How To Pay 0% Tax On Capital Gains Income
When you sell a stock, mutual fund, investment property, or a business, if you have made money on that investment, the IRS is kindly waiting for a piece of that gain in the form of capital gains tax. Capital gains are taxed differently than the ordinary income that you received via your paycheck or pass-through income from your business. Unlike ordinary
When you sell a stock, mutual fund, investment property, or a business, if you have made money on that investment, the IRS is kindly waiting for a piece of that gain in the form of capital gains tax. Capital gains are taxed differently than the ordinary income that you received via your paycheck or pass-through income from your business. Unlike ordinary income, which has a series of tax brackets that range from 10% to 37% in 2022, capital gains income is taxed at a flat rate at the federal level. Most taxpayers are aware of the 15% long term capital gains tax rate but very few know about the 0% capital gains tax rate and how to properly time the sale of your invest to escape having to pay tax on the gain.
Short-term vs Long-Term Gains
Before I get into this tax strategy, you first have to understand the difference between “short-term” and “long-term” capital gains. Short-term capital gains apply to any investment that you bought and sold in less than a 12 month period. Example, if I buy a stock today for $1,000 and I sell it three months later for $3,000, I would have a $2,000 short-term capital gain. Short-term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income like your paycheck. There is no special tax treatment for short-term capital gains and the 0% tax strategy does not apply.
Long-term capital gains on the other hand are for investments that you bought and then sold more than 12 months later. When I say “investments” I’m using that in broad terms. It could be a business, investment property, stock, etc. When you sell these investments at a gain and you have satisfied the 1 year holding period, you receive the benefit of paying tax on the gain at the preferential “long-term capital gains rate”.
What Are The Long Term Capital Gains Rates?
For federal tax purposes, there are 3 long term capital gains rates: 0%, 15%, and 20%. What rate you pay is determined by your filing status and your level of taxable income in the year that you sold the investment subject to the long term capital gains tax. For 2022, below are the capital gains brackets for single filers and joint filers.
As you will see on the chart, if you are a single filer and your taxable income is below $41,675 or a joint filer with taxable income below $83,350, all or a portion of your long term capital gains income may qualify for the federal 0% capital gains rate.
An important note about state taxes on capital gains income is that each state has a different way of handling capital gains income. New York state is a “no mercy state” meaning they do not offer a special tax rate for long term capital gains. For NYS income tax purposes, your long term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income. But let’s continue our story with the fed tax rules which are typically the lion share of the tax liability.
In a straight forward example, assume you live in New York, you are married, and your total taxable income for the year is $50,000. If you realize $25,000 in long term capital gains, you will not pay any federal tax on the $25,000 in capital gain income but you will have to pay NYS income tax on the $25,000.
Don’t Stop Reading This Article If Your Taxable Income Is Above The Thresholds
For many taxpayers, their income is well above these income thresholds. But I have good news, with some maneuvering, there are legit strategies that may allow you to take advantage of the 0% long term capital gains tax rate even if your taxable income is above the $41,675 single filer and $83,350 joint filer thresholds. I will include multiple examples below as to how our high net worth clients are able to access the 0% long term capital gains rate but I first have to build the foundation as to how it all works.
Using 401(k) Contributions To Lower Your Taxable Income
In years that you will have long term capital gains, there are strategies that you can use to reduce your taxable income to get under the 0% thresholds. Here is an example, I had a client sell a rental property this year and the sale triggered a long term capital gain for $40,000. They were married and had a combined income of $110,000. If they did nothing, at the federal level they would just have to pay the 15% long term capital gains tax which results in a $6,000 tax liability. Instead, we implemented the following strategy to move the $40,000 of capital gains into the 0% tax rate.
Once they received the sale proceeds from the house, we had them deposit that money to their checking account, and then go to their employer and instruct them to max out their 401(k) pre-tax contributions for the remainder of the year. Since they were both over 50, they were each able to defer $27,000 (total of $54,000). They used the proceeds from the house sale to supplement the income that they were losing in their paychecks due to the higher pre-tax 401(k) deferrals. Not only did they reduce their taxable income for the year by $54,000, saving a bunch in taxes, but they also were able to move the full $40,000 in long term capital gain income into the 0% tax bracket. Here’s how the numbers work:
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): $110,000
Pre-tax 401(k) Contributions: ($54,000)
Less Standard Deduction: ($25,900)
Total Taxable Income: $30,100
In their case, they would be able to realize $53,250 in long term capital gains before they would have to start paying the 15% fed tax on that income ($83,350 – $30,100 = $53,250). Since they were below that threshold, they paid no federal income tax on the $40,000 saving them $6,000 in fed taxes.
“Filling The Bracket”
The strategy that I just described is called “filling the bracket”. We find ways to reduce an individuals taxable income in the year that long term capital gains are realized to “fill up” as much of that 0% long-term capital gains tax rate that we can before it spills over into the 15% long-term capital gains rate.
More good news, it’s not an “all or none” calculation. If you are married, have $60,000 in taxable income, and $100,000 in long term capital gains, a portion of your $100,000 in capital gains will be taxed at the 0% rate with the majority taxed at the 15% tax rate. As you might have guessed the IRS is not going to let you get away with paying 0% on a $100,000 in long term capital gains because you maneuvered your taxable income into the 0% cap gain range. But in this case, $23,350 would be taxed at the 0% long term cap gain rate, and the reminder would be taxed at the 15% long term cap gain rate.
Do Capital Gains Bump Your Ordinary Income Into A Higher Bracket?
When explaining this “filling up the bracket” strategy to clients, the most common question I get is: “If long term capital gains count as taxable income, does that push my ordinary income into a higher tax bracket?” The answer is “no”. In the eyes of the IRS, capital gains income is determined to be earned “after” all of your other income sources.
In an extreme example, let’s say you have $70,000 in ordinary income and $200,000 in capital gains. If your total ordinary income was $70,000 and you file a joint tax return, your top fed tax bracket in 2022 would be 12%. However, if the IRS decided to look at the $200,000 in capital gain income first and then put your ordinary income on top of that, your top federal tax bracket would now be 24%. That would hurt tax wise. Luckily, it does not work that way. Even if you realized $1M in long term capital gains, the $70,000 in ordinary income would be taxed at the same lower tax brackets since it was earned first in the eyes of the IRS.
Work With Your Accountant
Before I get into the more advanced strategies for how this filling up the brackets strategy is used, I cannot stress enough the importance of working with your tax advisor when executing these more complex tax strategies. The tax system is complex and making a shift in one area could hurt you in another area.
Even though these strategies may lower the federal tax rate on your long-term capital gain income, capital gains will increase your AGI (adjusted gross income) for the year which could phase you out of certain deductions, tax credits, increase your Medicare premiums, reduce college financial aid, etc. Your accountant should be able to run tax projections for you in their software to play with the numbers to determine the ideal amount of long-term capital gains that can be realized in a given year without hurting the other aspects of your financial picture.
Strategy #1: I’m Retiring
When people retire, in many cases, their taxable income drops because they no longer have their paycheck and they are typically supplementing their income with social security and distributions from their investment accounts. This creates a tax planning opportunity because these taxpayers sometimes find themselves in the lowest tax bracket that they have been in over the past 30+ years. Here are some of the common examples.
Example 1: The First Year Of Retirement
If you retire at the beginning of the calendar year, you may only have had a few months of paychecks, so your income may be lower in that year. If you have built up cash in your savings account or if you have an after tax investment account that you can use to supplement your income for the remainder of the year to meet your expenses, this may create the opportunity to “fill up the bracket” and realize some long-term capital gains at a 0% federal tax rate in that year.
Example 2: Lower Expenses In Retirement
We have had clients that were making $150,000 per year and then when they retire they only need $40,000 per year to live off of. When you retire, the kids are typically through college, the mortgage is paid off, and your expenses drop so you need less income to supplement those expenses. A portion of your social security will most likely be counted as taxable income but if you do not have a pension, you may have some wiggle room to realize a portion of your long-term capital gains as a 0% rate each year.
Assume this is a single filer. Here is how the numbers would work:
Social Security & IRA Taxable Income: $40,000
Less Standard Deduction: ($12,000)
Total Taxable Income: $28,000
This individual would be able to realize $13,675 in long term capital gains each year at the 0% fed tax tax because the threshold is $41,675 and they are only showing $28,000 in taxable income. Saving $2,051 in fed taxes.
Strategy #2: Business Owner Experiences A Low Income Year
If you have been running a business for 5+ years, you have probably been through those one or two tough years where either revenue drops dramatically or the business incurs a lot of expenses in a single year, lowering your net profits. Do not let these low taxable income years go to waste. If you typically make $250,000+ per year and you have one of these low income years, start planning as soon as possible because once you cross that December 31st threshold, you have wasted a tax planning opportunity. If you are showing no income for that year, you may want to talk to your accountant about realizing some long term capital gains in your brokerage account to realize those gains at a 0% tax rate. Or you may want to consider processing a Roth conversion in that low tax year. There are a number of tax strategies that will allow you to make the most of that “bad year” income wise.
Strategy #3: Leverage Cash Reserves and Brokerage Accounts
If you have been building up cash reserves or you have a brokerage account that you could sell some holdings without incurring big taxable gains, you may be able to use that as your income source for the year which could result in little to no taxable income showing for that tax year. We have seen both retirees and business owners use this strategy.
Business owners have control over when expenses will be realized which influences how much taxable income is being passed through to the business owner. If you can overload expenses into a single tax year instead of splitting it evenly between two separate tax years, that could create some tax planning opportunities.
Strategy #4: Moving To Another State
It’s common for individuals to move to more tax friendly states in retirement. If you live in a state now, like New York, that makes you pay tax on long term capital gain income, and you plan to move to Florida next year and change your state of domicile, you may want to wait to realize your capital gains until you are resident of Florida to avoid having to pay state tax on that income. This has nothing to do with the 0% Fed tax strategy but it might reduce your state income tax bill on those capital gains.
Bottom Line
There are few strategies that allow you to pay 0% in federal taxes on any type of gain. If you are a high income earner, this strategy may not work for you every year but there may be opportunities to use them at some point if income drops or when you enter the retirement years. Again, don’t let those lower income years go to waste. Work with your accountant and determine if “filling the bracket” is the right move for you.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Understanding FAFSA & How To Qualify For More College Financial Aid
As the cost of college continues to rise, so does the financial stress that it puts on families trying to determine the optimal solution to pay for college. It’s never been more important for parents and family members of these students
As the cost of college continues to rise, so does the financial stress that it puts on families trying to determine the optimal solution to pay for college. It’s never been more important for parents and family members of these students to understand:
How is college financial aid calculated?
Are there ways to increase the amount of financial aid you can receive?
What are the income and asset thresholds where financial aid evaporates?
Understanding the FAFSA 2 Year Lookback Rule
The difference between financial aid at public colleges vs private colleges
In this article we will provide you with guidance on these topics as well as introduce strategies that we as financial planners use with our clients to help them qualify for more financial aid.
How is college financial aid calculated?
Too often we see families jump to the incorrect assumption that “I make too much to qualify for financial aid.” Depending on what your asset and income picture looks like there may be strategies that will allow you to shift assets around during the financial aid determination years to qualify for need based financial aid. But you first need to understand how need based financial aid is calculated.
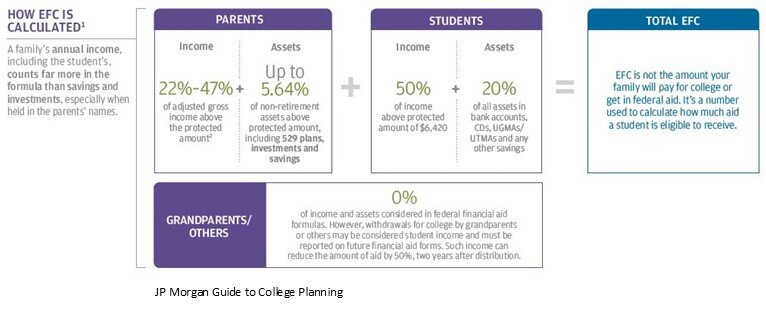
The Department of Education has a formula to calculate your “Expected Family Contribution” (EFC). The Expected Family Contribution is the amount that a family is expected to pay out of pocket each year before financial aid is awarded. Here is the general formula for financial aid:
It’s pretty simple and straight forward. Cost of the college, minus the EFC, equals the amount of your financial aid award. Now let’s breakdown how the EFC is calculated
Expected Family Contribution (EFC) Calculation
Both the parent’s income and assets, as well as the student’s income and assets come into play when calculating a family’s EFC. But they are weighted differently in the formula. Let’s look at the parent’s income and assets first.
Parent’s Income & Assets
Parents Income: The parent’s income is one of the largest factors in the EFC calculation. The percentage of the parents income that counts toward the EFC calculation is expressed as a range between 22% - 47% because it depends on a number of factors such as household size and the number of children that you have attending college at the same time.
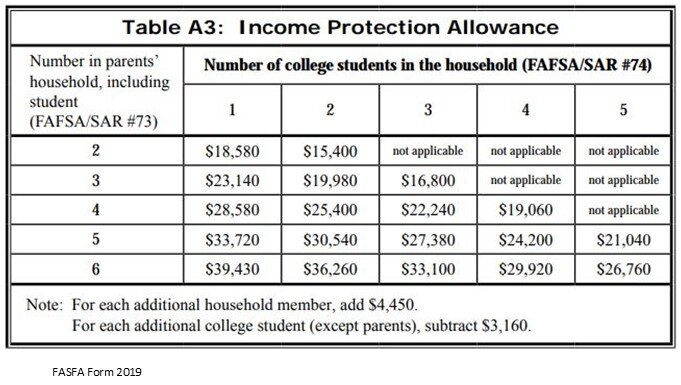
However, there is an “Income Protection Allowance” that allows parents to shelter a portion of their income from the formula based on the household size and the number of children attending college. See that chart below for the 2019-2020 FAFSA form:
Parents Assets: Any assets owned by the parents of the student are multiplied by 5.64% and that amount counts towards the EFC. Here are a few assets that are specifically EXCLUDED from this calculation:
Retirement Accounts: 401(k), 403(b), IRA’s, SEP, Simple
Pensions
Primary Residence
Family controlled business (less than 100 employees and 51%+ ownership by parents)
On the opposite side of that coin, here is a list of some assets that are specifically INCLUDED in the calculation:
Balance in 529 accounts
Real estate other than the primary residence
Even if held in an LLC – Reported separately from “business assets”
Non-retirement investment accounts, savings account, CD’s
Trusts where the student is a beneficiary of the trust (even if not entitled to distributions yet)
Business interest (less than 51% family owned by parents or more than 100 employees)
Similar to the Income Allowance Table, there is also a Parents’ Asset Protection Allowance Table that allows them to shelter a portion of their countable assets from the EFC formula. See the table below for the 2019-2020 school year.
Student’s Income & Assets
Now let’s switch gears over to the student side of the EFC formula. The income and the assets of the student are weighted differently than the parent’s income and assets. Here is the student side of the EFC formula:
As you can clearly see, income and assets in the student’s name compared to the parent name will dramatically increase the Expected Family Contribution and in turn decrease the amount of financial aid awarded. It is because of this, that as a general rule, if you think your asset and income picture may qualify you for financial aid, do not put assets in the name of your child. The most common error that we see people make are assets in an UGMA or UTMA account. Even though parents control those accounts, they are technically considered an asset of the child. If there is $30,000 sitting in an UTMA account for the student, they are automatically losing around $6,000 EACH YEAR in financial aid. Multiply that by 4 years of college, it ends up costing the family $24,000 out of pocket that otherwise could have been covered by financial aid.
EFC Formula Illustration
If we put all of the pieces together, here is an illustration of the full EFC Formula:
Grandparent Owned 529 Plans For The Student
As you will see in the EFC formula above, assets owned by the grandparents with the student listed as the beneficiary, like 529 accounts, are not counted at all toward the EFC calculation. This can be a very valuable college savings strategy for families since the parent owned 529 accounts count toward the Expected Family Contribution. However, there are some pitfalls and common mistakes that we have seen people make with regard to grandparent owned 529 accounts. See the article below for more information specific to this topic:
Article: Common Mistakes With Grandparent Owned 529 Accounts
Financial Aid Chart
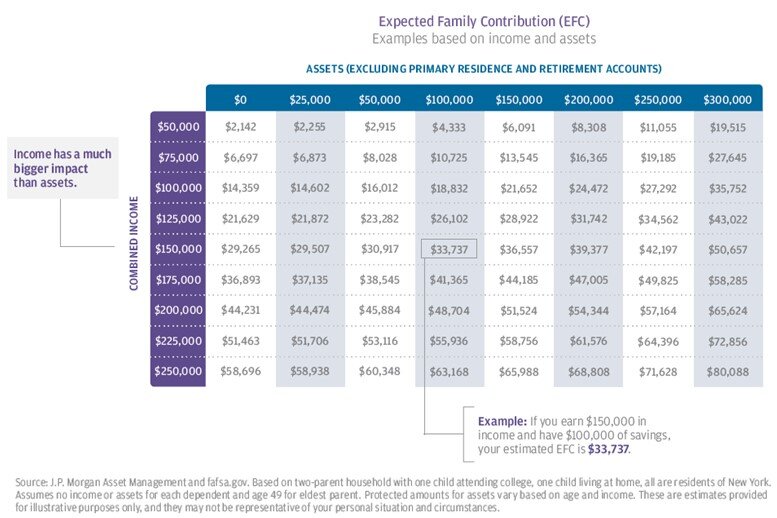
Our friends over at JP Morgan were kind enough to put a summary chart together for this EFC calculation which allows families to get a ballpark idea of what their Expected Family Contribution might be without getting out a calculator. The chart below is based on the following assumptions:
Two parent household
2 Children: One attending college and the other still at home
The child attending college has no assets or income
The oldest parent is age 49
Using the chart above, if the parents combined income is $150,000 and they have $100,000 in countable assets, the Expected Family Contribution would be $33,737 for that school year. What does that mean? If the student is attending a state college and the tuition with room and board is $26,000, since the EFC is greater than the total cost of college for that year, that family would receive no financial aid. However, if that student applies to a private school and the CSS Profile form results in approximately that same EFC of $33,737 but the private school costs $60,000 per year, then the family may receive need based financial aid or a grant from the private school equaling $26,263 per year.
Public Colleges vs. Private Colleges
It’s important to point out that FAFSA and the EFC calculation primarily applies to students that plan on attending a Community College, State College, or certain Private Colleges. Since Private Colleges do not receive federal financial aid they do not have to adhere to the EFC calculation that is used by FAFSA. Private college can choose to use to FAFSA criteria but many of the private colleges will require students to complete both the FAFSA form and the CSS Profile Form.
Here are a few examples of how the financial reporting deviates:
If the parents have a 100% family owned business, they would not have to list that as an asset on the FAFSA application but they would have to list the business as an assets on the CSS Profile form.
The equity in your primary residence is not counted as an asset for FAFSA but it is listed as an asset on the CSS Profile Form.
For parents that are divorced. FAFSA only looks at the assets and income of the custodial parent. The CSS Profile Form captures the assets and income of both the custodial and non-custodial parent.
Because of the deviations between the FAFSA application and the CSS Profile Form, we have seen situations where a student received no need based financial aid when applying to a $50,000 per year private school but they received financial aid for attending a state school even though the annual cost to attend the state school was half the cost of the private school.
Top 10 Ways To Increase College Financial Aid
Here is a quick list of the top strategies that we use to help families to qualify for more financial aid.
Disclosure: There are details associated with each strategy listed below that need to be executed correctly in order for the strategy to have a positive impact on the EFC calculation. Not all strategies will work depending on the financial circumstances of each household and where the child plans to attend college. Contact us for details.
Get assets out of the name of the student
Grandparent owned 529 accounts
Use countable assets of the parents to pay down debt
Move UTGMA & UGMA accounts to 529 UGMA or 529 UTMA accounts
Increase contributions to retirement accounts
Minimize distributions from retirement accounts
Minimize capital gain and dividend income
Accelerate necessary expenses
Use home equity line of credit instead of home equity loan
Families that own small businesses have a lot of advanced planning options
FAFSA – 2 Year Lookback
It’s important to understand the FAFSA application process because you have know when they take the snapshot of your income and assets for the EFC calculation in order to have a shot at increasing the financial aid that you may be able to qualify for.
FAFSA looks back 2 years to determine what your income will be for the upcoming school year. For example, if your child is going to be a freshman in college in the fall of 2020, you will report your 2018 income on the FAFSA application. This is important because you have to start putting some of these strategies into place in the spring of your child’s sophomore year in high school otherwise you could miss out on planning opportunities for their freshman year in college.
If your child is already a junior or senior in high school and you are just reading this article now, there is still an opportunity to implement some of the strategies listed above. Income has a 2 year lookback but assets are reported as of the day of the application. Also the FAFSA application is completed each year that your child is attending college, so even though you may have missed income reduction strategies for their freshman year, at some point the 2 year lookback will influence the financial aid picture during the four years of their undergraduate degree.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Income has a 2-year lookback
Asset balances are determined on the day that you submit the FAFSA Application
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
How Much Emergency Fund Should You Have And How To Get There
If you watched the nightly news during the latest government shutdown you would have seen stories about how people struggle when they aren’t getting a paycheck. Most Americans are not immune to having a set back at a job and it is a scary feeling to not know when the next paycheck will come. The emergency fund is what will help you bridge the
How Much Emergency Fund Should You Have And How To Get There
If you watched the nightly news during the latest government shutdown you would have seen stories about how people struggle when they aren’t getting a paycheck. Most Americans are not immune to having a set back at a job and it is a scary feeling to not know when the next paycheck will come. The emergency fund is what will help you bridge the gap in these hard times. This article should help determine how much emergency fund you should have and strategies on how you can get there.
We make a point of this in every financial plan we put together because of its importance. A lot of people will say their job is secure so they don’t need to worry about having an emergency fund. This may be true, nevertheless the emergency fund is not only for the most extreme circumstances but any unexpected expense. Anyone can have an unforeseen cost of $1,000 to $5,000 and most people would have to pay for this expense on a credit card that will accrue interest and take time to payoff.
Another common thought is, “I have disability insurance, so I don’t need an emergency fund”. Most disability insurance will not start until a 90-day elimination period has been met. This means you will be out of a check for that period but still have all the expenses you normally would.
Current Savings In The United States
“Smartasset” came out with a study in November 2018 that stated; of those Americans with savings accounts, the average savings account balance was $33,766.49. This seems like an amount that would be enough for most people to have in a “rainy day fund”. But that is the average. Super Savers with very large balances will skew this calculation so we use the median which more accurately reflects the state of most Americans. The median balance is only approximately $5,200 per “Smartasset”.
With a median balance of only $5,200, it doesn’t take much misfortune for that to be spent down to $0. At $5,200, it is safe to assume that most Americans are living paycheck to paycheck.
If your income only meets your normal expenses, you need to ask yourself the question “where am I coming up with the money for an unexpected cost?”. For a lot of people, it is a credit card, another type of loan, or dipping into their retirement assets. By taking care of the immediate need, you shift the burden to another part of your financial wellbeing.
Emergency Fund Calculator
There is no exact dollar amount but a consensus in the planning industry is between 4-6 months of living expenses. This is usually enough to cover expenses while you are searching for the next paycheck or to have other assistance kick in.
It is important for everyone to put together a budget. How do you know what 4-6 months of living expenses is if you don’t know what you spend? Putting together a budget takes time but you need to know where your money is going in order to make the adjustments necessary to save. If you are in a position that you don’t see your savings account increasing, or at least remaining the same, you are likely just meeting expenses with your current income.
Resource: EXPENSE PLANNER to help you focus on your spending.
I Know My Number, How Do I get There?
Determining the amount is the easy part, now it is getting there. The less likely option would be going to your boss asking, “I need to replenish my emergency fund, can you increase my pay?”. Winning the lottery would also be nice but not something you can count on.Changing spending habits is an extremely difficult thing to do. Especially if you don’t know what you’re spending money on. Once you have an accurate budget, you should take a hard look at it and make cuts to some of the discretionary items on the list. It will likely take a combination of savings strategies that will get you to an appropriate emergency fund level. Below is a list of some ideas;
Skip a vacation one year
Put any potential tax refund in savings
Put a bonus check into savings
Increase the amount of your paycheck that goes to savings when you get a raise
Side work
Don’t upgrade a phone every time your due
Downgrade a vehicle or use the vehicle longer once paid off
Reward Yourself
There is no doubt some pain will be felt if you are trying to save more and it also takes time. Set a goal and stick to it but work in some rewards to yourself. If you are making good progress after say 3 months, splurge on something to keep your sanity but won’t impact the main objective.
Where To Keep Your Emergency Fund?
This account is meant to be liquid and accessible. So locking it up in some sort of long term investment that may have penalties for early withdrawal would not be ideal. We typically suggest using an institution you are familiar with and putting it in a savings account that can earn some interest.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
How To Change Your Residency To Another State For Tax Purposes
If you live in an unfriendly tax state such as New York or California, it’s not uncommon for your retirement plans to include a move to a more tax friendly state once your working years are over. Many southern states offer nicer weather, no income taxes, and lower property taxes. According to data from the US Census Bureau, more residents
If you live in an unfriendly tax state such as New York or California, it’s not uncommon for your retirement plans to include a move to a more tax friendly state once your working years are over. Many southern states offer nicer weather, no income taxes, and lower property taxes. According to data from the US Census Bureau, more residents left New York than any other state in the U.S. Between July 2017 and July 2018, New York lost 180,360 residents and gained only 131,726, resulting in a net loss of 48,560 residents. With 10,000 Baby Boomers turning 65 per day over the next few years, those numbers are expected to escalate as retirees continue to leave the state.
When we meet with clients to build their retirement projections, the one thing anchoring many people to their current state despite higher taxes is family. It’s not uncommon for retirees to have children and grandchildren living close by so they greatly favor the “snow bird” routine. They will often downsize their primary residence in New York and then purchase a condo or small house down in Florida so they can head south when the snow starts to fly.
The inevitable question that comes up during those meetings is “Since I have a house in Florida, how do I become a resident of Florida so I can pay less in taxes?” It’s not as easy as most people think. There are very strict rules that define where your state of domicile is for tax purposes. It’s not uncommon for states to initiate tax audit of residents that leave their state to claim domicile in another state and they split time travelling back and forth between the two states. Be aware, the state on the losing end of that equation will often do whatever it can to recoup that lost tax revenue. It’s one of those guilty until proven innocent type scenarios so taxpayers fleeing to more tax favorable states need to be well aware of the rules.
Residency vs Domicile
First, you have to understand the difference between “residency” and “domicile”. It may sound weird but you can actually be considered a “resident” of more than one state in a single tax year without an actual move taking place but for tax purposes each person only has one state of “domicile”.
Domicile is the most important. Think of domicile as your roots. If you owned 50 houses all around the world, for tax purposes, you have to identify via facts and circumstances which house is your home base. Domicile is important because regardless of where you work or earn income around the world, your state of domicile always has the right to tax all of your income regardless of where it was earned.
While each state recognizes that a taxpayer only has one state of domicile, each state has its own definition of who they considered to be a “resident” for tax purposes. If you are considered a resident of a particular state then that state has the right to tax you on any income that was earned in that state. But they are not allowed to tax income earned or received outside of their state like your state of domicile does.
States Set Their Own Residency Rules
To make the process even more fun, each state has their own criteria that defines who they considered to be a resident of their state. For example, in New York and New Jersey, they consider someone to be a resident if they maintain a home in that state for all or most of the year, and they spend at least half the year within the state (184 days). Other states use a 200 day threshold. If you happen to meet the residency requirement of more than one state in a single year, then two different states could consider you a resident and you would have to file a tax return for each state.
Domicile Is The Most Important
Your state of domicile impacts more that just your taxes. Your state of domicile dictates your asset protection rules, family law, estate laws, property tax breaks, etc. From an income tax standpoint, it’s the most powerful classification because they have right to tax your income no matter where it was earned. For example, your domicile state is New York but you worked for a multinational company and you spent a few months working in Ireland, a few months in New Jersey, and most of the year renting a house and working in Florida. You also have a rental property in Virginia and are co-owners of a business based out of Texas. Even though you did not spend a single day physically in New York during the year, they still have the right to tax all of your income that you earned throughout the year.
What Prevents Double Taxation?
So what prevents double taxation where they tax you in the state where the money is earned and then tax you again in your state of domicile? Fortunately, most states provide you with a credit for taxes paid to other states. For example, if my state of domicile is Colorado which has a 4% state income tax and I earned some wages in New York which has a 7% state income tax rate, when I file my state tax return in Colorado, I will not own any additional state taxes on those wages because Colorado provides me with a credit for the 7% tax that I already paid to New York.
It only hurts when you go the other way. Your state of domicile is New York and you earned wage in Colorado during the year. New York will credit you with the 4% in state tax that you paid to Colorado but you will still owe another 3% to New York State since they have the right to tax all of your income as your state of domicile.
Count The Number Of Days
Most people think that if they own two houses, one in New York and one in Florida, as long as they keep a log showing that they lived in Florida for more than half the year that they are free to claim Florida, the more tax favorable state, as their state of domicile. I have some bad news. It’s not that easy. The key in all of this is to take enough steps to prove that your new house is your home base. While the number of days that you spend living in the new house is a key factor, by itself, it’s usually not enough to win an audit.
That notebook or excel spreadsheet that you used to keep a paper trail of the number of days that you spent at each location, while it may be helpful, the state conducting the audit may just use the extra paper in your notebook to provide you with the long list of information that they are going to need to construct their own timeline. I’m not exaggerating when I say that they will request your credit card statement to see when and where you were spending money, freeway charges, cell phone records with GPS time and date stamps, dentist appointments, and other items that give them a clear picture of where you spent most of your time throughout the year. If you supposedly live in Florida but your dentist, doctors, country club, and newspaper subscriptions are all in New York, it’s going to be very difficult to win that audit. Remember the number of days that you spend in the state is just one factor.
Proving Your State of Domicile
There are a number of action items that you should take if it’s your intent to travel back and forth between two states during the year, and it’s your intent to claim domicile in the more favorable tax state. Here is the list of the action items that you should consider to prove domicile in your state of choice:
Register to vote and physically vote in that state
Register your car and/or boat
Establish gym memberships
Newspapers and magazine subscriptions
Update your estate document to comply with the domicile state laws
Use local doctors and dentists
File your taxes as a resident
Have mail forwarded from your “old house” to your “new house”
Part-time employment in that state
Join country clubs, social clubs, etc.
Host family gatherings in your state of domicile
Change your car insurance
Attend a house of worship in that state
Where your pets are located
Dog Saves Owner $400,000 In Taxes
Probably the most famous court case in this area of the law was the Petition of Gregory Blatt. New York was challenging Mr Blatt’s change of domicile from New York to Texas. While he had taken numerous steps to prove domicile in Texas at the end of the day it was his dog that saved him. The State of New York Division of Tax Appeals in February 2017 ruled that “his change in domicile to Dallas was complete once his dog was moved there”. Mans best friends saved him more than $400,000 in income tax that New York was after him for.
Audit Risk
When we discuss this topic people frequently ask “what are my chances of getting audited?” While some audits are completely random, from the conversations that we have had with accountants in this subject area, it would seem that the more you make, the higher the chances are of getting audited if you change your state of domicile. I guess that makes sense. If your Mr Blatt and you are paying New York State $100,000 per year in income taxes, they are probably going to miss that money when you leave enough to press you on the issue. But if all you have is a NYS pension, social security, and a few small distributions from an IRA, you might have been paying little to no income tax to New York State as it is, so the state has very little to gain by auditing you.
But one of the biggest “no no’s” is changing your state of domicile on January 1st. Yes, it makes your taxes easier because you file your taxes in your old state of domicile for last year and then you get to start fresh with your new state of domicile in the current year without having to file two state tax returns in a single year. However, it’s a beaming red audit flag. Who actually moves on New Year’s Eve? Not many people, so don’t celebrate your move by inviting a state tax audit from your old state of domicile
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Accountant Put The Owner’s Kids On Payroll And Bomb Shelled The 401(k) Plan
The higher $12,000 standard deduction for single filers has produced an incentive in some cases for business owners to put their kids on the payroll in an effort to shift income out of the owner’s high tax bracket into the children’s lower tax bracket. However, there was a non-Wojeski accountant that advised his clients not only to put his kids on the
Big Issue
The higher $12,000 standard deduction for single filers has produced an incentive in some cases for business owners to put their kids on the payroll in an effort to shift income out of the owner’s high tax bracket into the children’s lower tax bracket. However, there was a non-Wojeski accountant that advised his clients not only to put his kids on the payroll but also to have their children put all of that W2 compensation in the company’s 401(k) plan as a Roth deferral.
At first look it would seem to be a dynamite tax strategy but this strategy blew up when the company got their year end discrimination testing back for the 401(k) plan and all of the executives, including the owner, were forced to distribute their pre-tax deferrals from the plan due to failed discrimination testing. It created a huge unexpected tax liability for the owners and all of the executives completely defeating the tax benefit of putting the kids on payroll. Not good!!
Why This Happened
If your client sponsors a 401(k) plan and they are not a “safe harbor plan”, then each year the plan is subject to “discrimination testing”. This discrimination testing is to ensure that the owners and “highly compensated employees” are not getting an unfair level of benefits in the 401(k) plan compared to the rest of the employees. They look at what each employee contributes to the plan as a percent of their total compensation for the year. For example, if you make $3,000 in employee deferrals and your W2 comp for the year is $60,000, your deferral percentage is 5%.
They run this calculation for each employee and then they separate the employees into two groups: “Highly Compensated Employees” (HCE) and “Non-Highly Compensation Employees” (NHCE). A highly compensated employee is any employee that in 2019:
is a 5% or more owner, or
Makes $125,000 or more in compensation
They put the employees in their two groups and take an average of each group. In most cases, the HCE’s average cannot be more than 2% higher than the NHCE average. If it is, then the HCE’s get pre-tax money kicked back to them out of the 401(k) plan that they have to pay tax on. It really ticks off the HCE’s when this happens because it’s an unexpected tax bill.
Little Known Attribution Rule
ATTRIBUTION RULE: Event though a child of an owner may not be a 5%+ owner or make more than $125,000 in compensation, they are automatically considered an HCE because they are related to the owner of the business. So in the case that I referred above, the accountant had the client pay the child $12,000 and defer $12,000 into the 401(k) plan as a Roth deferral making their deferral percentage 100% of compensation. That brought the average for the HCE way way up and caused the plan fail testing.
To make matters worse, when 401(k) refunds happen to the HCE’s they do not go back to the person that deferred the highest PERCENTAGE of pay, they go to the person that deferred the largest DOLLAR AMOUNT which was the owner and the other HCE’s that deferred over $18,000 in the plan each.
How To Avoid This Mistake
Before advising a client to put their children on payroll and having them defer that money into the 401(k) plan, ask them these questions:
Does your company sponsor a 401(k) plan?
If yes, is your plan a “safe harbor 401(k) plan?
If the company sponsors a 401(k) plan AND it’s a safe harbor plan, you are in the clear with using this strategy because there is no discrimination testing for the employee deferrals.
If the company sponsors a 401(k) plan AND it’s NOT a safe harbor plan, STOP!! The client should either consult with the TPA (third party administrator) of their 401(k) plan to determine how their kids deferring into the plan will impact testing or put the kids on payroll but make sure they don’t contribute to the plan.
Side note, if the company sponsors a Simple IRA, you don’t have to worry about this issue because Simple IRA’s do not have discrimination testing. The children can defer into the retirement plan without causing any issues for the rest of the HCE’s.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Does "Sell In May And Go Away" Really Work?
There is a well-known trading strategy that goes by the name of "Sell In May And Go Away". The strategy involves liquidating all of your stock holdings in May and then re-establishing your stock positions in November. The basic premise of this strategy is when you reference performance data from the stock market for the past 100 years, two of
There is a well-known trading strategy that goes by the name of "Sell In May And Go Away". The strategy involves liquidating all of your stock holdings in May and then re-establishing your stock positions in November. The basic premise of this strategy is when you reference performance data from the stock market for the past 100 years, two of the three worse months typically occur between May and October. But does it really work?
Losing Strategy
While there are years that we can point to that the "Sell In May" strategy would have worked, it would have been a losing strategy for the past 4 out of 5 years.
The only year that strategy would have worked within the last five years was in 2015 and you avoid a minuscule 1% loss. On the flip side, you missed a huge 11.6% gain in 2017. If you implemented this strategy every year for the past 5 years, it would have cost you 22.4% in investment returns. Not good.
Looking Back Further
Instead of looking back just 5 years, let’s look back 10 years from 2008 to 2017. The “Sell In May” strategy would have only worked 4 out of 10 times. So it would have been the losing strategy 60% of the time. Again, not good.
So why do you hear so much about it? Looking at the market data, even though it has not been a reliable source as to whether or not the stock market will be up or down during the May to October months, the return data of the Dow Jones Industrial Average suggests historically that the largest returns are found during the November through April months.
A perfect example is 2010. In 2010, the Dow Jones Industrial Average produced a return of 1% between May – October. However, the Dow Jones produced a 15.2% rate of return in 2010 between November and April. Implementing the “Sell In May” strategy would have cost you 1% in return since you were not invested during the summer months but you still captured the lion share of the return from the stock market for the year.
Also, when the economy is in a recession, May through October typically contains the months that produce the largest losses for the Dow. During the 2008 recession, the Dow was down 27.3% between May and October but it was only down 12.4% between November and April. Likewise, during the 2001 recession, the Dow was down 15.5% between May and October but it was actually positive 9.6% between November and April.
Measure of Magnitude Not Direction
The further you dig into the data, the more it seems that the "Sell In May" strategy is a more accurate measure of "magnitude" instead of direction. Let's compare the May to October vs. the November to April return data of the Dow Jones Industrial Average 2008 – 2015 from Stock Almanac.
Looking at this time period, the losses were either less severe or the gains were greater between the November and April time frame 6 out of 8 years or 75% of the time. Compared with only 3 out of the 8 years where the direction of the returns were different when comparing those two time frames or 37.5% of the time.
Recession vs. Expansion
I think there are a number of takeaways from looking at this data. One might conclude that when U.S. economy is in a period of expansion, the "Sell In May" strategy has less than a coin flip chance of creating a more favorable investment return. However, when the economy is in a recession, the historical data may also suggest that more weight be given to the strategy since May through October in the past two recessions has contained the largest drops in the stock market.With all of that said, timing the market is very difficult and many investment professionals even label it as foolish. In general, long term investors are often better served by selecting an asset allocation that is appropriate for their risk tolerance and time horizon and staying the course.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Don't Let Taxes Dictate Your Investment Decisions
Everyone hates to pay more in taxes. But this is something that has to be done. Sometimes taxes can often lead investors to make foolish investment decisions. The stock market bottomed in March 2009 and since then we have experienced the second-longest bull market rally of all time. This type of market environment typically creates a
Everyone hates to pay more in taxes. But this is something that has to be done. Sometimes taxes can often lead investors to make foolish investment decisions. The stock market bottomed in March 2009 and since then we have experienced the second-longest bull market rally of all time. This type of market environment typically creates a stockpile of unrealized gains in the equity portion of your portfolio. When you go to sell one of your investment holdings that has appreciated in value over the past few years there may be a big tax bill waiting for you. But when is it the right time to ignore the tax hit and execute the trade?
Do The Math
What sounds worse? Writing a check to the government for $10,000 in taxes or experiencing a 3% loss in your investment accounts? Most people would answer paying taxes. After all, who wants to write a check to the government for $10,000 after you have already paid your fair share of taxes throughout the year. It’s this exact situation that gets investors in a lot of trouble when the stock market turns or when that concentrated stock position takes a nosedive.
Before making this decision make sure you do the math. If you have $500,000 in your taxable investment account and the account value drops by 3%, your account just lost $15,000. It would have been better to sell the holding, pay the $10,000 in taxes, and you would still be ahead by $5,000. Before making the decision not to sell for tax reasons, make sure you run this calculation.
Gains Are Good
While most of us run from paying taxes like the plague, remember gains are good. It means that you made money on the investment. At some point you are going to have to pay tax on that gain unless your purposefully waiting for the investment to lose value or if you plan to die with that holding in your estate.
If you put $100,000 in an aggressive investment a year ago and it’s now worth $200,000, if you sell it all today, you will have to pay long term cap gains tax and possibly state tax on the $100,000 realized gain. But remember, what goes up by 100% can also go down by 100%. To avoid the tax bill, you make the decision to just sit on the investment and 3 months from now the economy goes into a recession. The value of that investment drops to $125,000 and you sell it before things get worse. While you successfully decreased your tax liability, the tax hit would have been a lot better than saying goodbye to $75,000.
As financial planners we are always looking for ways to reduce the tax bill for our clients but sometimes paying taxes is unavoidable. The more you make, the more you pay in taxes. In most tax years, investors try to use investment losses to help offset some of the realized taxable gains. However, since most assets classes have appreciated in value over the last few years, investors may be challenges to find investment losses in their accounts.
Capital Gains Tax
A quick recap of capital gains tax rates. There are long-term and short-term capital gains. They apply to investments that are held in non-retirement account. IRA’s, 401(k), and 403(b) plans are all tax deferred vehicles so you do not have worry about realizing capital gains tax when you sell a holding within those types of accounts.
In a taxable brokerage account, if you buy an investment and sell it in less than 12 months, if it made money, you realize a short-term capital gain. Short-term gains do not receive preferential tax treatment. You pay tax at the ordinary income tax rates.
However, if you buy an investment and hold it for more than a year before selling it, the gain is taxed at the preferential long-term capital gain rates. At the federal level, there are three flat rates: 0%, 15%, and 20%. At the state level, it varies based on what state you live in. If you live in New York, where we are headquartered, long-term capital gains do not have preferential tax treatment for state income tax purposes. They are taxed as ordinary income. While other states like Alaska, Florida, and Texas assess no taxes at the state level on capital gains.
The tax rate that you pay on your long-term capital gains at the federal level depends on your AGI for that particular tax year. Here are the thresholds for 2021:
A special note for investors that fall in the 20% category, in addition to being taxed at the higher rate, there is also a 3.8% Medicare surtax that is tacked onto the 20% rate. So the top long-term capital gains rate for high income earners is really 23.8%, not 20%.
Don't Forget About The Flat Rate
Investors forget that long-term capital gains are taxed for the most part at a flat rate. If your AGI is $200,000 and you are considering selling an investment that would cause you to incur a $100,000 long-term capital gain, it may not matter from a tax standpoint whether you sell it all this year or if you split the gain between two different tax years. You are still taxed at that flat 15% federal tax rate on the full amount of the gain regardless of when you sell it.There are of course exceptions to this rule. Here is a list of some of the exceptions that you need to aware of:
Your AGI limit for the year
The impact of the long-term capital gain on your AGI
College financial aid
Social security taxation
Health insurance through the exchange
First exception is the one-time income event that pushes your income dramatically higher for the year. This could be a big bonus, a good year for the company that you own, or you sell an investment property. In these cases you have to mindful of the federal capital gains tax thresholds. If it’s toward the end of the year and you are thinking about selling an investment that has a good size unrealized gain built up into it, it may be prudent to sell enough to keep yourself out of the top long-term capital gains bracket and then sell the rest in January when you enter the new tax year. That move could save you 8.8% in taxes on the realized gains. The 23.8% to tax rate minus the 15% median rate. If you are at the beginning or in the middle of a tax year trying to make this decision, the decision is more difficult. You will have to weigh the risk of the investment losing value before you flip into a new tax year versus paying a slightly higher tax rate on the gain.
To piggyback on the first exception, you have to remember that long term capital gains increase your AGI. If you make $300,000 and you realize a $200,000 long term capital gain on an investment, it’s going to bump you up into the highest federal long term capital gains tax rate.
College financial aid can be a big exception. If you have a child in college or a child that will be going to college within the next two years, and you expect to receive some type of financial aid based on income, be very careful about when you realize capital gains in your investment portfolio. The parent’s investment income can count against a student’s financial aid package. Also, FASFA looks back two years for purposes of determining your financial aid package so conducing this tax versus risk analysis requires some advanced planning.
For those receiving social security benefit, capital gains can impact how much of your social security benefit is subject to taxation.
For individuals that receive their health insurance through a state exchange platform (Obamacare) and qualify for income subsidies, the capital gains income could decrease the amount of the subsidy that you are receive for that year. Be careful.
Don't Make The This Mistake
Bottom line, nothing is ever simple. I wish I could say that in all instances you should completely ignore the tax ramifications and make the right investment decision. In the real world, it’s about determining the balance between the two. It’s about doing the math to better under the tax hit versus the downside risk of continuing to hold a security to avoid paying taxes.
While the current economic expansion may still have further to go, we are probably closer to the end than we are the beginning of the current economic expansion. When the expansion ends, investors are going to be tempted to hold onto certain investments within their portfolio longer than they should because they don’t want to take the tax hit. Don’t make this mistake. If you have a stock holding within your portfolio and it drops significantly in value, you may not have the time horizon needed to wait for that investment to bounce back. Or you may have the opportunity to preserve principal during the next market downturn and buy back that same investment at lower level.
In general, it’s good time for investors to revisit their investment portfolios from a risk standpoint. You may be faced with some difficult investment decisions within the next few years. Remember, selling an investment that has lost money is ten times easier than selling one of your “big winners”. Do the math, don’t get emotionally attached to any particular investment, and be prepared to make investment changes to your investment portfolios as we enter the later stages of this economic cycle.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Should I Rollover My Pension To An IRA?
Whether you are about to retire or if you were just notified that your company is terminating their pension plan, making the right decision with regard to your pension plan payout is extremely important. It's important to get this decision right because you only get one shot at it. There are a lot of variables that factor into choosing the right option.
Whether you are about to retire or if you were just notified that your company is terminating their pension plan, making the right decision with regard to your pension plan payout is extremely important. It's important to get this decision right because you only get one shot at it. There are a lot of variables that factor into choosing the right option. While selecting the monthly payment option may be the right choice for your fellow co-worker, it could be the wrong choice for you. Here is a quick list of the items that you should consider before making the decision.
Financial health of the plan sponsor
Your age
Your health
Flexibility
Monthly benefit vs lump sum amount
Inflation
Your overall retirement picture
Financial Health Of The Plan Sponsor
The plan sponsor is the company, organization, union, municipality, state agency, or government entity that is in charge of the pension plan. The financial health of the plan sponsor should weigh heavily on your decision in many cases. After all what good is a monthly pension payment if five years from now the company or entity that sponsors the plan goes bankrupt?
Pension Benefit Guarantee Corporation
But wait……..isn’t there some type of organization that guarantees the pension payments? The answer, there may or may not be. The Pension Benefit Guarantee Corporation (PBGC) is an organization that was established to protect your pension benefit. But PBGC protection only applies if your company participates in the PBGC. Not all pension plans have this protection.
Large companies will typically have PBGC protection. The pension plan is required to pay premiums to the PBGC each year. Those premiums are used to subsidize the cost of bankrupt pension plans if the PBGC has to step in to pay benefits. But it’s very important to understand that even through a pension plan may have PBGC protection that does not mean that 100% of the employee’s pension benefits are protected if the company goes bankrupt.
There is a dollar limited placed on the monthly pension benefit that the PBGC will pay if it has to step in. It’s a sliding scale based on your age and the type of pension benefit that you elected. If your pension payment is greater that the cap, the excess amount is not insured. Here is the PBGC 2021 Maximum Monthly Guarantee Table:
Another important note, if you have not reached age 65, your full pension benefit may not be insured even if it is less than the cap listed in the table.
Again, not all pension plans are afforded this protection by the PBGC. Pension plans offered by states and local government agencies typically do not have PBGC protection.
If you are worried about the financial health of the plan sponsor, that scenario may favor electing the lump sum payment option and then rolling over the funds into your rollover IRA. Once the money is in your IRA, the plan sponsor insolvency risk is eliminated.
Your Age
Your age definitely factors into the decision. If you have 10+ years to retirement and your company decides to terminate their pension plan, it may make sense to rollover your balance in the pension plan into an IRA or your current employer’s 401(k) plan. Primarily because you have the benefit of time on your side and you have full control over the asset allocation of the account.
Pension plans typically maintain a conservative to moderate growth investment object. You will rarely ever find a pension plan that has 80%+ in equity exposure. Why? It’s a pooled account for all of the employees of all ages. Since the assets are required to meet current pension payments, pension plans cannot be subject to high levels of volatility.
If your personal balance in the pension plan is moved into our own IRA, you have the option of selecting an investment objective that matches your personal time horizon to retirement. If you have a long time horizon to retirement, it allows you the freedom to be more aggressive with the investment allocation of the account.
If you are within 5 years to retirement, it does not necessarily mean that selecting the monthly pension payment is the right choice but the decision is less cut and dry. You really have to compare the monthly pension payment versus the return that you would have to achieve in your IRA to replicate that income stream in retirement.
Your Health
Your health is a big factor as well. If you are in poor health, it may favor electing the lump sum option and rolling over the balance into an IRA. Whatever amount is left in your IRA account will be distributed to your beneficiaries. With a straight life pension option, the benefit just stops when you pass away. However, if you are worried about your spouse's spending habits and your spouse is either in good health or is much younger than you, you may want to consider the pension option with a 100% survivor benefit.
Flexibility
While some retirees like the security of a monthly pension payment that will not change for the rest of their life, other retirees prefer to have more flexibility. If you rollover you balance to an IRA, you can decide how much you want to take or not take out of the account in a given year.
Some retirees prefer to spend more in their early years in retirement because that is when their health is the best. Walking around Europe when you are 65 is usually not the same experience as walking around Europe when you are 80. If you want to take $10,000 out of your IRA to take that big trip to Europe or to spend a few months in Florida, it provides you with the flexibility to do so. By making sure that you have sufficient funds in your savings at the time of retirement can help to make things like this possible.
Working Because I Want To
The other category of retirees that tend to favor the IRA rollover option is the "I'm working because I want to" category. It has becoming more common for individuals to retire from their primary career and want to still work doing something else for two or three days a week just to keep their mind fresh. If the income from your part-time employment and your social security are enough to meet your expenses, having a fixed pension payment may just create more taxable income for you when you don't necessarily need it. Rolling over your pension plan to an IRA allows you to defer the receipt of that income until at least age 70½. That is the age that distributions are required from IRA accounts.
Monthly Pension vs Lump Sum
It’s important to determine the rate of return that you would need to achieve in your IRA account to replicate the pension benefit based on your life expectancy. With the monthly pension payment option, you do not have to worry about market fluctuations because the onus is on the plan sponsor to produce the returns necessary to make the pension payments. With the IRA, you or your investment advisor are responsible for producing the investment return in the account.
Example 1: You are 65 and you have the option of either taking a monthly pension payment of $3,000 per month or taking a lump sum in the amount of $500,000. If your life expectancy is age 85, what is the rate of return that you would need to achieve in your IRA to replicate the pension payment?
The answer: 4%
If your IRA account performs better than 4% per year, you are ahead of the game. If your IRA produces a return below 4%, you run the risk of running out of money prior to reaching age 85.
Part of this analysis is to determining whether or not the rate of return threshold is a reasonable rate of return to replicate. If the required rate of return calculation results in a return of 6% or higher, outside of any special circumstances, you may be inclined to select the pension payments and put the responsibility of producing that 6% rate of return each year on the plan sponsor.
Low Interest Rate Environment
A low interest rate environment tends to favor the lump sum option because it lowers the “discount rate” that actuaries can use when they are running the present value calculation. Wait……what?
The actuaries are the mathletes that produce the numbers that you see on your pension statement. They have to determine how much they would have to hand you today in a lump sum payment to equal the amount that you would have received if you elected the monthly pension option.
This is called a “present value” calculation. This amount is not the exact amount that you would have received if you elected the monthly pension payments because they get to assume that they money in the pension plan will earn interest over your life expectancy. For example, if the pension plan is supposed to pay you $10,000 per year for the next 30 years, that would equal $300,000 paid out over that 30 year period. But the present value may only be $140,000 because they get to assume that you will earn interest off of that money over the next 30 years for the amount that is not distributed until a later date.
In lower interest rate environments, the actuaries have to use a lower assume rate of return or a lower “discount rate”. Since they have to assume that you will make less interest on the money in your IRA, they have to provide you with a larger lump sum payment to replicate the monthly pension payments over your life expectancy.
Inflation
Inflation can be one of the largest enemies to a monthly pension payment. Inflation, in its simplest form is “the price of everything that you buy today goes up in price over time”. It’s why your grandparents have told you that they remember when a gallon of milk cost a nickel. If you are 65 today and your lock into receiving $2,000 per month for the rest of your life, inflation will erode the spending power of that $2,000 over time.
Historically, inflation increases by about 3% per year. As an example, if your monthly car payment is $400 today, the payment for that same exact car 20 years from now will be $722 per month. Now use this multiplier against everything that you buy each month and it begins to add up quickly.
If you have the money in an IRA, higher inflation typically leads to higher interest rate, which can lead to higher interest rates on bonds. Again, having control over the investment allocation of your IRA account may help you to mitigate the negative impact of inflation compared to a fixed pension payment.
A special note, some pension plans have a cost of living adjustment (“COLA”) built into the pension payment. Having this feature available in your pension plan will help to manage the inflation risk associated with selecting the monthly pension payment option. The plan basically has an inflation measuring stick built into your pension payment. If inflation increases, the plan is allowed to increase the amount of your monthly pension payment to help protect the benefit.
Your Overall Financial Picture
While I have highlighted a number of key variables that you will need to consider before selecting the payout option for your pension benefit, at the end of the day, you have to determine how each option factors into your own personal financial situation. It’s usually wise to run financial projections that identify both the opportunities and risks associated with each payment option.
Don’t be afraid to seek professional help with this decision. They will help you consider what you might need to pay for in the future. Are you going to need money spare for holidays, transportation, even funeral costs should be considered. Where people get into trouble is when they guess or they choose an option based on what most of their co-workers selected. Remember, those co-workers are not going to be there to help you financially if you make the wrong decision.
As an investment advisor, I will also say this, if you meet with a financial planner or investment advisor to assist you with this decision, make sure they are providing you with a non-bias analysis of your options. Depending on how they are compensation, they may have a vested interest in getting you to rollover you pension benefit to an IRA. Even though electing the lump sum payment and rolling the balance over to an IRA may very well be the right decision, they should walk you through a thorough analysis of the month pension payments versus the lump sum rollover option to assist you with your decision.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Moving Expenses Are No Longer Deductible
If you were planning on moving this year to take a new position with a new company or even a new position within your current employer, the moving process just got a little more expensive. Not only is it expensive, but it can put you under an intense amount of stress as there will be lots of things that you need to have in place before packing up and
If you were planning on moving this year to take a new position with a new company or even a new position within your current employer, the moving process just got a little more expensive. Not only is it expensive, but it can put you under an intense amount of stress as there will be lots of things that you need to have in place before packing up and moving. Even things like how you are going to transport your car over to your new home, can take up a lot of your time, and on top of that, you have to think about how much it's going to cost. Prior to the tax law changes that took effect January 1, 2018, companies would often offer new employees a "relocation package" or "moving expense reimbursements" to help subsidize the cost of making the move. From a tax standpoint, it was great benefit because those reimbursements were not taxable to the employee. Unfortunately that tax benefit has disappeared in 2018 as a result of tax reform.
Taxable To The Employee
Starting in 2018, moving expense reimbursements paid to employee will now represent taxable income. Due to the change in the tax treatment, employees may need to negotiate a higher expense reimbursement rate knowing that any amount paid to them from the company will represent taxable income.
For example, let’s say you plan to move from New York to California and you estimate that your moving expense will be around $5,000. In 2017, your new employer would have had to pay you $5,000 to fully reimburse you for the moving expense. In 2018, assuming you are in the 35% tax bracket, that same employer would need to provide you with $6,750 to fully reimburse you for your moving expenses because you are going to have to pay income tax on the reimbursement amount.
Increased Expense To The Employer
For companies that attract new talent from all over the United States, this will be an added expense for them in 2018. Many companies limit full moving expense reimbursement to executives. Coincidentally, employees at the executive level are usually that highest paid. Higher pay equals higher tax brackets. If you total up the company's moving expense reimbursements paid to key employees in 2017 and then add another 40% to that number to compensate your employees for the tax hit, it could be a good size number.
Eliminated From Miscellaneous Deductions
As an employee, if your employer did not reimburse you for your moving expenses and you had to move at least 50 miles to obtain that position, prior to 2018, you were allowed to deduct those expenses when you filed your taxes and you were not required to itemize to capture the deduction. However, this expense will no longer be deductible even for employees that are not reimbursed by their employer for the move starting in 2018.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Warning To All Employees: Review The Tax Withholding In Your Paycheck Otherwise A Big Tax Bill May Be Waiting For You
As a result of tax reform, the IRS released the new income tax withholding tables in January and your employer probably entered those new withholding amounts into the payroll system in February. It was estimated that about 90% of taxpayers would see an increase in their take home pay once the new withholding tables were implemented.
As a result of tax reform, the IRS released the new income tax withholding tables in January and your employer probably entered those new withholding amounts into the payroll system in February. It was estimated that about 90% of taxpayers would see an increase in their take home pay once the new withholding tables were implemented. While lower tax rates and more money in your paycheck sounds like a good thing, it may come back to bite you when you file your taxes.
The Tax Withholding Guessing Game
Knowing the correct amount to withhold for federal and state income taxes from your paycheck is a bit of a guessing game. Withhold too little throughout the year and when you file your taxes you have a tax bill waiting for you equal to the amount of the shortfall. Withhold too much and you will receive a big tax refund but that also means you gave the government an interest free loan for the year.
There are two items that tell your employer how much to withhold for federal income tax from your paycheck:
Income Tax Withholding Tables
Form W-4
The IRS provides your employer with the Income Tax Withholding Tables. On the other hand, you as the employee, complete the Form W-4 which tells your employer how much to withhold for taxes based on the “number of allowances” that you claim on the form.
What Is A W-4 Form?
The W-4 form is one of the many forms that HR had you complete when you were first hired by the company. Here is what it looks like:
Section 3 of this form tells your employer which withholding table to use:
Single
Married
Married, but withhold at higher Single Rate
Section 5 tells your employer how many "allowances" you are claiming. Allowance is just another word for "dependents". The more allowances your claim, the lower the tax withholding in your paycheck because it assumes that you will have less "taxable income" because in the past you received a deduction for each dependent. This is where the main problem lies. Due to the changes in the tax laws, the tax deduction for personal exemptions was eliminated. This may adversely affect some taxpayers the were claiming a high number of allowances on their W-4 form because even though the number of their dependents did not change, their taxable income may be higher in 2018 because the deduction for personal exemptions no longer exists.
Even though everyone should review their Form W-4 form this year, employees that claimed allowances on their W-4 form are at the highest risk of either under withholding or over withholding taxes from their paychecks in 2018 due to the changes in the tax laws.
How Much Should I Withhold From My Paycheck For Taxes?
So how do you go about calculating that right amount to withhold from your paycheck for taxes to avoid an unfortunate tax surprise when you file your taxes for 2018? There are two methods:
Ask your accountant
Use the online IRS Withholding Calculator
The easiest and most accurate method is to ask your personal accountant when you meet with them to complete your 2017 tax return. Bring them your most recent pay stub and a blank Form W-4. Based on the changes in the tax laws, they can assist you in the proper completion of your W-4 Form based on your estimated tax liability for the year.If you complete your own taxes, I would highly recommend visiting the updated IRS Withholding Calculator. The IRS calculator will ask you a series of questions, such as:
How many dependents you plan to claim in 2018
Are you over the age of 65
The number of children that qualify for the dependent care credit
The number of children that will qualify for the new child tax credit
Estimated gross wages
How much fed income tax has already been withheld year to date
Payroll frequency
At the end of the process it will provide you with your personal results based on the data that you entered. It will provide you with guidance as to how to complete your Form W-4 including the number of allowances to claim and if applicable, the additional amount that you should instruct your employer to withhold from your paycheck for federal income taxes. Additional withholding requests are listed in Section 6 of the Form W-4.
Avoid Disaster
Having this conversation with your accountant and/or using the new IRS Withholding Calculator will help you to avoid a big tax disaster in 2018. Unfortunately, many employees may not learn about this until it's too late. Employees that are used to getting a tax refund may find out in the spring of next year that they owe thousands of dollars to the IRS because the combination of the new tax tables and the changes in the tax law that caused them to inadvertently under withhold federal income taxes throughout the year.
Action Item!!
Take action now. The longer you wait to run this calculation or to have this conversation with your accountant, the larger the adjustment may be to your paycheck. It's easier to make these adjustments now when you have nine months left in the year as opposed to waiting until November.I would strongly recommend that you share this article with your spouse, children in the work force, and co-workers to help them avoid this little known problem. The media will probably not catch wind of this issue until employees start filing their tax returns for 2018 and they find out that there is a tax bill waiting for them.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.