How Much Should I Contribute to Retirement?
A question I’m sure to address during employee retirement presentations is, “How Much Should I be Contributing?”. In this article, I will address some of the variables at play when coming up with your number and provide detail as to why two answers you will find searching the internet are so common.
A question I’m sure to address during employee retirement presentations is, “How Much Should I be Contributing?”. Quick internet search led me to two popular answers.
Whatever you need to contribute to get the match from the employer,
10-15% of your compensation.
As with most questions around financial planning, the answer should really be, “it depends”. We all know it is important to save for retirement, but knowing how much is enough is the real issue and typically there is more work involved than saying 10-15% of your pay.
In this article, I will address some of the variables at play when coming up with your number and provide detail as to why the two answers previously mentioned are so common.
Expenses and Income Replacement
Creating a budget and tracking expenses is usually the best way to estimate what your spending needs will be in retirement. Unfortunately, this is time-consuming and is becoming more difficult considering how easy it is to spend money these days. Automatic payments, subscriptions, payment apps, and credit cards make it easy to purchase but also more difficult to track how much is leaving your bank accounts.
Most financial plans we create start with the client putting together an itemized list of what they believe they spend on certain items like clothes, groceries, vacations, etc. A copy of our expense planner template can be found here. These are usually estimates as most people don’t track expenses in that much detail. Since these are estimates, we will use household income, taxes, and bank/investment accounts as a check to see if expenses appear reasonable.
What do expenses have to do with contributions to your retirement account now? Throughout your career, you receive a paycheck and use those funds to pay for the expenses you have. At some point, you no longer have the paycheck but still have the expenses. Most retirees will have access to social security and others may have a pension, but rarely does that income cover all your expenses. This means that the shortfall often comes from retirement accounts and other savings.
Not taking taxes, inflation, or investment gains into account, if your expenses are $50,000 per year and Social Security income is $25,000 a year, that is a $25,000 shortfall. 20 years of retirement times a $25,000 shortfall means $500,000 you’d need saved to fund retirement. Once we have an estimate of the coveted “What’s My Number?” question, we can create a savings plan to try and achieve that goal.
Cash Flow
As we age, some of the larger expenses we have in life go away. Student loan debt, mortgages, and children are among those expenses that stop at some point in most people’s lives. At the same time, your income is usually higher due to experience and raises throughout your career. As expenses potentially go down and income is higher, there may be cash flow that frees up allowing people to save more for retirement. The ability to save more as we get older means the contribution target amount may also change over time.
Timing of Contributions
Over time, the interest that compounds in retirement accounts often makes up most of the overall balance.
For example, if you contribute $2,000 a year for 30 years into a retirement account, you will end up saving $60,000. If you were able to earn an annual return of 6%, the ending balance after 30 years would be approximately $158,000. $60,000 of contributions and $98,000 of earnings.
The sooner the contributions are in an account, the sooner interest can start compounding. This means, that even though retirement saving is more cash flow friendly as we age, it is still important to start saving early.
Contribute Enough to Receive the Full Employer Match
Knowing the details of your company’s retirement plan is important. Most employers that sponsor a retirement plan make contributions to eligible employees on their behalf. These contributions often come in the form of “Non-Elective” or “Matching”.
Non-Elective – Contributions that will be made to eligible employees whether employees are contributing to the plan or not. These types of contributions are beneficial because if a participant is not able to save for retirement from their own paycheck, the company will still contribute. That being said, the contribution amount made by the employer, on its own, is usually not enough to achieve the level of savings needed for retirement. Adding some personal savings in addition to the employer contribution is recommended.
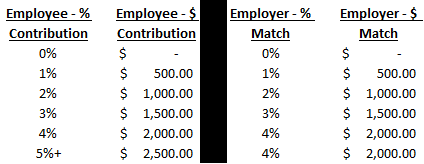
Matching – Employers will contribute on behalf of the employee if the employee is contributing to the plan as well. This means if the employee is contributing $0 to the retirement plan, the company will not contribute. The amount of matching varies by company, so knowing “Match Formula” is important to determine how much to contribute. For example, if the matching formula is “100% of compensation up to 4% of pay”, that means the employer will contribute a dollar-for-dollar match until they contribute 4% of your compensation. Below is an example of an employee making $50,000 with the 4% matching contribution at different contribution rates.
As you can see, this employee could be eligible for a $2,000 contribution from the employer, if they were to save at least 4% of their pay. That is a 100% return on your money that the company is providing.
Any contribution less than 4%, the employee would not be taking advantage of the employer contribution available to them. I’m not a fan of the term “free money”, but that is often the reasoning behind the “Contribute Enough to Receive the Full Employer Match” response.
10%-15% of Your Compensation
As said previously, how much you should be contributing to your retirement depends on several factors and can be different for everyone. 10%-15% over a long-term period is often a contribution rate that can provide sufficient retirement savings. Math below…
Assumptions
Age: 25
Retirement Age: 65
Current Income: $30,000
Annual Raises: 2%
Social Security @ 65: $25,000
Annualized Return: 6%
Step 1: Estimate the Target Balance to Accumulate by 65
On average, people will need an estimated 90% of their income for early retirement spending. As we age, spending typically decreases because people are unable to do a lot of the activities we typically spend money on (i.e. travel). For this exercise, we will assume a 65-year-old will need 80% of their income throughout retirement.
Present Salary - $30,000
Future Value After 40 Years of 2% Raises - $65,000
80% of Future Compensation - $52,000
$52,000 – income needed to replace
$25,000 – social security @ 65
$27,000 – amount needed from savings
X 20 – years of retirement (Age 85 - life expectancy)
$540,000 – target balance for retirement account
Step 2: Savings Rate Needed to Achieve $540,000 Target Balance
40 years of a 10% annual savings rate earning 6% interest per year, this person could have an estimated balance of $605,000. $181,000 of contributions and $424,000 of compounded interest.
I hope this has helped provide a basic understanding of how you can determine an appropriate savings rate for yourself. We recommend reaching out to an advisor who can customize your plan based on your personal needs and goals.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold, Partner at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
How Much Emergency Fund Should You Have And How To Get There
If you watched the nightly news during the latest government shutdown you would have seen stories about how people struggle when they aren’t getting a paycheck. Most Americans are not immune to having a set back at a job and it is a scary feeling to not know when the next paycheck will come. The emergency fund is what will help you bridge the
How Much Emergency Fund Should You Have And How To Get There
If you watched the nightly news during the latest government shutdown you would have seen stories about how people struggle when they aren’t getting a paycheck. Most Americans are not immune to having a set back at a job and it is a scary feeling to not know when the next paycheck will come. The emergency fund is what will help you bridge the gap in these hard times. This article should help determine how much emergency fund you should have and strategies on how you can get there.
We make a point of this in every financial plan we put together because of its importance. A lot of people will say their job is secure so they don’t need to worry about having an emergency fund. This may be true, nevertheless the emergency fund is not only for the most extreme circumstances but any unexpected expense. Anyone can have an unforeseen cost of $1,000 to $5,000 and most people would have to pay for this expense on a credit card that will accrue interest and take time to payoff.
Another common thought is, “I have disability insurance, so I don’t need an emergency fund”. Most disability insurance will not start until a 90-day elimination period has been met. This means you will be out of a check for that period but still have all the expenses you normally would.
Current Savings In The United States
“Smartasset” came out with a study in November 2018 that stated; of those Americans with savings accounts, the average savings account balance was $33,766.49. This seems like an amount that would be enough for most people to have in a “rainy day fund”. But that is the average. Super Savers with very large balances will skew this calculation so we use the median which more accurately reflects the state of most Americans. The median balance is only approximately $5,200 per “Smartasset”.
With a median balance of only $5,200, it doesn’t take much misfortune for that to be spent down to $0. At $5,200, it is safe to assume that most Americans are living paycheck to paycheck.
If your income only meets your normal expenses, you need to ask yourself the question “where am I coming up with the money for an unexpected cost?”. For a lot of people, it is a credit card, another type of loan, or dipping into their retirement assets. By taking care of the immediate need, you shift the burden to another part of your financial wellbeing.
Emergency Fund Calculator
There is no exact dollar amount but a consensus in the planning industry is between 4-6 months of living expenses. This is usually enough to cover expenses while you are searching for the next paycheck or to have other assistance kick in.
It is important for everyone to put together a budget. How do you know what 4-6 months of living expenses is if you don’t know what you spend? Putting together a budget takes time but you need to know where your money is going in order to make the adjustments necessary to save. If you are in a position that you don’t see your savings account increasing, or at least remaining the same, you are likely just meeting expenses with your current income.
Resource: EXPENSE PLANNER to help you focus on your spending.
I Know My Number, How Do I get There?
Determining the amount is the easy part, now it is getting there. The less likely option would be going to your boss asking, “I need to replenish my emergency fund, can you increase my pay?”. Winning the lottery would also be nice but not something you can count on.Changing spending habits is an extremely difficult thing to do. Especially if you don’t know what you’re spending money on. Once you have an accurate budget, you should take a hard look at it and make cuts to some of the discretionary items on the list. It will likely take a combination of savings strategies that will get you to an appropriate emergency fund level. Below is a list of some ideas;
Skip a vacation one year
Put any potential tax refund in savings
Put a bonus check into savings
Increase the amount of your paycheck that goes to savings when you get a raise
Side work
Don’t upgrade a phone every time your due
Downgrade a vehicle or use the vehicle longer once paid off
Reward Yourself
There is no doubt some pain will be felt if you are trying to save more and it also takes time. Set a goal and stick to it but work in some rewards to yourself. If you are making good progress after say 3 months, splurge on something to keep your sanity but won’t impact the main objective.
Where To Keep Your Emergency Fund?
This account is meant to be liquid and accessible. So locking it up in some sort of long term investment that may have penalties for early withdrawal would not be ideal. We typically suggest using an institution you are familiar with and putting it in a savings account that can earn some interest.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
How Much Should I Budget For Health Care Costs In Retirement?
The number is higher than you think. When you total up the deductibles and premiums for Medicare part A, B, and D, that alone can cost a married couple $7,000 per year. We look at that figure as the baseline number. That $7,000 does not account for the additional costs associated with co-insurance, co-pays, dental costs, or Medigap insurance
The number is higher than you think. When you total up the deductibles and premiums for Medicare part A, B, and D, that alone can cost a married couple $7,000 per year. We look at that figure as the baseline number. That $7,000 does not account for the additional costs associated with co-insurance, co-pays, dental costs, or Medigap insurance premiums which can quickly increase the overall cost to $10,000+ per year.
Tough to believe? Allow me to walk you through the numbers for a married couple.
Medicare Part A: $2,632 Per Year
Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility stays, some home health visits, and hospice care. While Part A does not have an annual premium, it does have an annual deductible for each spouse. That deductible for 2017 is $1,316 per person.
Medicare Part B: $3,582
Part B covers physician visits, outpatient services, preventive services, and some home health visits. The standard monthly premium is $134 per person but it could be higher depending on your income level in retirement. There is also a deductible of $183 per year for each spouse.
Medicare Part D: $816
Part D covers outpatient prescription drugs through private plans that contract with Medicare. Enrollment in Part D is voluntary. The benefit helps pay for enrollees’ drug costs after a deductible is met (where applicable), and offers catastrophic coverage for very high drug costs. Part D coverage is actually provided by private health insurance companies. The premium varies based on your income and the types of prescriptions that you are taking. The national average in 2017 for Part D premiums is $34 per person.
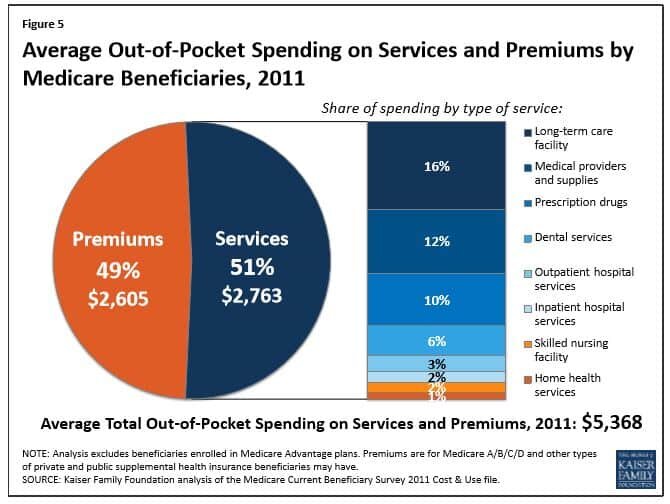
If you total up just these three items, you reach $7,030 in premiums and deductibles for the year. Then you start adding in dental cost, Medigap insurance premiums, co-insurance for Medicare benefits, and it quickly gets a married couple over that $10,000 threshold in health and dental cost each year. Medicare published a report that in 2011, Medicare beneficiaries spent $5,368 out of their own pockets for health care spending, on average. See the table below.
Start Planning Now
Fidelity Investments published a study that found that the average 65 year old will pay $240,000 in out-of-pocket costs for health care during retirement, not including potential long-term-care costs. While that seems like an extreme number, just take the $10,000 that we used above, multiply that by 20 year in retirement, and you get to $200,000 without taking into consideration inflation and other important variable that will add to the overall cost.
Bottom line, you have to make sure you are budgeting for these expenses in retirement. While most individuals focus on paying off the mortgage prior to retirement, very few are aware that the cost of health care in retirement may be equal to or greater than your mortgage payment. When we are create retirement projections for clients we typically included $10,000 to $15,000 in annual expenses to cover health care cost for a married couple and $5,000 – $7,500 for an individual.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Financial Planning To Do's For A Family
My wife and I just added our first child to the family so this is a topic that has been weighing on my mind over the last 40 weeks. I will share just one non-financial takeaway from the entire experience. The global population may be much lower if men had to go through what women do. That being said, this article is meant to be a guideline for some of the important financial items to consider with children. Worrying about your children will never end and being comfortable with the financial aspects of parenthood may allow you to worry a little less and be able to enjoy the time you have with the
My wife and I just added our first child to the family so this is a topic that has been weighing on my mind over the last 40 weeks. I will share just one non-financial takeaway from the entire experience. The global population may be much lower if men had to go through what women do. That being said, this article is meant to be a guideline for some of the important financial items to consider with children. Worrying about your children will never end and being comfortable with the financial aspects of parenthood may allow you to worry a little less and be able to enjoy the time you have with them.
There is a lot of information to take into consideration when putting together a financial plan and the larger your family the more pieces to the puzzle. It is important to set goals and celebrate them when they are met. Everything cannot be done in a day, a week, or a month, so creating a task list to knock off one by one is usually an effective approach. Using relatives, friends, and professionals as resources is important to know what should be on that list for topics you aren’t familiar with.
Create a Budget
It may seem tedious but this is one of the most important pieces of a family’s financial plan. You don’t have to track every dollar coming in and out but having a detailed breakdown on where your money is being spent is necessary in putting together a plan. This simple Expense Planner can serve as a guideline in starting your budget. If you don’t have an accurate idea of where your money is being spent then you can’t know where you can cut back or afford to spend more if needed. Also, the budget is a great topic during a romantic dinner.
You will always want to have 4-6 months expenses saved up and accessible in case a job is lost or someone becomes disabled and cannot work. Having an accurate budget will help you determine how much money you should have liquid.
Insurance
You want to be sure you are sufficiently covered if anything ever happened. One terrible event could leave your family in a situation that may have been avoidable. Insurance is also something you want to take care of as soon as possible so you know the coverage is there if needed.
Health Insurance
Research the policies that are available to you and determine which option may be the most appropriate in your situation. It is important to know the medical needs of your family when making this decision.
Turning one spouse’s single coverage into family coverage is one of the more common ways people obtain coverage for a family. Insurance companies will usually only allow changes to policies through open enrollment or when a “qualifying event” occurs. Having a child is usually a qualifying event but this may only allow the child to be added to one’s coverage, not the spouse. If that is the case, the spouse will want to make sure they have their own coverage until they can be added to the family plan.
It is important to use the resources available to you and consult with your health insurance provider on the ins and outs. If neither spouse has coverage through work, the exchange can be a resource for information and an option to obtain coverage (https://www.healthcare.gov/).
Life Insurance
The majority of people will obtain Term Life Insurance as it is a cost effective way to cover the needs of your family. Life insurance policies have an extensive underwriting process so the sooner you start the sooner you will be covered if anything ever happened. How Much Life Insurance Do I Need?, is an article that may help answer the question regarding the amount of life insurance sufficient for you.
Disability Insurance
The probability of using disability insurance is likely more than that of life insurance. Like life insurance, there is usually a long underwriting process to obtain coverage. Disability insurance is important as it will provide income for your family if you were unable to work. Below are some terms that may be helpful when inquiring about these policies.
Own Occupation – means that insurance will turn on if you are unable to perform YOUR occupation. “Any Occupation” is usually cheaper but means that insurance will only turn on if you can prove you can’t do ANY job.
60% Monthly Income – this represents the amount of the benefit. In this example, you will receive 60% of your current income. It is likely not taxable so the net pay to you may be similar to your paycheck. You can obtain more or less but 60% monthly income is a common benefit amount.
90 Day Elimination Period – this means the benefit won’t start until 90 days of being disabled. This period can usually be longer or shorter.
Cost of Living or Inflation Rider – means the benefit amount will increase after a certain time period or as your salary increases.
Wills, POA’s, Health Proxies
These are important documents to have in place to avoid putting the weight of making difficult decisions on your loved ones. There are generic templates that will suffice for most people but it is starting the process that is usually the most difficult. “What Is The Process Of Setting Up A Will?, is an article that may help you start.
College Savings
The cost of higher education is increasing at a rapid rate and has become a financial burden on a lot of parents looking to pick up the tab for their kids. 529 accounts are a great way to start saving early. There are state tax benefits to parents in some states (including NYS) and if the money is spent on tuition, books, or room and board, the gain from the investments is tax free. Roth IRA’s are another investment vehicle that can be used for college but for someone to contribute to a Roth IRA they must have earned income. Therefore, a newborn wouldn’t be able to open a Roth IRA. Since the gain in 529’s is tax free if used for college, the earlier the dollars go into the account the longer they have to potentially earn income from the market.
529’s can also be opened by anyone, not just the parents. So if the child has a grandparent that likes buying savings bonds or a relative that keeps purchasing clothes the child will wear once, maybe have them contribute to a 529. The contribution would then be eligible for the tax deduction to the contributor if available in the state.
Below is a chart of the increasing college costs along with links to information on college planning.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.