of scale of the total plan assets. In most cases the asset based fees for a 403(b) plan decreases as the plan assets become larger with that 403(b) provider. By splitting the assets between two 403(b) platforms, you are now creating two smaller plans which could result in larger all-in fees for the plan participants.
Now, it may very well be in the best interest of the plan participants to have two separate platforms but the college has to make sure that they have the appropriate documentation to verify that this due diligence is being conducts. This usually happens as a result of an RFP process. Here is an example. A college has been using the same 403(b) provider for the last 50 years but to satisfy their fiduciary obligation to the plan they going through the RFP process to verify that their plan fees are reasonable. Going into the RFP process they had no intention of change provides but as a result of the RFP process they realize that there are other 403(b) providers that offer better technology, more support for the plan sponsor, and lower fees than their current platform. While they are handcuffed by the individual contracts in the current 403(b) plan, they still have control over where the future contributions of the plan will be allocated so they decide that it’s in both the plan participants and the college’s best interest to direct the future contributions to the new 403(b) platform.
Too Many Investment Options
More is not always better in the retirement plan world. The 403(b) oversite committee, as a fiduciary, is responsible for selecting the investments that will be offered in accordance with the plan’s investment menu. Some colleges unfortunately take that approach that if we offer 80+ different mutual funds for the investment that should “cover all of their bases” since plan participants have access to every asset class, mutual fund family, and ten different small cap funds. The plaintiffs in these 403(b) lawsuits alleged that many of the plan’s investment options were duplicates, performed poorly, and featured high fees that are inappropriate for large 403(b) plans.
To make matters worse, if you have 80+ mutual funds on your 403(b) investment menu, you have to conduct regular and on-going due diligence on all 80+ mutual funds in your plan to make sure that they still meet the investment criteria set out in the plan’s IPS. If you have mutual funds in your plan that fall outside of the IPS criteria and those issues have not been addressed and/or documented, if a lawsuit is brought against the college it will be very difficult to defend that the college was fulfilling its fiduciary obligation to the investment menu.
Improper Mutual Fund Share Classes
To piggyback on this issue, what many plan sponsors don’t realize is that by selecting a more limited menu of mutual funds it can lower the overall plan fees. Mutual funds have different share classes and some share classes require a minimum initial investment to gain asset to that share class. For example you may have Mutual Fund A retail share class with a 0.80% internal expense ratio but there is also a Mutual Fund A institutional share class with a 0.30% internal expense ratio. However, the institutional share class requires an initial investment of $100,000 to gain access. If Mutual Fund A is a U.S. Large Cap Stock Fund and your plan offers 10 other U.S. Large Cap Stock Funds, your plan may not meet the institutional share requirement because the assets are spread between 10 different mutual funds within the same asset class. If instead, the committee decided that it was prudent to offer just Mutual Fund A to represent the U.S. Large Cap Stock holding on the investment menu, the plan may be able to meet that $100,000 minimum initial investment and gain access to the lower cost institutional share class.
Variable Annuity Products
While variable annuity products have historically been a common investment option for 403(b) plans, they typically charge fees that are higher than the fees that are charged by most standard mutual funds. In addition, variable annuities can place distribution restrictions on select investment investments which may not be in the plan participants best interest.
The most common issue we come across is with the TIAA Traditional investment. While TIAA touts the investment for its 3% guarantee, we have found that very few plan participants are aware that there is a 10 year distribution restriction associated with that investment. When you go to remove money from the TIAA Traditional fund, TIAA will inform you that you can only move 1/10th of your balance out of that investment each year over the course of the next ten years. You can see how this could be a problem for a plan participant that may have 100% of their balance in the TIAA Traditional investment as they approach retirement. Their intention may have been to retire at age 65 and rollover the balance to their own personal IRA. If they have money in the TIAA Traditional investment that is no longer an option. They would be limited to process a rollover equal to 1/10th of their balance in the TIAA Tradition investment between the age of 65 and 74. Only after age 74 would they completely free from this TIAA withdrawal restriction.
Consider Hiring A Consultant
While this may sound self-serving, colleges are really going to need help with the initial and on-going due diligence associate with keeping their 403(b) plan in compliance. For a reasonable cost, colleges should be able to engage an investment firm that specialized in this type of work to serve as a third party consultant for the 403(b) investment committee. Just make sure the fee is reasonable. The consulting fee should be expressed as a flat dollar amount fee, not an asset based fee, because they are fulfilling that role as a “consultant”, not the “investment advisor” to the 403(b) plan assets.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Top 2 Strategies For Paying Off Student Loan Debt
With total student loan debt in the United States approaching $1.4 Trillion dollars, I seem to be having this conversation more and more with clients. There has been a lot of speculation between president obama and student loans, but student loan debt is still piling up. The amount of student loan debt is piling up and it's putting the next generation of
With total student loan debt in the United States approaching $1.4 Trillion dollars, I seem to be having this conversation more and more with clients. There has been a lot of speculation between president obama and student loans, but student loan debt is still piling up. The amount of student loan debt is piling up and it's putting the next generation of our work force at a big disadvantage. While you yourself may not have student loan debt, at some point you may have to counsel a child, grandchild, friend, neighbor, or a co-worker that just can't seem to get ahead because of the financial restrains of their student loan payments. After all, for a child born today, it's projected that the cost for a 4 year degree including room and board will be $215,000 for a State College and $487,000 for a private college. Half a million dollars for a 4 year degree!!
The most common reaction to this is: "There is no way that this can happen. Something will have to change." The reality is, as financial planners, we were saying that exact same thing 10 years ago but we don't say that anymore. Despite the general disbelief that this will happen, the cost of college has continued to rise at a rate of 6% per year over the past 10 years. It's good old supply and demand. If there is a limited supply of colleges and the demand for a college degree keeps going up, the price will continue to go up. As many of us know, a college degree is not necessarily an advantage anymore, it's the baseline. You need it just to get the job interview and that will be even more true for types of jobs that will be available in future years.
No Professional Help
Making matters worse, most individuals that have large student loan debt don't have access to high quality financial planners because they do not have any investible assets since everything is going toward paying down their student loan debt. I wrote this article to give our readers a look into how we as Certified Financial Planners® help our clients to dig out of student loan debt. Unfortunately a lot of the advice that you will find by searching online is either incomplete or wrong. The solution for digging out of student loan debt is not a one size fits all solution and there are trap doors along the way.
Loan Inventory
The first step in the process is to the collect and organize all of the information pertaining to your student loan debt. Create a spreadsheet that lists the following information:
Name of Lender
Type of Loan (Federal or Private)
Name of Loan Servicer
Total Outstanding Loan Balance
Interest Rate
Fixed or Variable Interest Rate
Minimum Monthly Payment
Current Monthly Payment
Estimated Payoff Date
Now, below this information I want you to list January 1 of the current year and the next 10 years. It will look like this:
Total Balance
January 1, 2018
January 1, 2019
January 1, 2020
Each year you will record your total student loan debt below your itemized student loan information. Why? In most cases you are not going to be able to payoff your student loans overnight. It’s going to be a multi-year process. But having this running total will allow you to track your progress. You can even add another column to the right of the “Total Balance” column labelled “Goal”. If your goal is to payoff your student loan debt in five years, set some preliminary balance goals for yourself. When you receive a raise or a bonus at work, a tax refund, or a cash gift from a family member, this will encourage you to apply some or all of those cash windfalls toward your student loan balance to stay on track.
Order of Payoff
The most common advice you will find when researching this topic is “make minimum payments on all of the student loans with the exception of your student loan with the highest interest rate and apply the largest payment you can against that loan”. Mathematically this is the right strategy but we do not necessary recommend this strategy for all of our clients. Here’s why……..
There are two situations that we typically run into with clients:
Situation 1: “I’m drowning in student loan debt and need a lifeline”
Situation 2: “I’m starting to make more money at my job. Should I use some of that extra income to pay down my student loan debt or should I be applying it toward my retirement plan or saving for a house?”
Situation 1: I'm Drowning
As financial planners we are unfortunately running into Situation 1 more frequently. You have young professionals that are graduating from college with a 4 year degree, making $50,000 per year in their first job, but they have $150,000 of student loan debt. So they basically have a mortgage that starts 6 months after they graduate but that mortgage payment comes without a house. For the first few years of their career they are feeling good about their new job, they receive some raises and bonuses here and there, but they still feel like they are struggling every month to meet their expenses. The realization starts to set in the “I’m never going to get ahead because these student loan payments are killing me. I have to do something.”
If you or someone you know is in this category remember these words: “Cash is king”. You will hear this in the business world and it’s true for personal finances as well. As mentioned earlier, from a pure math standpoint, they fastest way to get out of debt is to target the debt with the highest interest rate and go from there. While mathematically that may work, we have found that it is not the best strategy for individuals in this category. If you are in the middle of the ocean, treading water, with the closest island a mile away, why are we having a debate about how fast you can swim to that island? You will never make it. Instead you just need someone to throw you a life preserver.
Life Preserver Strategy
If you are just barely meeting your monthly expense or find yourself falling short each month, you have to stop the bleeding. In these situations, you should be 100% focus on improving your current cash flow not whether you are going to be able to payoff your student loans in 8 years instead of 10 years. In the spreadsheet that you created, organize all of your student loan debt from the largest outstanding loan balance to the smallest. Ignore the interest rate column for the time being. Next, begin making the minimum payments on all of your student loans except for the one with the SMALLEST BALANCE. We need to improve your cash flow which means reducing the number of monthly payments that you have each month. Once the month to month cash flow is no longer an issue then you can graduate to Situation 2 and revisit the debt payoff strategy.
This strategy also builds confidence. If you have a $50,000 loan with a 7% interest rate and two other student loans for $5,000 with an interest rate of 4% while applying more money toward the largest loan balance will save you the most interest long term, it’s going to feel like your climbing Mt. Everest. “Why put an extra $200 toward that $50,000 loan? I’m going to be paying it until I’m 50.” There is no sense of accomplishment. We find that individuals that choose this path will frequently abandon the journey. Instead, if you focus your efforts on the loans with the smaller balances and you are able to pay them off in a year, it feels good. Getting that taste of real progress is powerful. This strategy comes from the book written by Dave Ramsey called the Total Money Makeover. If you have not read the book, read it. If you have a child or grandchild graduating from college, if you were going to give them a check for graduation, buy the book for them and put the check in the book. Tell them that “this check will help you to get a start in your new career but this book is worth the amount of the check multiplied by a thousand”.
Situation 2: Paying Off Your Student Loans Faster
If you are in Situation 2, you are no longer treading water in the middle of the ocean and you made it to the island. The name of this island is “Risk Free Rate Of Return”. Let me explain.
Individuals in this scenario have a good handle on their monthly expenses and they are finding that they now have extra discretionary income. So what’s the best use of that extra income? When you are younger there are probably a number items on your wish list, some of which you may debate looking into title loans near me to obtain. Here are the top four that we see:
Retirement savings
Saving for a house
Paying off student loan debt
Buying a new car
Don't Leave Free Money On The Table
Before applying all of your extra income toward your student loan payments, we ask our clients “what is the employer contribution formula for your employer’s retirement plan?” If it’s a match formula, meaning you have to put money in the plan to get the employer contribution, we will typically recommend that our clients contribute the amount needed to receive the full employer match. Otherwise you are leaving free money on the table.
The amount of that employer contribution represents a risk free rate of return. Meaning, unlike the investing in the stock market, you do not have to take any risk to receive that return on your money. If your company guarantees a 100% match on the first 5% of pay contribution out of your paycheck into the plan, your money is guaranteed to double up to 5% of your pay. Where else are you going to get a 100% risk free rate of return on your money?
Start With The Highest Interest Rate
Now that you have extra income each month you can begin to pick and choose how you apply it. You should list all of you student loans from the highest interest rate to the lowest. If it’s close between two interest rates but one is a fixed interest rate and the other is a variable interest rate, it’s typically better to pay down the variable interest rate loan first if interest rates are expected to move higher. Apply the minimum payment amount to all of your student loan payments and apply as much as you can toward the loan with the HIGHEST INTEREST RATE. Once the loan with the highest interest rate is paid off, you will move on to the next one.
Again, by applying more money toward your student loans, those additional payments represent a risk free rate of return equal to the interest rate that is being charges on each loan. For example, if the highest interest rate on one of your student loans is 7%, every additional dollar that you are apply toward paying off that loan you are receiving a 7% rate of return on because you are not paying that amount to the lender.
Here is a rebuttal question that we sometimes get: “But wouldn’t it be better to put it in the stock market and earn a higher rate of return?” However, that’s not an apple to apples comparison. The 7% rate of return that you are receiving by paying down that student loan balance is guaranteed because it represents interest that would have been paid to the lender that you are now keeping. By contrast, even though the stock market may average an 8% annualized rate of return over a 10 year period, you have to take risk to obtain that 8% rate of return. A 7% risk free rate of return is the equivalent of being able to buy a CD at a bank with a 7% interest rate guaranteed by the FDIC which does not exist right now.
But Can't I Deduct The Interest On My Student Loans?
It depends on how much you make. In 2018, if you are single, the deduction for student loan interest begins to phaseout at $70,000 of AGI and you completely lose the deduction once your AGI is above $85,000. If you are married filing a joint tax return, the deduction begins to phaseout at $140,000 of AGI and it’s completely gone once your AGI hits $170,000.
Also the deduction is limited to $2,500.
However, even if you can deduct the interest on your student loan, the tax benefit is probably not as big as you think. Let me explain via an example. Take the following fact set:
Tax Filing Status: Single
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): $50,000
Outstanding Student Loan Balance: $60,000
Interest Rate: 7% ($4,200 Per Year)
First, you are limited to deducting $2,500 of the $4,200 in student loan interest that you paid to the lender. At $50,000 of AGI your top federal tax bracket in 2018 is 22%. So that $2,500 equals $550 in actual tax savings ($2,500 x 22% = $550). If you want to get technical, taking the tax deduction into account, your after tax interest rate on your student loan debt is really 6.08% instead of 7%. Can you get a CD from a bank right now with a 6% interest rate? No. From both a debt reduction standpoint and a rate of return standpoint, it probably makes sense to pay down that loan more aggressively.
Striking A Balance
When you are younger, you typically have a lot of financial goals such as saving for retirement, paying off debt, saving for the down payment on your first house, starting a family, college savings for you kids, etc. While I'm sure you would like to take all of your extra income and really start aggressively reducing your student loans you have to determine what the right balance is between all of your financial goals. If you receive a $5,000 bonus from work, you may allocate $3,000 of that toward your student loan debt and deposit $2,000 in your savings account for the eventual down payment on your first house. We also recommend speaking a loan authority company to see what can be done to help you reach your goal. One example being to create that "goal" column in your student loan spreadsheet will help you to keep that balance and eventually lead to the payoff of all of your student loans.
Forgiveness Scheme
Although they are not very common and only a few people can qualify for one of these schemes, they will provide great help. A student loan forgiveness scheme can help a student pay off their loan over an extended period of time, a shorter period of time, reduce the amount they owe, or entirely pay off the loan for them. However, like I have already mentioned, this is based upon whether they qualify or not.I hope this has been of some assistance and i have provided you with some helpful advice on how to prepare for and manage your student loan.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
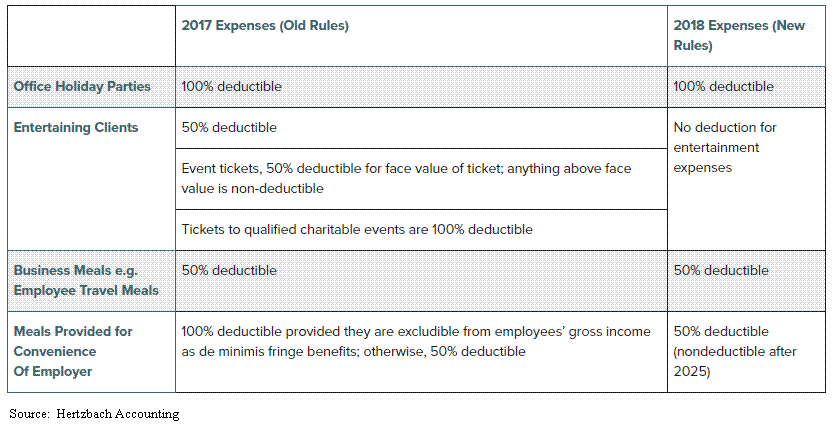
No Deduction For Entertainment Expenses In 2019. Ouch!!
There is a little known change that was included in tax reform that will potentially have a big impact on business owners. The new tax laws that went into effect on January 1, 2018 placed stricter limits on the ability to deduct expenses associated with entertainment and business meals. Many of the entertainment expenses that businesses
There is a little known change that was included in tax reform that will potentially have a big impact on business owners. The new tax laws that went into effect on January 1, 2018 placed stricter limits on the ability to deduct expenses associated with entertainment and business meals. Many of the entertainment expenses that businesses were able to deduct in 2017 will no longer we allowed in 2018 and beyond. A big ouch for business owners that spend a lot of money entertaining clients and prospects.
A Quick Breakdown Of The Changes
No Deduction in 2019
Prior to 2018, if the business spent money to take a client out to a baseball game, meet a client for 18 holes of golf, or to host a client event, the business would be able to take a deduction equal to 50% of the total cost associated with the entertainment expense. Starting in 2018, you get ZERO. There is no deduction for those expenses.
The new law specifically states that there is no deduction for:
Any activity generally considered to be entertainment, amusement, or recreation
Membership dues to any club organization for recreation or social purpose
A facility, or portion thereof, used in connection with the above items
This will inevitably cause business owners to ask their accountant: “If I spend the same amount on entertainment expenses in 2018 as I did in 2017, how much are the new tax rules going to cost me tax wise?”
Impact On Sales Professionals
If you are in sales and big part of your job is entertaining prospects in hopes of winning their business, if your company can no longer deduct those expenses, are you going to find out at some point this year that the company is going to dramatic limit the resources available to entertain clients? If they end up limiting these resources, how are you supposed to hit your sales numbers and how does that change the landscape of how you solicit clients?
Impact On The Entertainment Industry
This has to be bad news for golf courses, casinos, theaters, and sports arena. As the business owner, if you were paying $15,000 per year for your membership to the local country club and you justified spending that amount because you knew that you could take a tax deduction for $7,500, now what? Now that you can’t deduct any of it, you may decide to cancel your membership or seek out a cheaper alternative.
Impact On Charitable Organizations
How do most charities raise money? Events. As you may have noticed in the chart, in 2017 tickets to a qualified charitable event were 100% deductible. In 2018, it goes from 100% deductible to Zero!! It’s bad enough that the regular entertainment expenses went from 50% to zero but going from 100% to zero hurts so much more. Also charitable events usually have high price tags because they have to cover the cost of event and raise money for the charity. In 2018, it will be interesting to see how charitable organizations get over this hurdle. It may have to disclose right on the registration form for the event that the ticket cost is $500 but $200 of that amount is the cost of the event (non-deductible) and $300 is the charitable contribution.
Exceptions To The New Rules
There are some unique exceptions to the new rules. Many business owners will not find any help within these exceptions but here they are:
Entertainment, amusement, and recreation expenses you treat as compensation to your employees in their wages (In other words, the cost ends up in your employee’s W2)
Expenses for recreation, social, or similar activities, including facilities, primarily for employees, and it can’t be highly compensation employees (“HCE”). In 2018 an HCE employee is an employee that makes more than $120,000 or is a 5%+ owners of the company.
Expenses for entertainment goods, services, and facilities that you sell to customers
What’s The Deal With Meals?
Prior to 2018, employers could deduct 50% of expenses for business-related meals while traveling. Also meals provided to an employee for the convenience of the employer on the employer’s business premises were 100% deductible by the employer and tax-free to the recipient employee.
Starting in 2018, meal expenses incurred while traveling on business remain 50% deductible to the business. However, meals provided via an on-premises cafeteria or otherwise on the employers premise for the convenience of the employer will now be limited to a 50% deduction.
There is also a large debate going on between tax professional as to which meals or drinks may fall into the “entertainment” category and will lose their deduction entirely.
Impact On Business
This is just one of the many “small changes” that was made to the new tax laws that will have a big impact on many businesses. It may very well change the way that businesses spend money to attract new clients. This in turn will most likely lead to unintended negative consequences for organizations that operate in the entertainment, catering, and charitable sectors of the U.S. economy.
Disclosure: For education purposes only. Please seek tax advice from your tax professional
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
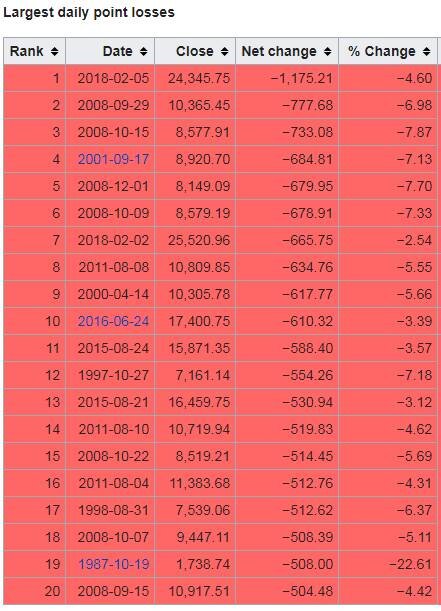
What Happened The Last Time The Dow Dropped By More Than 4% In A Day?
Yesterday was an “ouch”. The Dow Jones Industrial average dropped by more than 1000 points resulting in a 4.60% drop in the value of the index. While yesterday marked the largest “point” decline in the history of the Dow Jones Index, it was not anywhere near the largest percentage decline which is the metric that we care about.
Yesterday was an “ouch”. The Dow Jones Industrial average dropped by more than 1000 points resulting in a 4.60% drop in the value of the index. While yesterday marked the largest “point” decline in the history of the Dow Jones Index, it was not anywhere near the largest percentage decline which is the metric that we care about.
Below is a chart that shows the largest daily “point” losses in the history of the Dow Jones Industrial Index:
You will find yesterday at the top of the chart. Now look at the column all the way to the right labelled “% change”. You will notice that while yesterday topped the chart from a point decline, it does not come anywhere near the largest percentage decline that we have seen. In fact, it does not even make it in the top 20 worse days for the Dow. See the chart below that shows the largest daily percentage declines in the Dow’s history:
What Happened Last Time?
Whenever there is a big drop in the stock market, I immediately start looking back in history to find market events that are similar to the current one. So when was the last time the market dropped by more than 4% in a single day?
The answer: August 8, 2011
If you remember, 2011 was the start of the European Sovereign Debt Crisis. That was when Greece, Portugal, Spain, and Ireland announced that they were unable to repay their government debt and needed a bailout package from the European Union to survive. There were two single day declines in the month of August that rivaled what we saw yesterday.
How Long Did It Take The Market To Come Back?
If we are looking to history as a guide, how long did it take for the market to recoup the losses after these large single day declines? On July 31, 2011 the Dow Jones Industrial closed at 11,444, the Europe debt crisis hit, and the market experienced those two 4%+ decline days on August 4th and August 8th. By September 11, 2011, the Dow Jones closed at 11,509, recouping all of its losses from the beginning of August. Thus making the answer to the question: 38 days. The market took 38 days to recoup all of the losses from not one but two 4%+ decline days in 2011.
We Don’t Have A Crisis
The main difference between 2011 and now is we don’t have a global economic crisis. In my opinion, the market correction in 2011 was warranted. There was a real problem in Europe. We were not sure how and if those struggling Eurozone countries could be saved so the market dropped.
The only trigger that I hear analysts pointing to in an effort to explain the selloff yesterday is the 2.9% wage growth number that we got on Friday. This in turn has sparked inflation fears and in reaction, the Fed may decide to hike rates four times this year instead of three. Hardly a “crisis”. Outside of that nothing else meaningful has happened to trigger the volatility that we are seeing in the stock market. OK……so what should you do in reaction to this? Sometimes the right answer is “nothing”. It’s difficult to hear that because emotionally you want to pull money out of the market and run to cash or bonds but absent a sound economic reason for making that move, at this point, the best investment decision may be to just stay the course.
We Have Forgotten What Volatility Feels Like
When you are in a market environment like 2017, you very quickly forget what normal market volatility feels like. In 2017, the stock market just gradually climbed throughout the year without any hiccups. That’s not normal. Below is a chart that shows the magnitude of market corrections each year going back to 1990. As you will see, on average, when the economy is not in a recession, the market averages an 11.56% correction at some point during the year. In 2017, we only experienced a 3% correction.
Now the next chart shows you the big picture. Not only does it illustrate the amount of the largest market correction during the year but it also shows the return of the S&P 500 for the year.
Look at 2016. In 2016, at some point in the year the S&P 500 Index dropped by 11%. If you just held through it, the S&P 500 returned 10% for the year.
In 2011, the S&P 500 dropped by 19% during the year!! If you didn’t sell and just held through the volatility, you would have had a breakeven year.
Easier Said Than Done
Every big market correction feels like a new world ending crisis. It’s not. We have been fortunate enough to have a nice easy ride for the past 12 months but it seems like we are returning to more historical levels of volatility. Days like February 5, 2018 will test your patience and make you feel compelled to react. It’s easy to look back and confess that “yes, I should have just held through it” but it’s easier said than done.
It’s important to understand the catalysts that are driving the volatility in the markets. Sometimes the markets are dropping for a good reason and other times it’s just plain old fashion volatility. Based on what we have seen over the past few days and absent the emergence of a new economic, political, or global crisis, we expect it to be the later of the two.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
When Do Higher Interest Rates Become Harmful To The Stock Market?
On Friday, the jobs report came out and it was a strong report. The consensus was expecting 180,000 new jobs in January and the actual number released on Friday ended up being 200,000. So why did the markets drop? The answer: wage growth. The jobs report not only contains how many new employees were hired but it also includes the amount
On Friday, the jobs report came out and it was a strong report. The consensus was expecting 180,000 new jobs in January and the actual number released on Friday ended up being 200,000. So why did the markets drop? The answer: wage growth. The jobs report not only contains how many new employees were hired but it also includes the amount that wages for the current workforce either increased or decreased on a year over year basis. The report on Friday indicated that wages went up by 2.9% year over year. That is the strongest wage growth number since 2009.
Double Edged Sword
Wage growth is a double edged sword. On the positive side, when wages are going up, people have more money in their paychecks which allows them to spend more and consumer spending makes up 70% of our GDP in the United States. I'm actually surprised the market did not see this coming. The whole premise behind tax reform was "if we give U.S. corporations a tax break, they will use that money to hire more employees and increase wages." The big question people had with the tax reform was "would the trickle down of the dollars saved by the corporations eventually make it to the employees pockets?" Many corporations in January, as a result of tax reform, announced employee bonuses and increases to the minimum wage paid within their organizations. The wage growth number on Friday would seem to imply that this is happening. So again, I'm actually surprised that the market was not ready for this and while the market reacted negatively I see this more as a positive long term trend, instead of a negative one. If instead the U.S. corporations decided not to give the bonuses or increase wages for employees and just use the money from the tax reform savings to increase dividends or share buybacks, then you probably would have seen only a moderate increase in the wage growth number. But that also would imply that there would be no "trickle down" effect to the middle class.
The Downside
This all sounds really positive but what is the downside to wage growth? While wage growth is good for employees, it's bad for corporate earnings. If I was paying Employee A $50,000 in 2017 but now I'm paying them $55,000 per year in 2018, assuming the output of that employee did not change, the expenses to the company just went up by $5,000 per year. Now multiply that over thousands of employees. It's a simple fact that higher expenses without higher output equals lower profits.
Wage Growth = Inflation
There is another downside to wage growth. Wage growth is the single largest contributor to inflation. Inflation is what we use to measure the increase in the price of goods and services in the U.S.. Why are these two measurements so closely related? If your salary just increased by $300 per month, when you go to the grocery store to buy milk, you may not notice that the price of milk went up by $0.15 over last week because you are making more in your paycheck. That is inflation. The price of everything starts going up because, in general, consumers have more take home pay and it gives the sellers of goods and services more pricing power. Visa versa, when the economy is in a recession, people are losing their jobs, and wages are decreasing. If you sell cars and you decided to raise the price of the cars that you sell, that may cause the consumer to not buy from you and look for a lower priced alternative. Companies have less pricing power when the economy is contracting and you typically have "deflation" not inflation.
When Does Inflation Become Harmful?
Some inflation is good. It means the economy is doing well. A rapid increase in inflation is bad because it forces the Fed to use monetary policy to slow down the economy so it does not over heat. The Fed uses the Federal Funds Rate as their primary tool to keep inflation in check. When inflation starts heating up, the Fed will often raise the Fed Funds Rate to increase the cost of lending which in turn reduces the demand for lending. It’s like tapping the brakes in your car to make sure you do not accelerate too quickly and then go flying off the road.
If some inflation is good but too much inflation is bad, the question is at what point do higher interest rates really jeopardize economic growth? The chart below provides us with guidance as to what has happened in the past when interest rates were on the rise.
The chart compares every 2 year period in the stock market versus the level of the 10-Year Treasury yield between 1963 – 2017. For example, one dot would represent the time period 1963 – 1964. Another dot would represent 1964 – 1965 and so on. If the dot is above the “0.0” line, that means that there was a “positive correlation” between stock prices going up and the interest rate on the 10-Year Treasury yield going up during that same time period. Worded another way, when the dot is above the line that means the stock market was going up while interest rates were also increasing. In general, the dots above the line are good, when they are below the line, that’s bad.
Right now the 10-Year Treasury Bond is at 2.85% which is the red line on the chart. What we can conclude from this is going all the way back to 1963, at this data point, there has never been a two year period where interest rates were rising and stock prices were falling. Could it be different this time? It could, but it’s a low probability if we use historical data as our guide. History would suggest that we do not run into trouble until the yield on the 10-Year Treasury Bond gets above 4%. Once the yield on our 10-Year Treasury Bond reaches that level and interest rates are rising, historically the correlation between rising interest rates and stock prices turns negative. Meaning interest rates are going up but stock prices are going down.
It makes sense. Even though interest rates are moving up right now, they are still at historically low levels. So lending is still “cheap” by historical standards which will continue to fuel growth in the economy.
A Gradual Rise In Interest Rates
Most fixed income managers that we speak with are expecting a gradual rise in interest rates throughout 2018. While we expect interest rates to move higher throughout the year due to an increase in wage growth as a result of a tighter labor market, in our opinion, it’s a stretch to make the case that the yield on the 10-year Treasury will be at 4% by the end of the year.
If the U.S. was the only country in the world, I would feel differently. Our economy is continuing to grow, wages are increasing, the labor markets are tight which requires companies to pay more for good employees, and all of these factors would warrant a dramatic increase in the rate of inflation. But we are not the only country in the world and the interest rate environment in the U.S. is impacted by global rates.
The chart below illustrates the yield on a 10 year government bonds for the U.S., Japan, Germany, UK, Italy, Spain, and total “Global Ex-U.S.”.
On December 31, 2017 the yield on a 10-Year Government Bond in the U.S. was 2.71%. The yield on a 10-Year government bond in Germany was only 0.46%. So, if you bought a 10-Year Government Bond from Germany, they are going to hand you back a measly 0.46% in interest each year for the next 10 years.
Why is this important? The argument can be made that while the changes in the Fed Funds Rate may have a meaningful impact on short-term rates, it may have less of an impact on intermediate to longer term interest rates. When the U.S. government needs more money to spend they conduct “treasury auctions”. The government announces that on a specified date that they are going to be selling “30 million worth of 10-year treasury bonds at a 2.8% rate”. As long as there is enough demand to sell all of the bonds at the 2.8% rate, the auction is a success. If there is not enough demand, then they may have to increase the interest rate from 2.8% to 3% to sell all $30 million worth of the bonds. While the U.S. 10-Year Treasury Bond only had a yield of 2.71%, it’s a lot higher than the other trusted government lenders around the world. As you can see in the chart above, the average 10-year government bond yield excluding the U.S. is 1.03%. This keeps the demand for U.S. debt high without the need to dramatically increase the interest rate on new government debt issuance to attract buyers of the debt.
As for the trend in global interest rates, you will see in the chart that from September 30, 2017 to December 31, 2017, global 10-year government bond yields ex-U.S. decreased from 1.05% to 1.03%. While we are in the monetary tightening cycle in the U.S., there is still monetary easing happening around the world as a whole which should prevent our 10-year treasury yields from spiking over the next 12 months.
Impact on Investment Portfolios
The media will continue to pounce on this story about “the risk of rising interest rates and inflation” throughout 2018 but it’s important to keep it in context. If tax reform works the way that it’s supposed to, wage growth should continue but we may not see the positive impact of increased consumer spending due to the wage growth until corporate earnings are released for the first and second quarter of 2018. We just have to wait to see how the strength of consumer spending nets out against the pressure on corporate earnings from higher wages.
However, investors should be looking at the fixed income portion of their portfolio to make sure there is the right mix of bonds if inflation is expected to rise throughout the year. Bond duration and credit quality will play an important role in your fixed income portfolio in 2018.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Dow Dropped 362 Points Yesterday. Now What?
When you hear that the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped by over 300 points it gets your attention. It triggers that automatic emotional response which leads you to ask, "Is the market rally ending?" I'm going to start this article by saying "I'm not a cheerleader for the stock market". As a cheerleader, it's your job to cheer whether your team is
When you hear that the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped by over 300 points it gets your attention. It triggers that automatic emotional response which leads you to ask, "Is the market rally ending?" I'm going to start this article by saying "I'm not a cheerleader for the stock market". As a cheerleader, it's your job to cheer whether your team is winning or losing. Sometimes the general public views investment advisors that way. "Of course my advisor has a rosy outlook. He wants me to stay invested".
My view is when the cycle is ending it's ending. When the data tells us that we are headed toward the next recession, you just have to accept a lower expected rate of return and make the necessary allocation changes to preserve principal during the market downturn. The answer is not always "just hold through it" which is unfortunately the answer that some investors receive from their advisor regardless of what's happening in the markets and the economy.
What Has Changed?
Whenever you have a big down day in the market the first question you should ask yourself is "What changed?" I know the value of the stock market changed but the question I'm really asking is what fundamental change happened in the U.S. economy to trigger the selloff?
Did GDP growth rate pull back unexpectedly?
Did the monthly jobs report come up short? Did inflation increase by a large number that wasn't expected?
Are corporate earnings deteriorating?
Has the leading indicators index turned negative?
These are the real questions that you should be asking. Remember, the economy leads the stock market. The stock market does not lead the economy. Watching the fluctuations in the stock market and using that as a tool to make investment decisions is a recipe for disaster. You are much more likely to find success in your investments if you use a trading app uk that is able to help you track prices and automate your trading.
A growing economy typically means higher corporate earnings
Higher corporate earnings often results in higher stock prices
With that said, sometimes the market is down because it's reacting to poor economic data. In those cases, the market downturn may be warranted. However, that is not what I think happened yesterday. We did not get a bad jobs number or shortfall in GDP growth. In short, as of yesterday, nothing has changed from an economic standpoint. Days like yesterday are just a reminder of what volatility in the markets feels like.
Higher Volatility Ahead
If you asked me if I expect more or less days like yesterday in 2018, my guess would be more. We are all suffering from "recency bias". 2017 was this nice smooth ride higher with very few interruptions. When you get used to sailing in smooth waters, a small wave can seem like a tsunami. Below is a chart of the CBEO Vix Index from January 2002 – January 2018 which is used to gauge the level of volatility in the U.S. stock market:
As you can see, we are coming off of historically low levels of volatility and we have to remember that volatility is normal. Every down tick in the stock market is not necessarily a signal that a recession is coming.
The Math Is Different
What if I told you that the market was only down 177 points yesterday? It probably does not trigger the same fear reaction as being down over 350 points. The reason why I ask this question is you have to remember that the price level of the Dow has doubled over the last 6 years. So a 300 point drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average today does not mean the same thing as a 300 point drop in 2012. On February 17, 2012, the Dow Jones Industrial Average closed at 12,949. Today it sits just above 26,000. In percentage terms, a 300 drop in 2012 equaled a 2.3% drop in the stock market. If you translate that to where the stock market is today, you would need a 598 point drop in a single day to get that same 2.3% drop. It's just math but we have to remember this when the headlines in the media read:
"The Dow Dropped By 300 Points Today. Traders Are Worried That This Could Be The End Of The Rally?"
Never Hesitate
While I write these articles to help our clients and readers to become better investors and to put important market events into perspective, I have a special note that I want to leave off on for our clients. When you have that feeling of uncertainty, never hesitate to contact me. That quick phone call just to ask, "Mike, should I be worried?" That's what I'm here for. Have a great week everyone!!
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Past (kind of)
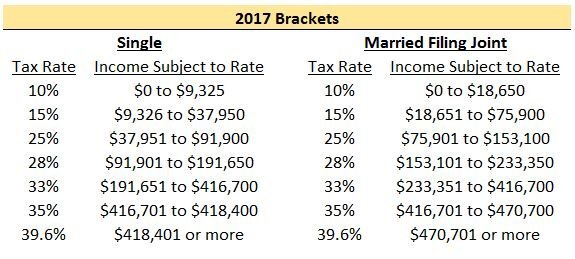
I say "kind of" because most people still have to file their 2017 tax return. Here is the 2017 tax table for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
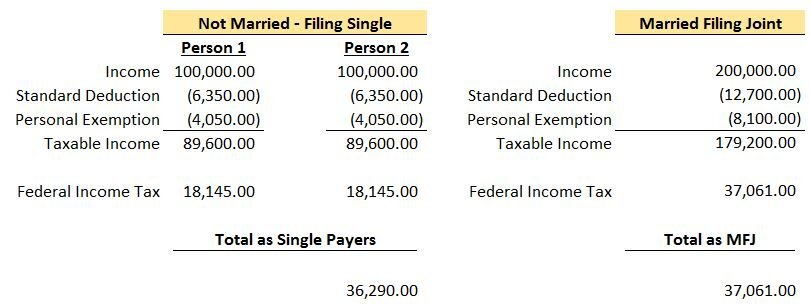
A reasonable person would think that the income subject to tax would simply double if you went from filing Single to Married Filing Joint. As you can see, this isn't the case once you are in the 25%+ tax bracket and it can mean big dollars! Let's take a look at a simple example where each person makes the same amount of money. We will also assume they will be taking the standard deduction in 2017.
Note: To calculate the “Federal Income Tax” amount above, you can use the IRS tables here 2017 1040 Tax Table Instructions. All of your income is not taxed at your top rate. For example, if your top income falls in the 25% tax bracket, as a single payer you will only pay 25% on income from $37,951 to $91,900. Everything below that range will be taxed at either 10% or 15%.
As you can see, because of the change in filing status, this couple owed a total of $771 more to the federal government. This is the “Marriage Penalty”. Typically as incomes rise, the dollar amount of the penalty becomes larger. For this couple, their top tax bracket went from 25% each when filing single to 28% filing joint.
The Present
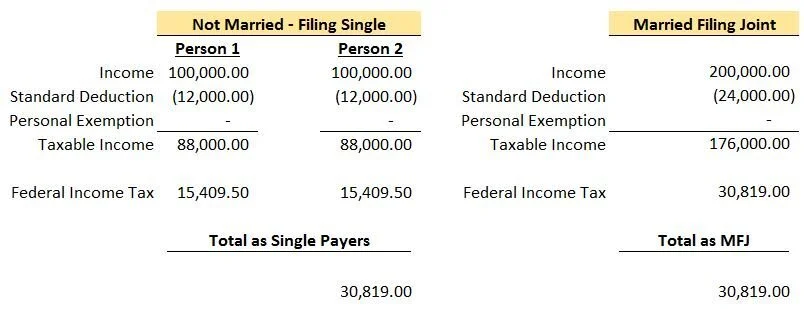
Here is the 2018 tax table in the new tax legislation for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
Upon review, you can see that the top income brackets are not doubled for Married Filing Joint. At 37%, a single person filing would reach the top rate at $500,001 while married filing joint would reach at $600,001. That being said, the “Marriage Penalty” appears to kick in at higher income levels compared to the past and therefore should impact less people. The income bracket for Married Filing Joint is doubled up until $400,000 of combined income compared to just $75,901 under the 2017 brackets.
Let’s take a look at the same couple in the example above.
Due to the income brackets doubling from single to married filing joint for this couple, the “Marriage Penalty” they would have incurred in 2017 appears to go away. In this example, they would also pay less in federal taxes in both situations. This article is more focused on the impact on the “Marriage Penalty” but having a lower tax bill is always a plus.
Standard vs. Itemized Deductions
The tax brackets aren’t the only penalty. Another common tax increase people see when going from single to married filing joint are the deductions they lose. If I’m single and own a home, it is likely I will itemized because the sum of my property taxes, mortgage interest, and state income taxes exceed the standard deduction amount. Assume the couple in the example above is still not married but Person 1 owns a home and rather than taking the standard deduction, Person 1 itemizes for an amount of $15,000. For 2017, their total deductions will be $21,350 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $6,350 Person 2) and for 2018, their total deductions will be $27,000 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $12,000 Person 2).
Now they get married and have to choose whether to itemize or take the standard deduction.
2017: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2017 they would still itemize because they have deductions of $15,000 for Person 1 and some additional items that Person 2 would bring to the table (i.e. their state income taxes). Say their total itemized deductions are $18,000 when married filing joint. They would still itemize because $18,000 is more than the Married Filing Joint standard deduction of $12,700. But now compare the $18,000 to the $21,350 they got filing single. They lose out on $3,350 of deductions. Usually, less deductions equals more taxes.
2018: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2018 they would no longer itemize. Assuming their total itemized deductions are still $18,000, that is less than the $24,000 standard deduction they can take when married filing joint. $24,000 standard deduction in 2018 is still less than the $27,000 they got filing separately by $3,000. Again, less deductions usually means more taxes. The “Marriage Penalty” lives on!
A lot of people will still lose out on deductions in 2018 but the “Marriage Penalty” will hit less people because of the increase in the standard deduction. If Person 1 has itemized deductions of $10,000 in 2017, they would itemize if they filed single and possibly take the standard deduction of $12,700 filing joint. In 2018 however, Person 1 would take the standard deduction both as a single tax payer ($12,000) and married filing joint ($24,000) which takes away the “Marriage Penalty” related to the deduction.
The Why?
Why do tax brackets work this way? Like most taxes, I assume the idea was to generate more income for the government. Some may also argue that typical couples don't make the same salaries which seems like an archaic point of view.Was it all fixed with the new tax legislation? It doesn't appear so but it does look like less people will be struck by Cupid's Marriage Penalty.
About Rob.........
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
The Government Is Shut Down. Should You Be Worried?
The senate was not able to pass a temporary spending bill in the late hours of the night so as of Saturday, January 20th the government is officially shut down. But what does that mean? How will it impact you? What will be the impact on the stock market?
The senate was not able to pass a temporary spending bill in the late hours of the night so as of Saturday, January 20th the government is officially shut down. But what does that mean? How will it impact you? What will be the impact on the stock market?
Don’t Let The Media Scare You
The media loves big disruptive events. Why? The news is a "for profit" business. The more viewers they have, the more profits they make. What makes you watch more news? Fear. If the weather forecasts is 80 degrees and sunny, you just go on with your day. Instead, if the weather is predicting “The Largest Winter Blizzard Of The Century”, my guess is you will be glued to the weather channel most of the day trying to figure out when the storm will hit, how many feet of snow is expected to fall, and are schools closing, etc.
You will undoubtedly wake up this morning to headlines about “The Government Shutdown” and all of the horrible things that could happen as a result. In the short term a government shutdown or a “funding gap” is not incredibly disruptive. Many government agencies have residual funding to keep operations going for a period of time. Only portions of the government really “shut down”. The “essential” government services continue to function such as national security and law enforcement. The risk lies in the duration of the government shutdown. If Congress does not pass either a temporary extension or reach a final agreement within a reasonable period of time, some of these government agencies will run out of residual funding and will be forced to halt operations.
The news will target the “what if’s” of the current government shutdown. What if the government stays shut down and social security checks stop? What if the U.S. cannot fund defense spending and we are left defenseless? All of these scenarios would require a very prolonged government shutdown which is unlikely to happen.
How Often Does This Happen?
When I woke up this morning, my first questions was “how often do government shutdowns happen?” Is this an anomaly that I should be worried about or is it a frequent occurrence? The last government shutdown took place on September 30, 2013 and the government stayed shut down for 16 days. Prior to the 2013 shutdown, you have to go back to December 15, 1995. The duration of the 1995 shutdown was 21 days. Making the current government shutdown only the third shutdown between December 15, 1995 – January 20, 2018. Not an anomaly but also not a frequent event.
But let’s look further back. How many times did the U.S. government experience a shutdown between 1976 – 2018? In the past 42 years, the U.S. government has experienced a shutdown 18 times. On average the government shutdowns lasted for about 7 days. This makes me less worried about the current government shutdown given the number of shutdowns that we have overcome in the past.
This Shutdown Could Be Longer
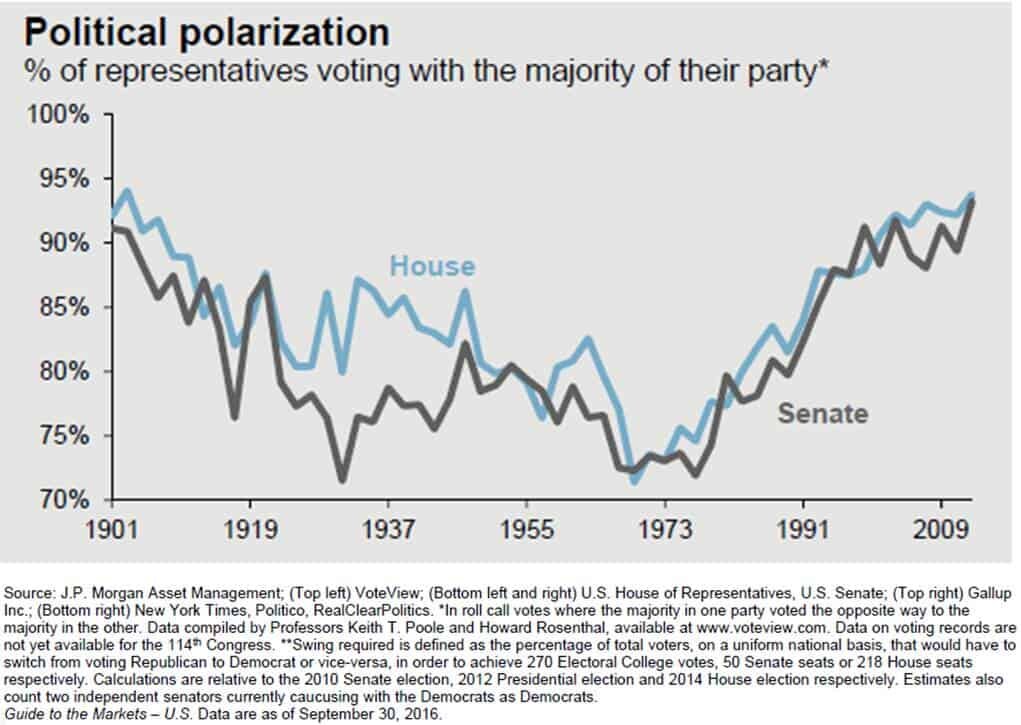
The only thing that worries me a little is the potential duration of the current government shutdown. I would not consider two data points to be a new “trend” but it is hard to ignore that the last two government shutdowns that occurred in 1995 and 2013 were much longer than the 7 day historical average. However, this could be the start of a new trend given how polarized Congress has become. It’s a clear trend that over the past 40 years fewer members of the Senate and House are willing to cross party lines during a vote. See the chart below: Back in 1973, only 73% of the members of Congress voted with the majority of their political party. It would seem rational to assume that during that time period members of Congress were more willing to step across the aisle for the greater good of the American people. Now, approximately 95% of the members of both the House and Senate vote with their own camp. This creates deadlock situations that take longer to resolve as the “blame game” takes center stage.
Impact On The Stock Market
In most cases, injecting uncertainty in our economy is never good for the stock market. However, given the fact that U.S. corporations are still riding the high of tax reform, if the government shutdown is resolved within the next two weeks it may have little or no impact on the markets.
If it were not for the recent passage of tax reform, my guess is this government shutdown may have been completely avoided. Not choosing a side here but just acknowledging the Democratic Party was delivered a blow with passage of tax reform in December. Since the spending bill requires 60 votes to pass in the Senate, it will require support from the Democrats. This situation provides the Democratic party with a golden opportunity to negotiate terms to help make up for some the lost ground from the passage of the Republican led tax bill. This challenging political environment could lengthen the duration of the government shutdown. However, it’s also important to remember that neither party benefits from a government shutdown, especially in a midterm election year.
Over the next two weeks, I would recommend that investors take all the media hype with a grain of salt. However, if a permanent or temporary spending bill is not passed within the next two weeks, it could result in increased volatility and downward pressure on the stock market as government agencies run out of cash reserves and begin to put workers on furlough. At this point, we are really in a “wait and see” environment.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
More Taxpayers Will Qualify For The Child Tax Credit
There is great news for parents in the middle to upper income tax brackets in 2018. The new tax law dramatically increased the income phaseout threshold for claiming the child tax credit. In 2017, parents were eligible for a $1,000 tax credit for each child under the age of 17 as long as their adjusted gross income (“AGI”) was below $75,000 for single
There is great news for parents in the middle to upper income tax brackets in 2018. The new tax law dramatically increased the income phaseout threshold for claiming the child tax credit. In 2017, parents were eligible for a $1,000 tax credit for each child under the age of 17 as long as their adjusted gross income (“AGI”) was below $75,000 for single filers and $110,000 for married couples filing a joint return. If your AGI was above those amounts, the $1,000 credit was reduced by $50 for every $1,000 of income above those thresholds. In other words, the child tax credit completely phased out for a single filer with an AGI greater than $95,000 and for a married couple with an AGI greater than $130,000.
Note: If you are not sure what the amount of your AGI is, it’s the bottom line on the first page of your tax return (Form 1040).
New Phaseout Thresholds In 2018+
Starting in 2018, the new phaseout thresholds for the Child Tax Credit begin at the following AGI levels:
Single Filer: $200,000
Married Filing Joint: $400,000
If your AGI falls below these thresholds, you are eligible for the full Child Tax Credit. For taxpayers with an AGI amount that exceeds these thresholds, the phaseout calculation is the same as 2017. The credit is reduced by $50 for every $1,000 in income over the AGI threshold.
Wait......It Gets Better
Not only will more families qualify for the child tax credit in 2018 but the amount of the credit was doubled. The new tax law increased the credit from $1,000 to $2,000 for each child under the age of 17.
In 2017, a married couple, with three children, with an AGI of $200,000, would have received nothing for the child tax credit. In 2018, that same family will receive a $6,000 tax credit. That’s huge!! Remember, “tax credits” are more valuable than “tax deductions”. Tax credits reduce your tax liability dollar for dollar whereas tax deductions just reduce the amount of your income subject to taxation.
Tax Reform Giveth & Taketh Away
While the change to the tax credit is good news for most families with children, the elimination of personal exemptions starting in 2018 is not.
In 2017, taxpayers were able to take a tax deduction equal to $4,050 for each dependent (including themselves) in addition to the standard deduction. For example, a married couple with 3 children and $200,000 in income, would have been eligible received the following tax deductions:
Standard Deduction: $12,700
Husband: $4,050
Wife: $4,050
Child 1: $4,050
Child 2: $4,050
Child 3: $4,050
Total Deductions $32,950
Child Tax Credit: $0
This may lead you to the following question: “Does the $6,000 child tax credit that this family is now eligible to receive in 2018 make up for the loss of $20,250 ($4,050 x 5) in personal exemptions?”
By itself? No. But you have to also take into consideration that the standard deduction is doubling in 2018. For that same family, in 2018, they will have the following deductions and tax credits:
Standard Deduction: $24,000
Personal Exemptions: $0
Total Deductions: $24,000
Child Tax Credit: $6,000
Even though $24,000 plus $6,000 is not greater than $32,950, remember that credits are worth more than tax deductions. In 2017, a married couple, with $200,000 in income, put the top portion of their income subject to the 28% tax bracket. Thus, $32,950 in tax deductions equaled a $9,226 reduction in their tax bill ($32,950 x 28%).
In 2018, due to the changes in the tax brackets, instead of their top tax bracket being 28%, it’s now 24%. The $24,000 standard deduction reduces their tax bill by $5,760 ($24,000 x 24%) but now they also have a $6,000 tax credit with reduces their remaining tax bill dollar for dollar, resulting in a total tax savings of $11,760. Taxes saved over last year: $2,534. Not a bad deal.
For many families, the new tax brackets combined with the doubling of the standard deduction and the doubling of the child tax credit with higher phaseout thresholds, should offset the loss of the personal exemptions in 2018.
This information is for educational purposes only. Please consult your accountant for personal tax advice.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.