How Much Should I Budget For Health Care Costs In Retirement?
The number is higher than you think. When you total up the deductibles and premiums for Medicare part A, B, and D, that alone can cost a married couple $7,000 per year. We look at that figure as the baseline number. That $7,000 does not account for the additional costs associated with co-insurance, co-pays, dental costs, or Medigap insurance
The number is higher than you think. When you total up the deductibles and premiums for Medicare part A, B, and D, that alone can cost a married couple $7,000 per year. We look at that figure as the baseline number. That $7,000 does not account for the additional costs associated with co-insurance, co-pays, dental costs, or Medigap insurance premiums which can quickly increase the overall cost to $10,000+ per year.
Tough to believe? Allow me to walk you through the numbers for a married couple.
Medicare Part A: $2,632 Per Year
Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility stays, some home health visits, and hospice care. While Part A does not have an annual premium, it does have an annual deductible for each spouse. That deductible for 2017 is $1,316 per person.
Medicare Part B: $3,582
Part B covers physician visits, outpatient services, preventive services, and some home health visits. The standard monthly premium is $134 per person but it could be higher depending on your income level in retirement. There is also a deductible of $183 per year for each spouse.
Medicare Part D: $816
Part D covers outpatient prescription drugs through private plans that contract with Medicare. Enrollment in Part D is voluntary. The benefit helps pay for enrollees’ drug costs after a deductible is met (where applicable), and offers catastrophic coverage for very high drug costs. Part D coverage is actually provided by private health insurance companies. The premium varies based on your income and the types of prescriptions that you are taking. The national average in 2017 for Part D premiums is $34 per person.
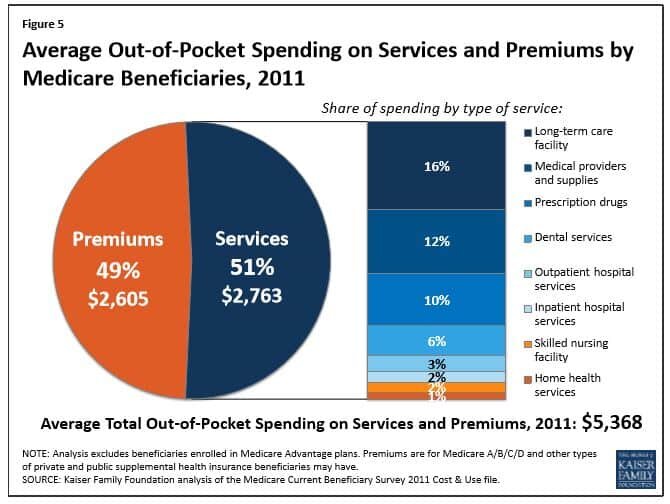
If you total up just these three items, you reach $7,030 in premiums and deductibles for the year. Then you start adding in dental cost, Medigap insurance premiums, co-insurance for Medicare benefits, and it quickly gets a married couple over that $10,000 threshold in health and dental cost each year. Medicare published a report that in 2011, Medicare beneficiaries spent $5,368 out of their own pockets for health care spending, on average. See the table below.
Start Planning Now
Fidelity Investments published a study that found that the average 65 year old will pay $240,000 in out-of-pocket costs for health care during retirement, not including potential long-term-care costs. While that seems like an extreme number, just take the $10,000 that we used above, multiply that by 20 year in retirement, and you get to $200,000 without taking into consideration inflation and other important variable that will add to the overall cost.
Bottom line, you have to make sure you are budgeting for these expenses in retirement. While most individuals focus on paying off the mortgage prior to retirement, very few are aware that the cost of health care in retirement may be equal to or greater than your mortgage payment. When we are create retirement projections for clients we typically included $10,000 to $15,000 in annual expenses to cover health care cost for a married couple and $5,000 – $7,500 for an individual.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Tax Reform: Your Company May Voluntarily Terminate Your Retirement Plan
Make no mistake, your company retirement plan is at risk if the proposed tax reform is passed. But wait…..didn’t Trump tweet on October 23, 2017 that “there will be NO change to your 401(k)”? He did tweet that, however, while the tax reform might not directly alter the contribution limits to employer sponsored retirement plans, the new tax rates
Make no mistake, your company retirement plan is at risk if the proposed tax reform is passed. But wait…..didn’t Trump tweet on October 23, 2017 that “there will be NO change to your 401(k)”? He did tweet that, however, while the tax reform might not directly alter the contribution limits to employer sponsored retirement plans, the new tax rates will produce a “disincentive” for companies to sponsor and make employer contributions to their plans.
What Are Pre-Tax Contributions Worth?
Remember, the main incentive of making contributions to employer sponsored retirement plans is moving income that would have been taxed now at a higher tax rate into the retirement years, when for most individuals, their income will be lower and that income will be taxed at a lower rate. If you have a business owner or executive that is paying 45% in taxes on the upper end of the income, there is a large incentive for that business owner to sponsor a retirement plan. They can take that income off of the table now and then realize that income in retirement at a lower rate.
This situation also benefits the employees of these companies. Due to non-discrimination rules, if the owner or executives are receiving contributions from the company to their retirement accounts, the company is required to make employer contributions to the rest of the employees to pass testing. This is why safe harbor plans have become so popular in the 401(k) market.
But what happens if the tax reform is passed and the business owners tax rate drops from 45% to 25%? You would have to make the case that when the business owner retires 5+ years from now that their tax rate will be below 25%. That is a very difficult case to make.
An Incentive NOT To Contribute To Retirement Plans
This creates an incentive for business owners NOT to contribution to employer sponsored retirement plans. Just doing the simple math, it would make sense for the business owner to stop contributing to their company sponsored retirement plan, pay tax on the income at a lower rate, and then accumulate those assets in a taxable account. When they withdraw the money from that taxable account in retirement, they will realize most of that income as long term capital gains which are more favorable than ordinary income tax rates.
If the owner is not contributing to the plan, here are the questions they are going to ask themselves:
Why am I paying to sponsor this plan for the company if I’m not using it?
Why make an employer contribution to the plan if I don’t have to?
This does not just impact 401(k) plans. This impacts all employer sponsored retirement plans: Simple IRA’s, SEP IRA’s, Solo(k) Plans, Pension Plans, 457 Plans, etc.
Where Does That Leave Employees?
For these reasons, as soon as tax reform is passed, in a very short time period, you will most likely see companies terminate their retirement plans or at a minimum, lower or stop the employer contributions to the plan. That leaves the employees in a boat, in the middle of the ocean, without a paddle. Without a 401(k) plan, how are employees expected to save enough to retire? They would be forced to use IRA’s which have much lower contribution limits and IRA’s don’t have employer contributions.
Employees all over the United States will become the unintended victim of tax reform. While the tax reform may not specifically place limitations on 401(k) plans, I’m sure they are aware that just by lowering the corporate tax rate from 35% to 20% and allowing all pass through business income to be taxes at a flat 25% tax rate, the pre-tax contributions to retirement plans will automatically go down dramatically by creating an environment that deters high income earners from deferring income into retirement plans. This is a complete bomb in the making for the middle class.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Social Security Filing Strategies
Making the right decision of when to turn on your social security benefit is critical. The wrong decision could cost you tens of thousands of dollars over the long run. Given all the variables surrounding this decision, what might be the right decision for one person may be the wrong decision for another. This article will cover some of the key factors to
Making the right decision of when to turn on your social security benefit is critical. The wrong decision could cost you tens of thousands of dollars over the long run. Given all the variables surrounding this decision, what might be the right decision for one person may be the wrong decision for another. This article will cover some of the key factors to consider:
Normal Retirement Age
First, you have to determine your "Normal Retirement Age" (NRA). This is listed on your social security statement in the "Your Estimated Benefits" section. If you were born between 1955 – 1960, your NRA is between age 66 – 67. If you were born 1960 or later, your NRA is age 67. You can obtain a copy of your statement via the social security website.
Before Normal Retirement Age
You have the option to turn on social security prior to your normal retirement age. The earliest you can turn on social security is age 62. However, they reduce your social security benefit by approximately 7% per year for each year prior to your normal retirement age. See the chart below from USA Today which illustrates an individual with a normal retirement age of 66. If they turn on their social security benefit at age 62, they would only receive 75% of their full benefit. This reduction is a permanent reduction. It does not increase at a later date, outside of the small cost of living increases.
The big questions is: “If I start taking it age 62, at what age is the breakeven point?” Remember, if I turn on social security at 62 and my normal retirement age is 66, I have received 4 years of payments from social security. So at what age would I be kicking myself wishing that I had waited until normal retirement age to turn on my benefit. There are a few different ways to calculate this accounting for taxes, the rates of return on other retirement assets, inflations, etc. but in general it’s sometime between the ages of 78 and 82.
Since the breakeven point may be in your early 80’s, depending on your health, and the longevity in your family history, it may or may not make sense to turn on your benefit early. If we have a client that is in ok health but not great health and both of their parents passed way prior to age 85, then it may make sense to for them to turn on their social security benefit early. We also have clients that have pensions and turning on their social security benefit early makes the different between retiring now or have to work for 5+ more years. As long as the long-term projections work out ok, we may recommend that they turn on their social security benefit early so they can retire sooner.
Are You Still Working?
This is a critical question for anyone that is considering turning on their social security benefits early. Why? If you turn on your social security benefit prior to reaching normal retirement age, there is an “earned income” penalty if you earn over the threshold set by the IRS for that year. See the table listed below:
In 2016, for every $2 that you earned over the $15,720 threshold, your social security was reduced by $1. For example, let’s say I’m entitled to $1,000 per month ($12,000 per year) from social security at age 62 and in 2016 I had $25,000 in W2 income. That is $9,280 over the $15,720 threshold for 2016 so they would reduce my annual benefit by $4,640. Not only did I reduce my social security benefit permanently by taking my social security benefit prior to normal retirement age but now my $12,000 in annual social security payments they are going to reduce that by another $4,640 due to the earned income penalty. Ouch!!!
Once you reach your normal retirement age, this earned income penalty no longer applies and you can make as much as you want and they will not reduce your social security benefit.
Because of this, the general rule of thumb is if you are still working and your income is above the IRS earned income threshold for the year, you should hold off on turning on your social security benefits until you either reach your normal retirement age or your income drops below the threshold.
Should I Delay May Benefit Past Normal Retirement Age
As was illustrated in first table, if you delay your social security benefit past your normal retirement age, your benefit will increase by approximately 8% per year until you reach age 70. At age 70, your social security benefit is capped and you should elect to turn on your benefits.
So when does it make sense to wait? The most common situation is the one where you plan to continue working past your normal retirement age. It’s becoming more common that people are working until age 70. Not because they necessarily have too but because they want something to keep them busy and to keep their mind fresh. If you have enough income from employment to cover you expenses, in many cases, is does make sense to wait. Based on the current formula, your social security benefit will increase by 8% per year for each year you delay your benefit past normal retirement age. It’s almost like having an investment that is guaranteed to go up by 8% per year which does not exist.
Also, for high-income earners, a majority of their social security benefit will be taxable income. Why would you want to add more income to the picture during your highest tax years? It may very well make sense to delay the benefit and allow the social security benefit to increase.
Death Benefit
The social security death benefit also comes into play as well when trying to determine which strategy is the right one for you. For a married couple, when their spouse passes away they do not continue to receive both benefits. Instead, when the first spouse passes away, the surviving spouse will receive the “higher of the two” social security benefits for the rest of their life. Here is an example:
Spouse 1 SS Benefit: $2,000
Spouse 2 SS Benefit: $1,000
If Spouse 1 passes away first, Spouse 2 would bump up to the $2,000 monthly benefit and their $1,000 monthly benefit would end. Now let’s switch that around, let’s say Spouse 2 passes away first, Spouse 1 will continue to receive their $2,000 per month and the $1,000 benefit will end.
If social security is a large percentage of the income picture for a married couple, losing one of the social security payments could be detrimental to the surviving spouse. Due to this situation, it may make sense to have the spouse with the higher benefit delay receiving social security past normal retirement to further increase their permanent monthly benefit which in turn increases the death benefit for the surviving spouse.
Spousal Benefit
The “spousal benefit” can be a powerful filing strategy. If you are married, you have the option of turning on your benefit based on your earnings history or you are entitled to half of your spouse’s benefit, whichever benefit is higher. This situation is common when one spouse has a much higher income than the other spouse.
Here is an important note. To be eligible for the spousal benefit, you personally must have earned 40 social security “credits”. You receive 1 credit for each calendar quarter that you earn a specific amount. In 2016, the figure was $1,260. You can earn up to 4 credits each calendar year.
Another important note, under the new rules, you cannot elect your spousal benefit until your spouse has started receiving social security payments.
Here is where the timing of the social security benefits come into play. You can turn on your spousal benefit as early as 62 but similar to the benefit based on your own earnings history it will be reduce by approximately 7% per year for each year you start the benefit prior to normal retirement age. At your normal retirement age, you are entitled to receive your full spousal benefit.
What happens if you delay your spousal benefit past normal retirement age? Here is where the benefit calculation deviates from the norm. Typically when you delay benefits, you receive that 8% annual increase in the benefits up until age 70. The spousal benefit is based exclusively on the benefit amount due to your spouse at their normal retirement age. Even if your spouse delays their social security benefit past their normal retirement age, it does not increase the 50% spousal benefit.
Here is the strategy. If it’s determine that the spousal benefit will be elected as part of a married couple’s filing strategy, since delaying the start date of the benefits past normal retirement age will only increase the social security benefit for the higher income earning spouse and not the spousal benefit, in many cases, it does not make sense to delay the start date of the benefits past normal retirement age.
Divorce
For divorced couples, if you were married for at least 10 years, you can still elect the spousal benefit even though you are no longer married. But you must wait until your ex-spouse begins receiving their benefits before you can elect the spousal benefit.
Also, if you were married for at least 10 years, you are also entitled to the death benefit as their ex-spouse. When your ex-spouse passes away, you can notify the social security office, elect the death benefit, and you will receive their full social security benefit amount for the rest of your life instead of just 50% of their benefit resulting from the “spousal benefit” calculation.
Whether or not your ex-spouse remarries has no impact on your ability to elect the spousal benefit or death benefit based on their earnings history.
Consult A Financial Planner
Given all of the variables in the mix and the importance of this decision, we strongly recommend that you consult with a Certified Financial Planner® before making your social security benefit elections. While the interaction with a fee-based CFP® may cost you a few hundred dollars, making the wrong decision regarding your social security benefits could cost you thousands of dollars over your lifetime. You can also download a Financial Planner Budget Worksheet to give you that extra help when sorting out your finances and monthly budgeting.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Planning for Long Term Care
The number of conversations that we are having with our clients about planning for long term care is increasing exponentially. Whether it’s planning for their parents, planning for themselves, or planning for a relative, our clients are largely initiating these conversations as a result of their own personal experiences.
The number of conversations that we are having with our clients about planning for long term care is increasing exponentially. Whether it’s planning for their parents, planning for themselves, or planning for a relative, our clients are largely initiating these conversations as a result of their own personal experiences.
The baby-boomer generation is the first generation that on a large scale is seeing the ugly aftermath of not having a plan in place to address a long term care event because they are now caring for their aging parents that are in their 80’s and 90’s. Advances in healthcare have allowed us to live longer but the longer we live the more frail we become later in life.
Our clients typically present the following scenario to us: “I have been taking care of my parents for the past three years and we just had to move my dad into the nursing home. What an awful process. How can I make sure that my kids don’t have to go through that same awful experience when I’m my parents age?”
“Planning for long term care is not just about money…….it’s about having a plan”
If there are no plans, your kids or family members are now responsible for trying to figure out “what mom or dad would have wanted”. Now tough decisions need to be made that can poison a relationship between siblings or family members.
Some individuals never create a plan because it involves tough personal decisions. We have to face the reality that at some point in our lives we are going to get older and later in life we may reach a threshold that we may need help from someone else to care for ourselves or our spouse. It’s a tough reality to face but not facing this reality will most likely result in the worst possible outcome if it happens.
Ask yourself this question: “You worked hard all of your life to buy a house, accumulate assets in retirement accounts, etc. If there are assets left over upon your death, would you prefer that those assets go to your kids or to the nursing home?” With some advance planning, you can make sure that your assets are preserved for your heirs.
The most common reason that causes individuals to avoid putting a plan in place is: “I have heard that long term care insurance is too expensive.” I have good news. First, there are other ways to plan for the cost of a long term care event besides using long term care insurance. Second, there are ways to significantly reduce the cost of these policies if designed correctly.
The most common solution is to buy a long term care insurance policy. The way these policies work is if you can no longer perform certain daily functions, the policy pays a set daily benefit. Now a big mistake many people make is when they hear “long term care” they think “nursing home”. In reality, about 80% of long term care is provided right in the home via home health aids and nurses. Most LTC policies cover both types of care. Buying a LTC policy is one of the most effective ways to address this risk but it’s not the only one.
Why does long term care insurance cost more than term life insurance or disability insurance? The answer, most insurance policies insure you against risks that have a low probability of happening but has a high financial impact. Similar to a life insurance policy. There is a very low probability that a 25 year old will die before the age of 60. However, the risk of long term care has a high probability of happening and a high financial impact. According to a study conducted by the U.S Department of Human Health and Services, “more than 70% of Americans over the age of 65 will need long-term care services at some point in their lives”. Meaning, there is a high probability that at some point that insurance policy is going to pay out and the dollars are large. The average daily rate of a nursing home in upstate New York is around $325 per day ($118,625 per year). The cost of home health care ranges greatly but is probably around half that amount.
So what are some of the alternatives besides using long term care insurance? The strategy here is to protect your assets from Medicaid. If you have a long term care event you will be required to spend down all of your assets until you reach the Medicaid asset allowance threshold (approx. $13,000 in assets) before Medicaid will start picking up the tab for your care. Often times we will advise clients to use trusts or gifting strategies to assist them in protecting their assets but this has to be done well in advance of the long term care event. Medicaid has a 5 year look back period which looks at your full 5 year financial history which includes tax returns, bank statements, retirement accounts, etc, to determine if any assets were “given away” within the last 5 years that would need to come back on the table before Medicaid will begin picking up the cost of an individuals long term care costs. A big myth is that Medicare covers the cost of long term care. False, Medicare only covers 100 days following a hospitalization. There are a lot of ins and outs associated with buildings a plan to address the risk of long term care outside of using insurance so it is strongly advised that individuals work with professionals that are well versed in this subject matter when drafting a plan.
An option that is rising in popularity is “semi self-insuring”. Instead of buying a long term care policy that has a $325 per day benefit, an individual can obtain a policy that covers $200 per day. This can dramatically reduce the cost of the LTC policy because it represents less financial risk to the insurance company. You have essentially self insured for a portion of that future risk. The policy will still payout $73,000 per year and the individual will be on the line for $45,625 out of pocket. Versus not having a policy at all and the individual is out of pocket $118,000 in a single year to cover that $325 per day cost.
As you can see there are a number of different options when it come to planning for long term care. It’s about understanding your options and determining which solution is right for your personal financial situation.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.